Analysis of Earthmoving Equipment
Earthmoving equipment is typically used due to the high efficiency of the construction work. In early era human power has been used to move earth requiring plenty of time and manpower. But with the development of technology earthmoving equipment has been introduced to the construction field and nowadays more advanced and easily maneuverable earthmoving equipment are available. Thus the time consumption and manpower is greatly reduced resulting a more efficient and time saving construction methods. There are number of earthmoving equipment that can be used for the construction and each equipment provides a different purpose.
(equipment, 2014)
Excavators

Figure 1: Excavator
Excavators are mainly se to excavate soil. Excavators are very useful in deep excavations as well as it can be used for different applications by changing the bucket to different gadgets. Typically excavators are used in cutting trenches, digging holes and foundation pits, Handling of Material , Construction, General grading or landscaping work, Mining of minerals and gems, River dredging, pile driving, , shafts drilling for footings and blasting of rocks etc.(equipment, 2014)
Backhoe

Figure 2: Backhoe
Backhoe is a versatile equipment which widely used in construction industry. It is a combination of an excavator and bulldozer. It can be used for quick earthmoving work and it can replace both excavator and bulldozer if the scale of the work is low. Also due to its 4 wheel system it can easily move through any rough terrain. Hence backhoe is typically seen on any construction field. The levers are operated by hydraulic pistons and the bucket can be replaced with other useful add-ons accordance to the requirement. (equipment, 2014)
Bulldozer

Figure 3: Bulldozer
Bulldozer is a very powerful equipment which can be used to move earth and prepare surfaces. Due to its high power and belt wheel system it is used to move heavy soil lumps in one go. It has a large plate or blade attached to its front which facilitates pushing mechanism of large soil, rubble, gravel or other materials. By changing the blade to a ripper it can be used for farming or ground loosening work.
Skid steer loader

Figure 4: Skid Steer Loader
Skid steer loader is a small scale equipment which can be used for quick work and for the places where large equipment cannot be accessible. Easily maneuverability is one of the main advantage of the equipment. Also it can be used to load soil into dump trucks. The main characteristic of this equipment is its wheel can be rotated independently allowing it to turn in limited spaces. (equipment, 2014)
Trencher

Figure 5: Trencher
Trencher is another useful equipment that can be used to dig trenches in construction work.trencher has a long arm equipped with rotating belt of blades. The blades dig trenches while the equipment is moving along the required line. This can also be used for digging of irrigation channels, foundation trenches, road drainages etc. trenchers are also used in farming industry as well. (equipment, 2014)
Motor Grader

Figure 6: Motor Grader
Motor grader is another useful earthmoving equipment. This equipment is heavily used in road construction. The main purpose of a motor grader is to prepare surfaces according to required slopes and angles. With the long blade attached to front arm of the equipment it can prepare flat surfaces. The motor grader is also referred to as road grader due to its heavy usage in road construction. This equipment is also used in irrigation construction as well.
(“History of the Bulldozer”. Retrieved 2008-12-17.)
For the given project I would use excavators, backhoes and Skid steer loader. The main reason for the excavator the amount of soil needs to be excavated to prepare the basement. Backhoes will be used to small scale work and slope preparation work. Skid steer loaders will be used for the small work where space is limited for big equipment.
To ensure the equipment is used efficiently, effectively and economically I will preplan the earth moving process and schedule the work plan with allocating time for each equipment so that every equipment is not used at once wasting time. Also I will allocate specific tie limit for each equipment and the operator should be able to finish the allocated work within the given period of time. With such management mechanisms I can use the provided equipment effectively, efficiently and economically.
What methods and resources will you employ to ensure safe and productive operations in deep excavations and trenching for your project? Justify your choice. Support your answer with examples.
I will use shoring method to ensure the stability of soil while deep excavating and also a safety officer should be allocated for supervision of excavation work. Excavations will not be done on rainy days. Also the excavations will be done maintaining minimum slope angles for stability.
There are several steps that need to be taken in order to assure safe and productive opertaions in deep excavations
- Preplanning of the work to be done taking following factors into account
- Traffic
- Proximity and physical condition of nearby structures
- Soil classification
- Surface and ground water
- Location of the water table
- Overhead and underground utilities
- Weather
- Quantity of shoring or protective systems that may be required
- Fall protection needs
- Number of ladders that may be needed
- Other equipment needs
- Protective Systems
OSHA generally requires that employers protect workers from cave-ins by:Â Sloping and benching the sides of the excavation; supporting the sides of the excavation; or Placing a shield between the side of the excavation and the work area.
Define types of temporary works required to deal with stability and groundwater problems in the project.
Typically during excavation process dewatering has to be done while maintaining stability of slopes. There are several practices used in industry maintain stability.
Caissons
Caisson is a structure that is developed at area if the site is ashore, yet in the event that the venture site is seaward, it is built ashore and afterward skimmed to the site seaward. In the caisson technique for development, the unearthing is performed from inside the permanent structure. After the caisson is in position, uncovering from inside the caisson structure starts. As the unearthing is done, the caisson structure begins to sink by its own weight, or if fundamental, by forced burdens. This strategy proceeds until the coveted foundation level is accomplished. Figure demonstrates this procedure schematically.
( Wilson,1873)
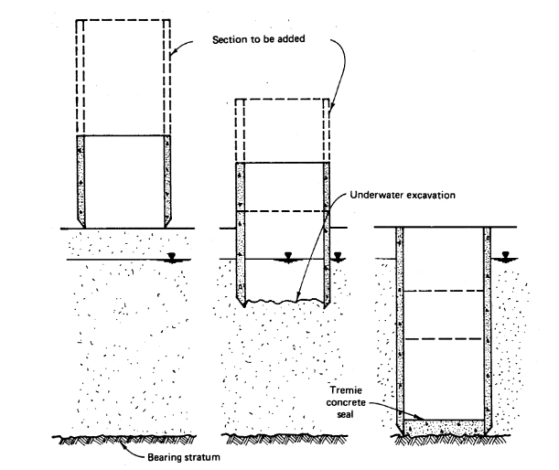
Figure 7: Caissons Installing
Ground Freezing
The theory of ground solidifying is to change the water in the soil into a strong mass of ice. This mass of ice is totally impermeable. Ground solidifying is utilized for groundwater cutoff, for earth bolster, for brief supporting, for adjustment of earth for passage removal, to capture landslides and to balance out deserted mineshafts. The principals of ground solidifying are undifferentiated from pumping groundwater from wells. To solidify the ground, a column of stop channels are set vertically in the soil and warmth vitality is expelled through these funnels. Isotherms (an isotherm is a line interfacing areas with equivalent temperature) move out from the stop channels with time like groundwater forms around a well.
Once the earth temperature comes to 32 °F (0 °C), water in the soil pores swings to ice. At that point additionally cooling continues. The groundwater in the pores promptly solidifies in granular soils, for example, sands. For example, soaked sand accomplishes magnificent quality at just a couple of degrees underneath the point of solidification. On the off chance that the temperature is brought down further, the quality increments hardly. In strong soils, for example, muds, the ground water is molecularly fortified at any rate to some degree to the soil particles. On the off chance that delicate mud is chilled off to solidifying temperature, a few segments of its pore water to start to stop and it causes the earth to harden. With further decrease in temperature, more pore water solidifies and subsequently more quality pick up is accomplished. When planning for solidified earth structures in firm soils, it might be important to determine generously bring down temperatures to accomplish the required quality, than in attachment less soils. A temperature of +20 °F might be adequate in sands, though temperatures as low as -20 °F might be required in delicate soils. The outline of a solidified earth obstruction is represented by the warm properties of the fundamental oils and related reaction to the solidifying framework. Arrangement of solidified earth boundary creates at various rates relying upon the warm and water powered properties of every stratum. Ordinarily, shake and coarse-grained soils solidify quicker than muds and sediments. (Jessica Morrison ,2013)
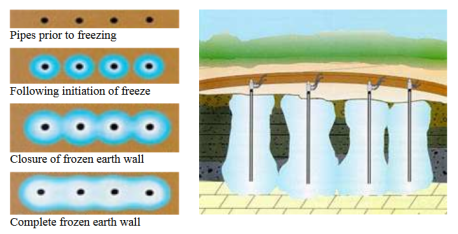
Figure 8: Ground freezing method
Dewatering Methods – Wellpoints
The wellpoint comprises of an opened or punctured pipe which is secured with a screen work. At the foot of this pipe is a hole which licenses flying of the pipe into the ground amid foundation. A well-point dewatering framework comprises of a progression of firmly set little distance across wells introduced to shallow profundities. These wells are associated with a pipe or header that encompasses the removal and is joined to a vacuum pump. The development ventures in the well point framework are:
1. The wellpoints are jetted into the ground;
2. The annulars void is filled with filter media;
3. The wellpoints are connected to a header pipe by means of a riser;
4. The header pipe is connected to suction pumps for pumping.
Powers, J. Patrick (1992).

Figure 9: Well points
What types of plant and equipment will you use in substructure and drainage activities in your project? Justify your choice. Support your answer with examples.
For the given project first thing that needs to do is providing drainage. While providing proper drainage by means of dewatering pumps and wells. Then to stabilize the earth proper shoring should be needed. Once the shoring is properly established further excavation and substructure work can be commenced.
Drainage and dewatering
- Backhoes
- Dewatering pumps
- Drilling machines
- Hoses
- Generators etc.
Earth stabilizing
- Shoring machines
- Cranes
- Welding plants
- Backhoes and excavators
Substructure work
- Skid Steer loader
- Backhoe
- Excavator
- Piling machine
What techniques of installing piling systems and ground stabilization activities will you use in your project? Justify your choice. Support your answer with examples.
The foundation procedure and technique for foundations are similarly critical components as of the outline procedure of heap foundations. Pilefoundation techniques are foundation by heap mallet and exhausting by mechanical auger.In request to evade harms to the piles, amid plan, foundation Methods and foundation hardware ought to be precisely selected.If foundation is to be done utilizing pile pound, then the accompanying components ought to be taken into thought:
- Size of the pile and the weight of the pile
- The available head room and space
- The availability of supporting equipment and machinery
- The noise pollution and regulations.
- The driving resistance for the designed drilling
Pile driving methods (displacement piles)
Methods of pile driving can be categorised as follows:
- Dropping weight
- Explosion
- Vibration
- Jacking (restricted to micro-pilling)
- Jetting
   Drop hammers
A hammer with around the heaviness of the pile is brought a reasonable stature up in a guide and discharged to strike the pile head. This is a straightforward type of mallet utilized as a part of conjunction with light casings and test piling, where it might be uneconomical to bring a steam heater or compressor on to a site to drive extremely set number of piles.
There are two main types of drop hammers
1. Single-acting pile hammers which operates using steam or compressed-air comprise a large weight in a cylindrical container. Steam or compressed air rises it up the fixed piston rod. At the top of the blow, or at a reduced height which can be operated by the operator, the steam is cut off and the cylinder falls freely on the pile helmet.
2. Double-acting pile hammers can be run by steam or compressed air. A pilling mount is not mandatory with this mode of hammer which can be fixed to the upperpart of the pile by leg-guides, the pile being directed by a timber structure. When used with a pile mount, back directs are fastened to the hammer to engage with leaders, and only short leg-guides are used to stop the hammer from moving relatively to the top of the pile. These type of hammers are used mainly for sheet pile driving.
Pile driving by vibrating
Vibratory sledges are normally electrically fueled or using pressurized water controlled and comprises of contra-pivoting unconventional masses inside a lodging connecting to the heap head. The abundancy of the vibration is adequate to separate the skin erosion on the sides of the heap. Vibratory strategies are most appropriate to sandy or gravelly soil.
Jetting:to help the entrance of piles into sand or sandy rock, water streaming might be utilized. In any case, the strategy has exceptionally restricted impact in firm to solid muds or any dirt containing much coarse rock, cobbles, or stones.
Boring methods (non-displacement piles)
Continuous Flight Auger (CFA)
Hardware contains a portable base transporter fitted with an empty stemmed flight wood screw which is pivoted into the ground to required profundity of pilling. To shape the heap, cement is put through the flight twist drill as it is pulled back from the beginning. The twist drill is fitted with defensive top on the outlet at the base of the focal tube and is pivoted into the ground by the top mounted turning pressure driven engine which keeps running on a transporter joined to the pole. On achieving the required profundity, profoundly workable cement is pumped through the empty stem of the wood screw, and under the weight of the solid the defensive top is disconnected. While pivoting the wood screw in an indistinguishable bearing from amid the exhausting stage, the ruin is removed vertically as the twist drill is pulled back and the heap is shaped by loading with cement. In this procedure, it is essential that pivot of the wood screw and stream of cement is coordinated that fall of sides of the opening above cement on lower flight of twist drill is evaded. This may prompt to voids in loaded with soil in cement.
The strategy is particularly viable on delicate ground and empowers to introduce an assortment of exhausted heaps of different widths that can infiltrate a large number of soil conditions. Still, for fruitful operation of revolving twist drill the dirt must be sensibly free of tree roots, cobbles, and stones, and it must act naturally supporting. Amid operation little soil is brought upwards by the twist drill that horizontal burdens are kept up in the dirt and voiding or extreme slackening of the dirt limit. Be that as it may, if the pivot of the wood screw and the progress of the twist drill are not coordinated, bringing about evacuation of soil amid penetrating perhaps prompting to fall of the side of the gap.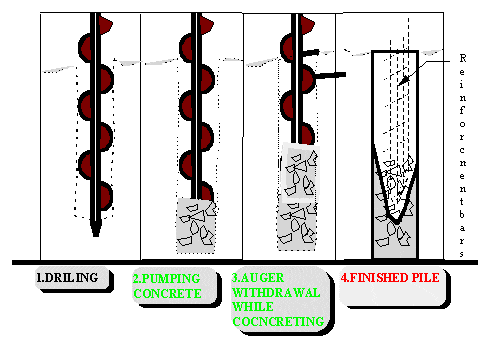
Figure 10: Piling and Auguring
Underreaming
An extraordinary component of wood screw exhausted heaps which is here and there used to empower to misuse the bearing limit of appropriate strata by giving a developed base. The dirt must be fit for standing open unsupported to utilize this method. Firm and to hard muds, for example, the London dirt, are perfect. In its shut position, the underreaming instrument is fitted inside the straight area of a heap shaft, and after that extended at the base of the heap to create the underream appeared in fig. 3.Normally, after establishment and before cement is threw, a man conveying enclosure is brought down and the pole and the underream of the heap is reviewed. (Fleming et al, 1985,)
What methods and processes of constructing foundations including will you use in your project? Justify your choice. Describe the resources that you will use for the construction of foundations. Justify your choice.
In the event of soils having low bearing limit, overwhelming auxiliary burdens are generally bolstered by giving Raft or tangle establishments. Likewise if the structure is defenseless against subsidence on being situated in mining range or because of questionable conduct of its sub-soil water condition, flatboat or tangle establishments ought to be favored. Raft or Mat Foundations gives an efficient answer for troublesome site conditions, where heap establishment can’t be utilized profitably and free section balance gets to be distinctly impracticable.
Raft or tangle establishments comprises of thick fortified solid slab covering the whole range of the base of the structure like a story. The piece is strengthened with bars running at right points to each other both close base and top face of the section. Now and again it is important to convey the over the top section stack by a course of action of reversed principle shafts and auxiliary bars, cast solidly with the flatboat piece.
The Raftslab for the most part ventures for a separation of 30 cm. to 45cm. on every one of the sides of the external dividers of the structure in that capacity the region of exhuming is marginally more than the range of the structure itself. The unearthing is made to the required profundity and the whole uncovered territory is very much united. This surface, when dry, gives the base whereupon the flatboat or tangle section is laid. Every one of the precautionary measures that are important to be seen amid the strengthened solid development are entirely clung to and promote development is begun simply after the curing of the Raft has been completely done.Halpin, Daniel W.; Senior, Bolivar A. (2010).

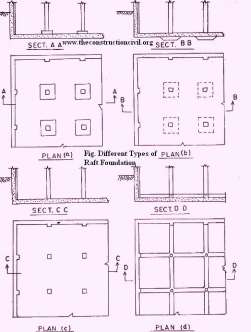
Describe methods and resources that you will use in processes, undertaking drainage works including culverts and installing services in your project.
Culverts and drainage works
Excavation
The area of the proposed drainage will be set out on the ground by checking with paint and pegs at pit areas. Where works are along edge of existing roadway movement light or stop/go framework might be set up to do works. A trench will then be unearthed between pits utilizing an excavator with material stacked to dump truck. The trench width will differ contingent upon the measure of the pipe.
Installation
Where drains are being introduced a layer of geotextile material should be put along the framework of the trench and a layer of channel stone might then be put in base of trench to get pipe work. The pipe work should then be laid to the right line and level by utilizing a review laser
Backfilling of Ducting
The remaining stone might then be put by six ton dumper up to underside of topping where geotextile should be turned out under topping layer. The rest of the depleted might be bested up once surfacing works are done up to wearing course level. Establishment of layer of Geogrid should likewise be done at this stage. All chambers on the deplete lines might be built with pre-thrown solid catch pits and should be put as pipeline continues. (Turner-Fairbank Highway research Center ,1998)
Figure 12: Culverts
What types of plant and equipment will you use in the construction of superstructure your project? Justify your choice. Support your answer with examples.
Construction of superstructure requires lot of machinery and equipment and the uses may vary throughout the different stages of the project. Following are a list of equipment and the uses of each equipment.
|
Equipment |
Uses |
|
Batching plant |
Concrete Production |
|
Concrete pump |
Concrete pouring to higher levels |
|
Tower crane |
Shifting materials |
|
Elevator |
Shifting materials and laborers |
|
Formwork systems |
Form the structure |
|
Scaffolding |
For higher level work |
|
Poker vibrator |
For compaction of concrete |
The batching plant will produce concrete required to construction and concrete mixture truck and pump will support to pour concrete to slabs, columns and beams. Tower crane and elevator will help to move goods and laborers respectively. Scaffoldings, formwork systems and poker vibrator will be used for concrete pouring and form the columns, slabs and beams of the building.
What methods and resources will you use in undertaking the main forms of structural activities in you project? Include the use of concrete in its various forms as well as the use of structural steelwork. Provide relevant examples. Justify your choices.
Mainly concrete will be used together with steel to form the superstructure. Typically formwork will be established first and then concrete together with steel will be used to cast columns, beams and slabs of the building. For the aforementioned task concrete pumps, poker vibrators, laborers and skilled supervisors will be needed.
Concrete is typically used for this type of construction work due to its workability. Liquid state of concrete allows us to cast different required shapes and forms of structures with ease. Whereas steel is a pre-fabricated material hence steel does not provide the freedom to use for different shapes. But steel is also a very good construction material which facilitates fast construction. Structural steelwork can be used together with concrete to produce composite structures. Also steel can be used alone for buildings as well. (Concrete Association, 2013)
What methods of false work and formwork will you use in the superstructure activities in your project? Provide examples. Justify your choice. What processes of concrete production, delivery and placement will you use in your project? Justify your choice.
Formwork implies the surface of the frame and surrounding used to contain and shape wet cement until it is self-supporting.
Formwork incorporates the structures on or inside which the solid is poured and the casings and propping which give soundness. Albeit ordinarily alluded to as a component of the formwork get together, the joists, bearers, propping, establishments and footings are actually alluded to as false work. Formwork development may include high hazard exercises like working fueled portable plant like cranes, working at stature and unearthing establishments.
The outline of the last solid structure can majorly affect the simplicity of formwork development and the wellbeing and security of individuals amid development. For the most part the more essential and basic the last solid structure, the more secure it is to develop, erect and destroy the formwork.
An accomplished formwork creator ought to be counseled amid the plan of in-situ solid structures to empower the wellbeing and dangers amid formwork development and destroying to be considered in the outline. The formwork originator must be equipped in formwork configuration including reporting brief work stages and exceptional gear required for safe formwork development on location. A creator may utilize a specialized standard or a blend of gauges and building standards significant to the plan prerequisites the length of the result is an outline that meets administrative necessities.
Concrete production – Concrete Batching plant
Concrete will be produced in a batching plant to ensure the quality and strength of the concrete.
Concrete Delivery – Mixture truck
Mixture trucks will be used to deliver concrete to the site from the batching plant to prevent loss of workability and quality of concrete
Concrete Placement- Concrete pump truck
Concrete will be placed to higher levels using a concrete pumping truck. This way we can efficiently pour concrete. (Concrete Association, 2013)
Identify and assess the hazards arising from the substructure activities.
- Falling of unstabilized soil
- Falling to deep excavated trenches and pits
- Hazards associated with excavators
- Shorings can be weak
- Damages to underground electrical wires
Explain the legal framework of health, safety and welfare and the requirements of the current CDM Regulations.
The Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2015 (CDM 2015) addresses the management of health, safety and welfare of workers in construction projects. CDM 2015 substituted the Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2007 (CDM 2007) and the Accepted Code of Practice which is providing supporting direction on CDM 2007 was inhibited.
CDM 2015 aims to uplift health and safety in the industry by providing guidance to:
- Rationally plan the work so the risks tangled are succeededthroughout.
- Have the correct people for the correct job at the correct time
- collaborate and organize your work
- have the properinfo about the risks and how they are managed
- convey information efficiently to those who need to know
- consult and occupy workers for the risks management activities and educate them how they are being managed
The CDM2007 Regulations expect to lessen development mischances and sick wellbeing in Great Britain by empowering the different partners of the development business to enhance in arranging and dealing with their activities contemplating matters of security and wellbeing at an early stage in the venture definition. By beginning concentrating on these basic focuses toward the start of a venture, dangers can be recognized and supervisors can use sound judgment in front of challenges. In this new form of the directions, the HSC concentrates on correspondence and co-appointment between every one of the gatherings required in the development venture and set up a few obligations for each of the distinctive partners. It likewise highlights that the measure of printed material and all the administration brought on by the past rendition of the controls ought to be diminished and the attention put on the arranging and administration.
The CDM set up commitments for customers and fashioners. The fundamental commitment forced to the customer is to delegate the primary partners for the arranging and the acknowledgment of development work. By ‘development work’, the CDM extensively alludes to ‘the doing of building, structural designing or building development word’ .Among the dutyholders which take an interest to the doing of the venture are the Client, the Designer, the CDM-Coordinator, the Principal Contractor and the Contractors.
(The Construction (Design and Management) Regulations ,2007)
Evaluate and justify the role of the planning coordinator who has been appointed to the project.
Construction project coordinators plan, organize, and guide the actions of a construction project, under the guidance of a manager. He works on-site most of the time, over looking the day-to-day tasks of the project. He works for residential, commercial and industrial construction companies or for construction departments of companies outside the construction industry.
Generally, construction project coordinators:
- Make contracts and negotiate alterations to contracts with architects, consultants, clients, suppliers, and subcontractors.
- Suggest and implement QC programs.
- Make progress reports for clients.
- Control the acquisition of building materials and land.
- Hire and supervise subcontractors and staff.
During the excavation works the contractor found that the sub-soil in a section of the site to be contaminated. All site activities were halted pending further investigations. Following the investigations it was found that the site was contaminated with caustic soda and from material linked to buried heavy fuel tanks. The client has asked for a design solution to the problem.
- The contaminated ground can be treated with 5% ferric chloride treat the caustic soda contamination.
- Proper waterproofing of basement can further ensure that the caustic soda intrusion is completely blocked.
- Burried heavy fuel tanks should be properly sealed to prevent further leakages.
- If the contaminated section can be completely removed it should be removed and disposed safely to continue construction work.
(Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Human Health Evaluation Manual)
Produce a risk assessment for the above problem.
Hazard identification
- Caustic Soda and Heavy fuel Contamination.
- Laborers and stakeholders can be affected
- Sub soil needs to be treated or removed
- Treatment can be done with 5% ferric chloride for caustic soda
- Heavy fuel needs to be completely removed
- Waterproofing of basement should be done
Earthwork calculations
Area of the building
From given details =
Section 1= 30×40 = 1200 m2
Section 2 = (40+d)x32-(25+d)x5 = 1315m2
D= 5.94
Total Area = 2515 m2
Total depth to be excavated for basement = 5m
Hence total cut volume = 2515×5 = 12575m3
Total land area
a= 8.43
b= 9.06
c= 5.06
Total available land area = 165.43×122.22-1380-57.5-34.5-485-159
= 18102.8 m2
Average depth to be cut to level the area = 27.3-25.6=1.7 m
Since cross sectional details are not enough I will assume that the average depth is 1.3 m
Hence total cut volume = 18102.8×1.3= 23533.4m3=
Hence total cut volume of project = 36108.64m3
A hydraulic excavator can excavate 242.4242 m3 of soil in one day
Hence total number of days required if one excavator is used = 149 days
That is too much. Hence we can use 2 excavators = 149/2 = 74.5 days ( 2 .5 months)
Together with that we need 4 dump trucks , 2 skid steer loaders and 2 backhoe loaders to support the excavators.
Bibliography
- Caisson” def. 3. Knight, Edward Henry. Knight’s American mechanical dictionary A description of tools, instruments, machines, processes, and engineering; history of inventions; general technological vocabulary; and digest of mechanical appliances in science and the arts. vol. 1 Boston: Houghton, Mifflin and Co., 1877. 420. Print.
- Wilson, Theodore Delavan, and Edward J. Reed. An outline of ship building, theoretical and practical.. New York: J. Wiley & son, 1873. 383. Print.
- “History of the Bulldozer”. Retrieved 2008-12-17.
- Jessica Morrison (2013-10-30). “How Engineers Use Ground Freezing to Build Bigger, Safer, and Deeper”. PBS. Archived from the original on 2014-04-11. Retrieved 2014-07-22. The basic premise behind ground freezing is that soil-made up of bits of minerals and organic matter, water, and air-becomes stronger and less penetrable when its water freezes and expands.
- Powers, J. Patrick (1992). Construction dewatering: new methods and applications. New York City: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-60185-3. OCLC 24502054. Retrieved 15 May 2009.
- Fleming, W. G. K. et al., 1985, Piling Engineering, Surrey University Press; Hunt, R. E., Geotechnical Engineering Analysis and Evaluation, 1986, McGraw-Hill.
- Halpin, Daniel W.; Senior, Bolivar A. (2010), Construction Management (4 ed.), Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, p. 9, ISBN 9780470447239, retrieved May 16, 2015
- Turner-Fairbank Highway research Center (1998). “Hydraulic Design of Highway Culverts” (PDF), Report #FHWA-IP-85-15 U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, McLean, Virginia.
- “Concrete in Practice: What, Why, and How?”(PDF). NRMCA-National Ready Mixed Concrete Association. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- “The Construction (Design and Management) Regulations 2007”. Legislation.gov.uk. Retrieved 2014-06-12.
- Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund, Human Health Evaluation Manual, Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington D.C. 20450