Characteristics of Change Management Models
1.1 Evaluate the characteristics and application of a range of change management models for different organisational structures.
Organisational structure is there to determine how the roles, power and responsibility are assigned, controlled and coordinated and how information flows between the different levels of management. There are many different structures and this depends on the organisation’s objectives and strategy.
- Hierarchical – this structure has a longer chain of command, each on a different level one above the other, like a pyramid. The advantages of this is authority and responsibility are clear and well defined, opportunity for promotion motivates employees and employees can specialise and develop expertise in their field. On the other hand the disadvantages are communication between departments may be less effective, decision making can take longer, may be harder to adapt and change or even rivalry between departments.
- Functional – this is one of the most common especially in larger businesses they do this by dividing the business via departments such as sale, marketing, finance, human resources etc. The advantages of this structure is that it is specialised so departments focus on one area of work, productivity as they are specialised the staff are skilled in the tasks they perform, accountability there are clear lines of management and clarity everyone understands their roles. On the other hand the disadvantages may be closed communication, co-ordination may become difficult and they may be resistant to change.
- Flat – this occurs when there are no management levels, when all staff report to one overall manager mainly seen in small businesses. The advantages to this structure are: better communication and relationship between different roles, simple, fast decision making process, easier to change and adapt. On the other hand the disadvantages may be that employees may be less specialised and it is difficult to maintain this structure as the company grows.
I would say we are between a flat and hierarchical structure because we are still relatively a small business but growing, there are fewer levels of management. We have our directors, managers and room leaders so it is a fairly direct chain of command with leaders having access to the directors very easily as we all work very closely together but you can see as we grow levels will be added.
Change management theories
Business environments are constantly changing and evolving such as social media and mobile capability have changed they way we do business which means there is an ever increasing need to change and therefore change management. Change is a key source of competitive advantage and change is all about survival. There are several key change management models such as Kotter J.P.(2012) invented the eight step model for leading change.
- Create a sense of urgency – if people think the organisation is doing fine there will be little motivation for change. It is important that your employees see the need for change. This is the most important and difficult step to make sure everyone is on the same page in order to make the change happen.
- Bring everyone together – it is essential to have a strong leader to convince employee that the change is necessary.
- Create a clear vision and strategy – having a clear vision allows people to remember easily what your are asking them to do.
- Communicate your vision to others- share the visions and make sure all staff understand what we are aiming for. It is important to talk about your vision often and use it daily to make decision and solve problems.
- Remove obstacles- to clear obstacles and have a can do attitude this will help empower employees execute your vision and move forward.
- Motivate with short term wins- this will build confidence and allowing staff achieve short term goals will give them a taste of success. You want it to be achievable with little room for failure, so that they will want to get to the final stage of the change process.
- Build on the change- saying the above you need to be careful not reward too early and keep moving forward and building on the change.
- Change to become the core of the organisation- to avoid old habits creeping back in the change that came in place needs to be imbedded into the heart of the company.
The real change requires a subtle motivation driven approach and is broad based rather than narrow and built on inclusion. Therefore collaboration is the base for success and to achieve that there must be a wide spread perception for change. We need to look at our own competitive situation and effective communication is key to getting the word out and achieving employee engagement. Change is only possible if everyone participates.
In relation to how this Kotter’s change model is suitable for a change process with our organisational structure can be shown through an example of change we have currently put into action in our company.
As part of a requirement by our governing body in the childcare industry we must keep a learning journal for each child, tracking and tracing the developments in their learning during their time in our nursery. For many year this was a manual hand written process, each child had a large word processed book that our members of staff needed to complete throughout the child’s duration in the nursery. We then needed to keep these records for numerous years. Looking back on this now it was a lot of paperwork and you need a lot of space to store these records. Over the last two years we have introduced a change in this form of record keeping procedure and are now processing everything on a on-line program called Tapestry. This on-line learning journal is an innovative, time effective and kind to the environment form of keeping these records. We can give this change as an example of how we can use Kotter’s theory to bring this change to life.
As stage one says the hardest job of this change was to explain the need of it to the staff. It was important to educate the staff and get them to understand the urgency for this change. The urgency being to move with the times and go paper less and digital, this was a daunting thought for them as many did not have strong IT skills and feared this process being difficult. We need to match our competitors and make sure we were part of the change that was happening in the industry. This application Tapestry is not only for inputting information about a child but it has an interactive live element to it where parents can log in and see the work we are doing and their child’s achievements. This was a major reason for us wanting to introduce this change so that we can improve our communication with parents and give them a live insight to what we do with the children in our setting.
After numerous meetings and discussions with our staff they understood the need for this change which really helped us move forward. By educating them and giving them so much information about the program, training them how to use it and explaining the benefits to us all they all came on board excited to get started. We created a clear vision and made sure it was communicated and brought in to our daily working lives.
We set them small and achievable steps to show them they can do it and motivated them with rewards for their achievements. We recognised the staff that did a great job and told them all that by working and helping each other we can be better. We offered a lot of training in groups and one on one so that no one was left behind or struggling.
We empowered them by setting deadlines for information about their key children to be inputted and then checked their work and give them feedback on their achievements. This really motivated them as they were proud of what they have accomplished and felt that we really took time out of our day to say well done.
Now two year into this change we are about to go live to parents and are looking forward to this being the start of a new era. Using this programme has really become a part of our daily working life and cant imagine going back to the old way. There are so many ways we can and are moving forward in our industry today but this is just one example of how we can manage change.
In saying the above we can look at how Kubler-Ross (1960) change curve model can be discussed in relation to the example of us changing programs to Tapestry. Kubler- Ross Change Curve is a reliable tool to understand change and the stages associated with it, it is about us being able to help our employees adapt to change and move towards success.
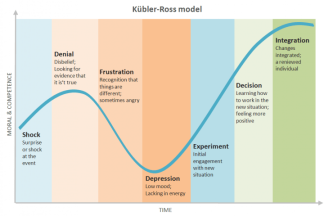
As we can see from the model above it is translated into the 5 stages of the grieving process. The 5 stages included in this model are denial, anger, bargaining, depression and acceptance, this also holds true when it comes to business or employment and we need to understand during the change process at what stage our employees are at. If our employees do not make personal changes or transitions during our change process we will not see the benefits of this change or move forward.
It is important to support our staff through every stage of any change we implement in order for us to ensure success, this can be shown in the amount of training we invest in and support we give our staff to give them the tools they need to achieve.
At stage one this can be shock or denial to the fact that change needs to occur and they may need to adapt to something new. Information is key at this stage, it will take time to digest and giving them knowledge and constantly communicating will empower them to be confident in the change.
Stage two once all has settled and everything becomes clear they may begin to feel fear of what lies ahead of them. It is natural to panic and believe that you can not make this change happen and question yourself and your capability. It can also make them feel anger or resentful because they may have been comfortable in what they were doing and change means learning something new. This is an important stage to manage and ensure it is controlled so that employees stick with you. Once again communication is essential.
Stage three at this point employees understand the change and may start to bargain and possibly learn only what they think is necessary. This is when training is key and vital to ensure that everyone receives the best information and access to mentoring. It is important not to rush this stage and why we have taken nearly two years for our staff to trial the program before it goes live to parents. Allowing them to make mistakes and learn from them so that we are well equipped when this system is introduced.
Stage four is the point at which moral and motivation can be low so when providing our training we try and make it as interactive and fun as possible so not only do they remember what is being taught but enjoy themselves in the process meaning they will do their best.
Stage five is when we all really start to embrace the change and when we will really start moving forward.
There are numerous other theories available for us to look at when discussing change management but for the two that I have analysed we can clearly see the difference between the two model but their relevance and importance are still the same in the example I have given regarding Tapestry. In conclusion it has shown me that when it comes to any change within the organisation we need to ensure everyone is on board, educated, supported and enthusiastic about the project in order for it to succeed. Change can not be made to happen by one person it takes the whole company to want to come together to move us forward, therefore we need to make sure we are able to manage the change/project, our staff and ourselves throughout the whole process.
1.2 Analyse stakeholder mapping techniques used for managing and evaluating change
When it comes to managing projects and implementing ideas the actions you take can effect a lot of people and some of these people will have more influence over the success of our project more than others. Therefore knowing who these people are before you start is incredibly important. This is because you are more likely to succeed if you have the support of your key stakeholders. Stakeholders are people interested in our business they can be internal i.e. employees and owners or external i.e. suppliers, customers and government. It is important to understand who our key stakeholders are, this is where you would use a stakeholders map. The actions you take when you look at the power versus interest the stakeholder has being high or low.
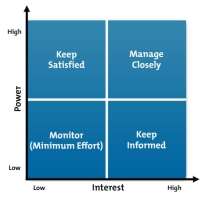 Stakeholder Power and Interest Mapping Bryson (2004)
Stakeholder Power and Interest Mapping Bryson (2004)
(Sourced: Mindtools.com)
From the drawing above you can see there are four types of stakeholders, those of:
- High power/high interest – these are your most important stakeholders that you should keep informed and close to your project. For us this would be our Directors and managers
- High power/low interest – these stakeholders are to be kept satisfied, their power is high so they can influence your project but their interest is low so this is unlikely.
- Low power/high interest – keep these people informed as this can support your project. For us this would be our employees and customers.
- Low power/low interest – to be monitored with little effort as these stakeholders cant influence your project and are unlikely to be involved.
This analytical tool will help you better understand where to focus your energy and time. It is important to spend a lot of strategic effort thinking about where your real power is held and knowing how to keep our key stakeholders engaged. In relation to keeping them engaged we need to ensure we are communicating with them using the right channels and tools of communication. The disadvantage of this tool is that unless you really know your stakeholders well you can place them incorrectly on your grid. A common mistake is by putting a stakeholder where you want them to be not where they really should be. That’s why it is important to know who they are, meet them, interview them and understand their values and beliefs, this knowledge will help place them in the correct position on the grid and will really give us a clear picture of who to focus on.
In regards to managing and evaluating change such as the example I gave above of us introducing a new on-line learning journal Tapestry I would use this grid to pin point all stakeholders and approach them about my project. I would do research on their thoughts and ideas for this new system and use this information to make my decisions.
Making informative decisions is the key to success and having lots of information from the relevant people will make my project and change run smoothly. The more preparation we take at this beginning stage the easier the transition will be to make a big change in our business.
Stakeholder Salience model (Mitchell 1997)
Unlike the power/interest grid above this model uses three parameters to categorise: power – is the ability to influence the business, legitimacy – is the authority and level of involvement they have on a business and urgency – is the time expected to respond to their expectations.
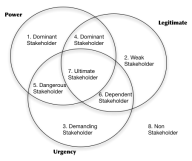
Source: Creative communication
From the diagram above where these three factors meet shows you who your ultimate stakeholder is and these are the people you need to focus on. The other type of stakeholder that should have your attention is the dominant one as their power and legitimacy is high but their urgency is low.
1.3 Analyse techniques to evaluate change
It is important and vital for us to evaluate the changes we make and measure their results. We need to know if we were successful or not in order to learn for future projects. Evaluating ourselves and our projects allows to better make decisions and helps reduce uncertainty, increases learning and control of what we are doing.
One method of evaluating change is through Key Performance Indicators (KPI) this is when measures can be set against our objective to see if they are working. We need to gather data and information over time. By doing this it gives us a snapshot of our company and give us warnings to something that may be wrong. We need to look at what the key factors of our business for us is our customers and ensuring that people keep enquiring and joining our nursery. We can measure the number of enquires we get and then look at the success rates of those enquirers, did they register and did they join the nursery? These questions and results will give us a clear picture of what we are doing wrong and how we can do better.
What can come out of this is that we need more training for the people who are giving the nursery tours, educate them in marketing and sales techniques to ensure every person that steps through our door leaves wanting to be a part of our business. When we look at a KPI we need to make sure they are meaningful to us and that we are tracking something that will help us make better decisions.
In relation to the example I have been giving above use moving to using Tapestry we are currently at the piloting stage where we are going live to 4 parents to trial the system and learn about the other side the customers point of view, what do they see, how useful is it, what problems do they have using it etc. We are using this trial period to educate us before we go live to the whole nursery, we are selecting a variety of parents and children to get a broad perspective of their views.
This evaluation stage is key to seeing if this change was worth the effort and time. Obviously before this point we are confident that we made the right choice to move the company forward in regards to technology and moving with the times but we could be wrong and that this system will not bring that many benefits but until we listen to our customer, ask the questions we need answering we will not know, we would be assuming.
1.4 Evaluate the relationship between change management, business continuity and crisis management
This is a process of preparing for something that most likely will never happen, we may find this a waste of time but it is important. Change management as we have seen is about thoughtful planning, implementation, consultation and involvement of the people affected by the change. From this we have learnt that there are many theories and models to manage change but overall its about preparation which links into business continuity. Its all about being ready for example like the Y2K crisis everyone believed the whole world would shut down in the year 2000.
Business continuity is about anticipating the worst and being as ready as you can for this. Anything that interrupts normal business activity such as power outages, system failure, natural disasters etc can happen and we need to think about this and be prepared. An example of something basic we do is fire drills, invacuations, risk assessment etc. These are small examples but if we are well prepared then it can not end in disaster.
Crisis is not about if it will happen to you its about how, when and why will it happen. It may seem like a single event but its not it can set off a chain reaction. It is important to identify the things that are creating conditions where crisis can happen and proactively form a divert crisis portfolio. This about preparing for a wide era of crisis and pick up early warning signals, look at key assumptions, build a damage control plan, think and act. Coming out of a crisis well can really move your business forward or not being crisis prepared can damage our company to points of no return.
Examples can be what if our utilities failed such as our toilets, heating etc, we need to have maintenance companies on hand to have things repaired quickly so that we don’t need to close the nursery. This happened last week when on of our toilets broke, I have a contract with a company that can help with plumbers, electricians, decorators etc so if I call they can send me anyone to repair the problem. It is important that I am prepared if something goes wrong, closing the nursery is the last measure. I have to have contacts and information of people who can help me in times of need. Another crisis issue we deal with is recruitment, we can do our best to have a bank of staff CV’s but once a staff member has handed notice we don’t have long to find someone to replace them. The only way to avoid this crisis is about prediction and having good communication with your staff and knowing if they are unhappy or are looking to further their career. If we have this information then we will not be surprised if they want to leave or we can try and get them to stay with incentives like pay increase, further training, promotions etc.
This simple information can really make a difference to the way we prepare for these events. Knowledge is power and allows you to be in control.
I need to know how to identify risk and how to handle them. We do daily risk assessments and check our building to make sure we are catching early signs of anything going wrong to ensure it doesn’t become crisis point, its about being aware and proactive. Because we are taking these proactive measures everyday to instil trust in our employees, customers and stakeholders that we know what we are doing. If something was to happen we are well prepared and trained in handling the situations. If you are not prepared for the worst it can destroy your company and you will loss your reputation.