Analysis of India’s Service Sector
The services sector is not only the dominant sector in India’s GDP, but has also appealed significant foreign security tides, significantly backing to exports as well as provide large-scale employment. India’s services sector covers a wide variety of activities such as trade, hotel and restaurants, transport, storage and communication, financing, insurance, real estate, business services, community, social and personal services, and services associated with construction. Labor productivity in services is the chief and it has amplified tirelessly. India’s service sector is recognized by its magnitude and vigor accounting for more than 55% to gross domestic product (GDP) which is progressively increasing by 10 % p.a. and contributing to around 25% to aggregate employment and having major provisions in FDI invasions and 33% of total exports. The statistics pertaining to a number of aspects of service sector was collected from secondary source such as published articles, journals and reports. The report aims to analyze the performance, growth and also challenges faced by service sector in India. The results revealed that amongst different countries India levels 12th position, sharing service sector to Indian economy. (IBEF, 2017)
The services sector’s evolution was expressively faster than the 6.6% for the joint agriculture and industry sectors annual output growth. Further, India with a services sector share of 52% in national GDP in 2009 and 55.2 per cent in 2009-10 associates well even with the developed countries in the top 12 countries with the highest overall GDP. It was observed that there was an upsurge in share of service sector to countries GDP at existing prices from 30.5 to 55 % during 1950-2010. The report also conveys that the performance of service sector such as communication, transportation and storage was high with an growth of 15 % in 2009-10 when compared to other sectors and hotels and restaurants had an adverse growth rate in the economy. Further, the major challenges in service sector was to retain the competitiveness and preserve the traditional service sectors such as shipping and tourism. Furthermore, there is lot of scope for India’s domestic market such as sectors like education, accounting and health care service. Hence, the reading suggest that if these challenging issues can be taken care still the service sector can be boosted with good discretionary growth for offering many employment opportunities and also maintaining balance of trade. (AOISS, 2016)
The contribution of service sectors in country’s GDP (factor cost) has increased from 30% to 55% during the period of 1950 to 2010. Apart from this, the GDP contribution can be increased if these sectors are further enriched and take account of construction sector, then it will be around 63% share in 2009-2010. There is a continues debate on counting either construction can be induced into secondary or tertiary sector even as RBI and many international institutions like WTO which consider construction sector under service sectors. The classification of the services sector consists of four major categories given by Central Statistical Organization (CSO). Among 4 sectors, in first group, over the years hotels and restaurants were positive and gradually they declined showing negative growth with and however, for trade it was a positive growth. On the other hand Social, Community and personnel services, it is evident that country’s overall GDPÂ growth rate has increased from 5.7 % to 8.6 % during the period of 1990 and 2004 to 2010. This increased percentage growth was due to the acceleration of service sectors which was increased from 7.5 % to 10.3 % from 2004 to 2009-10. Contrariwise, during the same period it was around 6.6 % for inclusion of both primary and secondary sectors. Despite of global recession since 2008, it is observed that service sector has been showing growth rate of 10% p.a. The findings of World Trade Organization (WTO) reveals that India has maximum share in net exporter of services over a period of 2006-07 to 2008-09 with an increase percentage of GDP from $29.5 to $54 Billion when compared to other sectors in the economy. However, during the global recession period exports of services were abruptly declined and imports of services where deliberately increasing in nature which resulted in 2.8 % of GDP during the year 2009-10. The WTO feels that global crisis has downgraded the global business and where as in case of software service(IT sector) it was found to be positive and uninterruptedly growing.
India is a major protagonist of liberalizing services equally in the WTO and in its bilateral trade treaties. Though, there are some concerns. Economic growth has slowed down. Growth in service employment has not been proportionate with the share of the sector in GDP. A large part of the employment is in the non-corporate or unorganized sector, with partial job security. Although India is depicted as a major exporter of services, its rank among WTO member countries in services exports is lower than that of China’s and its export competitiveness focuses in few sectors and a few markets. The report identifies a number of barriers faced by the services sectors and suggests policy measures, which, if implemented, will lead to inclusive growth, increased productivity, generate quality employment, increase trade and investment, and enhance India’s global competitiveness in services.
|
Country |
Rank |
OVERALL GDP(US$ BILLIONS) |
Share of Services(% of GDP) |
|||||
|
Overall Service |
At current Prices |
At Constant Prices |
||||||
|
GDP |
GDP |
2014 |
2014 |
2000 |
20013 |
2014 |
||
|
United States |
1 |
1 |
14119 |
12899 |
74.1 |
76.8 |
76.5 |
|
|
Japan |
2 |
2 |
5069 |
4451 |
71 |
71.3 |
71 |
|
|
China |
3 |
3 |
4984 |
3544 |
39 |
39.1 |
392 |
|
|
Germany |
4 |
4 |
3330 |
2847 |
61.6 |
64.4 |
66.1 |
|
|
France |
5 |
5 |
2649 |
2192 |
68.6 |
70 |
71.1 |
|
|
UK |
6 |
6 |
2170 |
2285 |
65.4 |
63.3 |
70.5 |
|
|
Italy |
7 |
7 |
2113 |
1725 |
62.5 |
64.6 |
66.6 |
|
|
Brazil |
8 |
8 |
1572 |
1021 |
55.5 |
55.8 |
57.3 |
|
|
Spain |
9 |
9 |
1464 |
1182 |
59.3 |
61.9 |
63.6 |
|
|
Canada |
10 |
10 |
1336 |
1168 |
59.5 |
64 |
65.5 |
|
|
India |
11 |
11 |
1287 |
1141 |
45.9 |
52.4 |
52 |
|
|
Russia |
12 |
12 |
1231 |
865 |
50.2 |
52.4 |
54 |
|
|
World |
* |
* |
58069 |
49356 |
63.7 |
64 |
64.2 |
|
(AOISS, 2016)
The Indian services sector which includes financial, banking, insurance, non-financial/business, outsourcing, research and development, courier and technical test analysis, Professional services, personal services, health services, ancillary services, etc. are a few example/types of services in the Indian service sector prevailing at the movement. Given below is the contribution of each service individually for GDP.
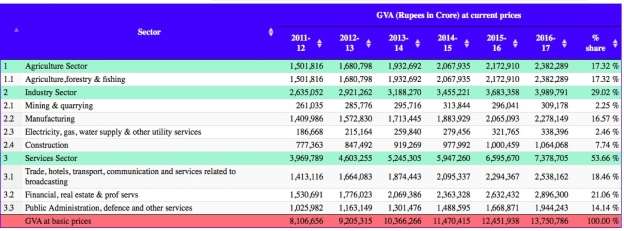
The above chart demonstrations 55.66% India’s service sector share in GDP.
The services sector in India has remained the most vibrant sector in terms of contribution to national and state incomes, trade flows, FDI inflows, and employment.
Foreign direct investment (FDI)
There is increase in 22% in 2014 from 34 billion US$ over 2013. There has been a significant growth in FDI in 2014-15 and 2015-16(April – October) in general and in Services Sector in particular. In 2014-15, FDI inflows to the Services Sector grew by a whopping 70.4% to 16.4 billion US$. It show rising trend in first seven months of 2015-16 with FDI equity inflows of service sector growing by 74.7% to 14.8 billion US$. Liberalization taking place ensure that India remains an attractive investment destination.
.
India’s Services Trade
Services exports has crucial element in India’s trade and globalization in recent years. India constitutes 7.5% of GDP and shows 8th largest service exporter in the world. Exports has raised from 16.8 billion US$ in 2001 to 155.6 billion US$ in 2014. Economy reflects openness at 50% which higher in 2014-15 compared to 38% in 2004-05. India’s Services Import was 81.1 billion US$ which rose by 3.3% in 2014-15. Initiatives were also taken by the government of India to promote services exports including the Service Export from India Scheme (SEIS) and organizing Global Exhibition on Services (GES).
Tourism
Economic growth depends major on tourism which creates employment for diverse kinds. Tourism growth was 10.2% in terms of foreign Tourist Arrival (FTA) and 9.7% in terms of foreign exchange Earnings (FEE) in 2014 by economic survey of India. After this it fell by 4.5% and 2.8% in terms of FTAs and FEEs in 2015. Lower in FTAs and FEEs in 2015 is due to low growth in FTAs and high spending was done by tourists originating from Europeans countries like France, Germany and UK. Domestic tourism showed important contribution to sector and it grew by 12.9%. The top five states in contributing in 2014 are Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh. Two schemes were launched in 2014-15 for thematic development of tourism which were Swadesh Darshan and National Mission on Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual Augmentation Drive (PRASAD). Healthcare portal and advantage health care India was launched for promotion of medical tourism.
Shipping & Port Services
Around 95% and 68% India trade by volume and value is transported by sea. UNCTAD shows that India with 11.7 million twenty-foot equivalent units of container and world share of 1.7%. It ranks ninth in 2014 amongst developing countries in containership operations. Increase in the share of coastal/inland waterways transport mode from 7% to 10% by 2019-20 which was vision by coastal shipping tourism and regional development. 1052.21 million tons in 2014-15 cargo traffic of India ports rise by 8.2%. The target for the years 2020 is 3130 millions tones of port capacity and investment is around INR296000 crores by Maritime Agenda.
IT Services
The IT shows flexibility as per the economic survey which estimated share of 9.5% of GDP and over 45% total services exports is 2015-16. E-commerce should reach 17 billion US$ which shows 21.4% of GDP. India ranks third largest technology starts ups in the world. 40 percent of startups have grown in one year by offering 80 to 85 thousand jobs in 2015. The emerging sectors will fillip to startup India program.
Research and Development Services
According to CSO’s (Central Statistical Organization) says that there is no separate head for research and development as it is a part of professional scientific and technical activity which includes R & D. Research and development rise at 3.8% and 25.5 respectively in 2013-14 and 2014-15. Survey concludes India’s R&D globalization and services market is going to double by 2020 to 38 billion US$.
Consultancy Services
The Survey shows Consultancy Services is one of the fastest growing service segments in India. Initiatives are taken by government like the Marketing Development Assistance and Market Access Initiative Scheme among others for capacity development of domestic consultants.
Real Estate and Housing
It constituted 8.0% of the India’s GVA (Gross Value Added) in 2014-15 and rise by 9.1%. Since 2011-12 sector has grown by 8.1%. However, the construction sector has slowdown in last few years due to weak domestic and global growth. The Government has launched plans to build 6 crore houses by the year 2022 under the Housing for All scheme.
Internal Trade
Survey tells, Rs. 12, 31,073 crore trade and repair services sector share 10.7% in GVA, rose by 10.8% in 2014-15. India’s retail market is expected to rise to 1.3 trillion US$ by 2020 and India will be the world’s fastest growing major developing market. 16 billion US$ is the expectation to grow by 2015 because of growing internet population and increased online shoppers.
Media and Entertainment Services
According to the Economic Survey, the industry has recorded unexpected growth over the last two decades. It has become one the fastest growing industries in India. CAGR of 13.9% is projected to reach 1964 billion rupees by 2019. Digital advertising and gaming, which rise by 44.5% and 22.4% respectively in 2014, are predicated to drive the growth of this sector in the coming years.
Postal Services
India Posts is the largest Postal network in world. From 30.86 crore it increased to 33.97 crore post office savings bank and total deposits in POSB accounts and cash certificate to Rs. 6.53 lakhs crore in the last one year. More than 80 lakh Sukanya Samridhi Yojna accounts have been opened. The IT Modernization Project of the Department of Posts, with a total outlay of Rs. 4909 crore, involves computerization and networking of all the post offices.
Though service sector contributes highly in India’s economy there are still problems which are faced by this sector, which stops it from maximizing its growth potential. The GVA for 2016-17 in service sector was Rs. 7,378,705 which is 56.66% of the total economy, more than half of contribution comes from the service sector, but it only provides around 25% of employment. But still, both existing as well as start-up firms in service sector are facing several problems and challenges while growing as well as surviving in the Indian economy.
Starting with Infrastructure, being the most common sector, the infrastructure facilities are inadequate both in rural as well as urban areas. We want accelerated growth for India, but we are not willing to see the fact that in a lot of places we don’t have enough infrastructure which causes problems like unemployment, lack of quality of services as compared to the rest of the world, hence decelerating the growth.
Talking about another aspect, which is tourism, we want people to think highly about India, but we don’t have tourism facilities and infrastructure to attract foreign tourists, we don’t have enough information and guidance on how to use public transport services. Foreign tourists often get cheated and looted in India, hence causing another problematic aspect. India has great potential for tourism if all these issues are removed and public sector tourism and transportation services are refined and enhanced including, Airports, Railway Stations, Bus stations etc.
On the other hand, service trades are also facing several issues such as lack of setup of export councils in several industries, several barriers like visa issues, sector specific restrictions. Also the service sector cannot grow alone, it needs a holistic support from other primary and secondary sectors in the country, such as banking support, insurance etc.
Another interesting point is that India which is a key preference area for outsourcing BPO’s are facing strong competition from other developing countries, they have to improve their quality and assistance to stay strong in the industry of BPO.
Though, rising automation of transactions and reduction in problems and restrictions in licenses and permits; and the activities of a free, vocal and critical media have improved transparency for business, but feedback from businesses active in the Indian market still show that there are several issues that need to be adhered to. Government can also encourage solving these problems by R&D, forming teams to assess problems and tackle them effectively one problem at a time.
The services sector is heterogeneous and contains lots of different agencies, different services are getting integrated due to technological developments.
The government should therefore consider this in the planning of budget. In the case of sectors like transport and energy the different departments of the government should work together to design policy in 5 year and 10 year plans.
Now moving towards the employment issues, the service sector has not been able to generate employment in terms of numbers as well as quality. There is shortage of labor in sectors like IT, Automobiles etc. Studies have shown that although employees prefer to work in the organized sector, skill requirements are different and it is not easy for employees to shift from unorganized to organized sector. Gross enrolment ratio is low and there are various institutes where people are not able to get jobs Degrees granted by some private universities are not recognized even within India, further affecting the employability of people.
In many scenarios, companies in the services sector have to invest a lot in training and development of their employees. The government’s education policy and funding have focused on higher education and have neglected primary education, still there are problems on both ends.
Talking about startups, when a service startup finds their market, demand for its services will increase, and the company will need to grow and involve and take care of the needs of its growing customers. Growing at this fast rate is a challenge for small and difficult for startups, wherein high growth rate in other industries is seen as a plus point, startups need the support from government to cater such accelerating needs. This also means to finding and hiring new talent to help tackle the issues.
Therefore we can conclude that, the scope of growth is very high in service sector industry in India, but there lots of barriers, visible as well as invisible, so as we move forward removing these barriers, we can become the top economy with the highest growing service sector in the world, but at first we as people should be more vigilant, less corrupted and more contributing towards the society, for enabling change in the country.
Growth of service sector
Services is a set of economic activities like transportation, trade, tourism, communications, banking and insurance, real estate and so on. There are a few factors responsible for growth of service sector in India like demographic, social, economic and political.
Demographic changes:
With a rise in the standard of living the life expectancy has risen which in turn is increasing the size of the retired population and creating a new demand for travel and leisure, as well as for healthcare, nursing and life insurance. The need for infrastructural support services has increased due to the development of new towns and regions.
Social changes:
The population of working women has drastically increased which has led to traditional domestic functions being performed outside the home. With an addition of an earning member in the house the demand for consumer services, including retailing, real estate and personal financial services have continuously been increasing. With the rising income, the standard of life has also improved. Smaller families with double income have started spending more on entertainment, travel and hospitality services than before. Also with increase in communication and travel the children and adults these days are making new demands on learning establishments, so that they can develop the skills needed in order to compete. In today’s dynamic environment all this has created market for knowledge and information based services.
Economic changes:
Due to globalization the demand for communication, travel and information services has increased and this gap has been filled by constantly updating with new information technology. With increasing degree of specialization in ever industry the economy has led to a reliance on specialist service providers.
Political and legal changes:
A country’s government plays an important role in its growth, a country with minimum leakages will have better growth rate because of less corruption. With a constant growth in international trade, the demand on legal and other professional services have increased, cutting across national boundaries. The Indian government realizes the importance of promoting growth in the area and is creating an environment that will promote sectors such as healthcare, tourism, communications, information technology, and many others.
REASONS FOR THE GROWTH OF SERVICES IN INDIA:
Changing Role of Women:
Traditionally Indian women were seen as people involved with household activities. But with the changing time there has been a change in the traditional way of thinking in the society. Women are now allowed to work. They are employed in many service sectors across the country like defence services, software services, health services, hospital services, police services, postal services, entertainment industries, Business Process Outsourcing and so on.
The percentage of working women has been increasing rapidly. This changing of traditional role of women has led to demand for various product and services. Now days earning women prefer to charter services in order to reduce the numerous roles that they are required to perform. The changing role of women activities from household activities to working individuals is forcing service organizations to be more innovative in their approach.
Cultural Changes:
During the last century there is a lot that has been westernized in the Indian culture. People have started living in nuclear family in the place of traditional joint families which has created a demand for a number of services like education, health care, entertainment, telecommunication, transport, tourism and so on. Also there has been a change in the thought processes relating to investment, general expenditure, leisure time perception and so on which has created a huge demand in various sectors based on choices.
I.T. Revolution:
From the past decade India has been constantly working hard and has been able to occupy a vital position in the field of Information Technology. For Indians IT became one of the key service businesses. Currently the highest software skilled population in the world is in India and because of which the domestic market as well as the international market has grown substantially. The government is realizing the potential for this area and have already prioritized their expenditure for such purposes in different states.
Development of Markets:
With changing environment the competition in all the industries have drastically increased. The number of wholesalers and retailers during the last few decades have increased in the country. Urban India has become a cluster of wholesaling and retailing business. A new type of organisations, offering marketing based services has come up. The government is also offering marketing services to the small-scale agricultural farmers, artisans and other traditional businesses.
Migration of population:
With increasing inflation and overall cost of living people have started migrating from rural to semi-urban and urban areas in search of better jobs which has resulted in the expansion of cities and townships due to which businesses like real estates, rentals, transportation and infrastructure services are rapidly expanding.
Export potential:
India is considered to be the hub of the affordable services. India currently offers services like banking, insurance, accounting services, construction labour, designing, entertainment, education, health services, software services and tourism to various parts of the world. The advantage of having the highest number of software skilled population helps in doing this at affordable prices.