Analysis of Macroscopic Traffic Flow Parameters
ANALYSIS OF MACROSCOPIC TRAFFIC FLOW PARAMETERS OF HETEROGENEOUS TRAFFIC – A CASE STUDY OF SELECTED STRETCH OF DAKOR
Abstract –
Keywords: Traffic flow, macroscopic parameter, capacity, level of service.
Transportation refers as a movement of persons, animals and goods from one place (origin) to another place (destination). Now a days, transportation is going to be a part of our life to achieve our necessity. Increase in transportation is because of increase in population basically. The population of India is growing rapidly with a national average growth rate of 2.7 percent per annum (Census of India, 2010). The growing cities have generated the high levels of demand for travel by motor vehicles in the cities. This has resulted in tremendous increase in the population of automobiles in the cities. The Indian population increased with a decadal growth of 17.64% (census 2011) and annual growth rate of 1.2% (World Bank report). Next to this, the revolution in the automobile industry, liberalized economy and change in people’s life has led to tremendous increase in the vehicle ownership levels. This has resulted in changing in nature of traffic characteristics on road network and ultimately it affects the capacity of roadway, level of service on stream and congestion on roadway. Hence reduce in speed, unwanted traffic delays, road accidents, traffic jam, increase in travel time etc. are resulted. Therefore, the analysis of traffic stream parameter is needed to study for the effective planning, design, operation and maintenance of roadway system.
Homogeneous traffic has strict lane discipline and has traffic entity types whose physical dimensions do not vary much. In the nonhomogeneous traffic they loose lane discipline prevails. The physical dimensions of the traffic entities vary greatly. Operationally, acceleration and deceleration characteristics vary greatly because nonmotorized traffic entities exist along with motorized vehicles on the road. The most of the studies in such traffic make use of the methods and concepts developed for homogeneous traffic.
In India, it seems that the traffic is greatly differ due to vehicular and road user characteristics. The interaction between different size vehicles and their drivers as well as the infrastructure gives rise to many complex phenomena on our roads. To understand traffic flow, relationships have been established between the two main characteristics: flow and velocity. Flow, speed, and density are the critical parameters used to describe characteristics of traffic flow. A traffic flow fundamental diagram is used to characterize the relation between these three parameters, and plays an important role in traffic flow theory and traffic engineering. In capacity analysis, speed-flow relation models are used to determine the level of service. The time gap between successive vehicle arrivals, namely, time headway between vehicles is an important traffic flow characteristic that affects the safety, level of service and road capacity. Understanding time headways and their distributions will enable better management of traffic.
The aim of study is to analyse the macroscopic traffic flow parameters of heterogeneous traffic on selected stretch of Dakor. The objectives of study are as following,
- To estimate the basic traffic flow parameters for different traffic stream under study.
- To develop analytical relationship among traffic flow parameters.
- To determine the congestion, capacity and level of service of selected road stretch under study.
- To suggest the suitable solution for the observed problem of congestion.
Dakor is a pilgrim area and it is observed that a large amount of trip attraction takes place. The surrounding area comprise of large numbers of quarries, as a result of this major traffic observed at the site are multi axle trucks, resulting into considerable congestion. Hence it is necessary to understand the traffic behavior at the chosen site. Dakor, in its earlier phases as pilgrimage center in Gujarat, was famous for the Danknath temple, a place of Shiva worship. Recently, Dakor is included in one of the six major pilgrimage places under “Yatradham Vikas Board” by Government of Gujarat for development as a well-planned and well organized pilgrimage place to facilitate the lacs and lacs of visiting pilgrims. More than 70-80 lacs of pilgrims visit the place every year and a continuous increase is witnessed every year. Dakor is located at 22.75°N 73.15°E. By visual observation and pilot survey, it is examine that the traffic density increases to jam density.
METHODOLOGY
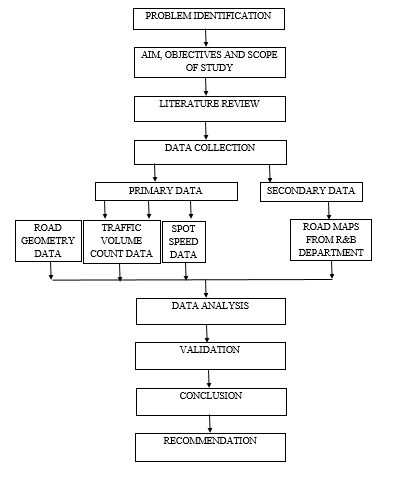
DATA COLLECTION
The study consist of conducting various surveys on selected stretches of Dakor. Data collection is carried out carefully as it is the raw data for final analysis. There are two types of data collected in data collection namely Primary Data and Secondary Data. Primary data is collected from spot speed survey, classified volume count survey and road geometry data by self-measurement of road stretch. Whenever secondary data is collected from the maps given by Road & Building Department of Kheda District.
Primary data collection
Road inventory, traffic volume count and spot speed study is carried out manually.
Classified volume count
Number of vehicles passing through a point or entering a stretch is considered in the analysis of roadway operations. Traffic volume can be counted by manual or video graphic techniques. Here manual traffic survey is carried out for 09:00 am to 7:00 pm with 15 minute time interval and volume of traffic is calculated using tally counter on mid-block section of Dakor to Umreth road.
Analysis of traffic volume data has been done and following results shows the composition if traffic on road and variation of traffic on road.
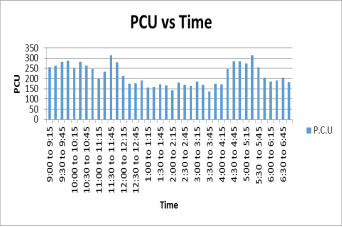
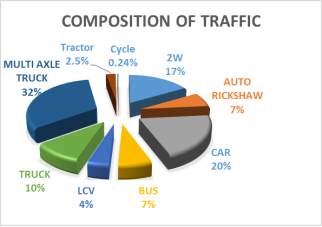
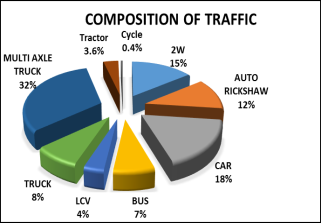
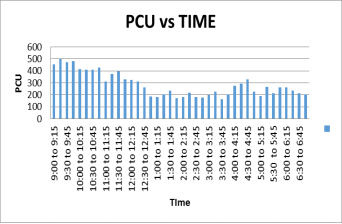
Figure: Traffic volume analysis for Dakor to Umreth
Figure: Traffic volume analysis for Umreth to Dakor
Spot speed study
Speed is one of the most important characteristic of traffic as measure of effectiveness of traffic system performance. Speed is highly sensitive to the interaction among vehicles in the stream. The spot speed study is carried out on Dakor to Umreth road. The average speed, time mean speed, space mean speed, standard deviation is calculated from spot speed data.
|
Spot speed study data analysis on Umreth to Dakor road |
||||||
|
standard deviation |
Space mean speed (km/hr) |
time mean speed (km/hr) |
median speed (km/hr) |
minimum speed (km/hr) |
maximum speed (km/hr) |
|
|
2-w |
8.07 |
37.11 |
38.75 |
38.57 |
25.71 |
56.84 |
|
3-w |
8.12 |
33.48 |
35.16 |
31.76 |
22.04 |
54 |
|
4-w |
11.31 |
37.47 |
40.46 |
37.91 |
26.34 |
63.53 |
|
Bus |
7.33 |
35.67 |
37.07 |
36.62 |
26.34 |
51.43 |
|
Truck |
3.29 |
32.65 |
33.01 |
32.73 |
27.69 |
40.00 |
|
Multi Axle Truck |
4.79 |
35.98 |
36.61 |
36.00 |
27.69 |
46.96 |
|
LCV |
4.30 |
34.59 |
35.09 |
34.29 |
27.69 |
51.43 |
|
Spot speed study data on Dakor to Umreth road |
||||||
|
standard deviation |
Space mean speed (km/hr) |
time mean speed (km/hr) |
median speed (km/hr) |
minimum speed (km/hr) |
maximum speed (km/hr) |
|
|
2-w |
4.65 |
38.23 |
37.70 |
37.96 |
30.86 |
60 |
|
3-w |
5.83 |
33.86 |
34.85 |
33.75 |
24 |
46.96 |
|
4-w |
7.29 |
41.47 |
42.97 |
41.54 |
23.48 |
60 |
|
Bus |
5.73 |
34.57 |
35.49 |
34.29 |
23.48 |
54 |
|
Truck |
5.14 |
35.34 |
36.05 |
34.84 |
27.69 |
49.05 |
|
Multi Axle Truck |
3.68 |
36.97 |
37.32 |
37.31 |
30 |
46.96 |
|
LCV |
3.10 |
37.80 |
38.05 |
37.96 |
30.86 |
45.00 |