Efficiency of Different Market Structures
|
Question 1 Since the recent Great Recession of 2007-2009, there has been increasing disillusionment with the free market system. Briefly define “free market system” and identify and describe at least three of its major concepts or attributes. Then, critically analyze the view that the free market system is the best and only realistic alternative for determining the allocation of resources in an economy. Provide evidence to support your analysis. Question 2 Every society, regardless of its wealth and power, must make certain choices about production and distribution. Specifically, every society faces three basic economic decisions:
Briefly explain how these questions are answered in your country. How does the availability of resources in your country influence the economic decisions for individuals, organizations, and government? Question 3 Evaluate the economic efficiency of different market structures and their effect on consumers. To answer this question:
|
Questions 1
The generation of 70th-80th still remembers the epoch of communism. The Soviet Union was considered to be stable and solid system, competing with the China and holding the cold War with USA. It was a phenomenon: for the short period of time, country ruined after the Second World War could rebuilt the main industries again, just guided by the pure enthusiasm. The government was controlling all: market, media, and companies. Tough censure was everywhere: not to destroy the image of government in front of people, and to impose the style of life and needed behavior. Ridiculous, but the old generation reminds this time with the nostalgia – long lines in the central supermarket in order to buy the same goods, as there was no variety and choice. The competition on the market was forbidden and consumers were happy with the available products. All the resources were allocated as per government order and were offered for affordable prices.
Nowadays, the society is trying to build the ideal market relations, free from any interaction from the government side. The free market system, according to its nature is a weal, but after appears marketing and unscrupulous competition and manufacturers. On the free market there is no control and involvement from the government side, which gives an opportunity to set the price on the market according to the supply and demand. Government is playing the role of the reference, when there is a need to protect copyright. Participants deciding by themselves: what produce and in what quantities to manufacture; and what goods and service to buy. The free market system due to it flexibility, allows satisfying better the needs of society in goods and services (Business Dictionary 2015).
According to Adam Smith, relations on the free market are regulated and stabilizing by the invisible hand (Investopedia 2016). Desire of individuals to satisfy their personal rational needs, bringing social useful results. From the above we can summarize, that the free market it is mainly:
- private property and high competition, so the sellers are trying to present the best goods and services in order to profit;
- high variety of goods and services to satisfy any demand and taste;
- Limited influence on the market processes from the government side (Moffat 2016).
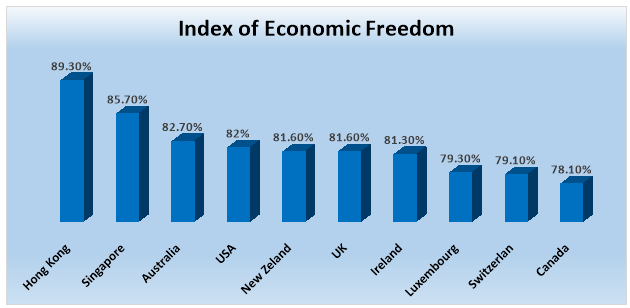
However, absolutely free market does not exist. The free market – is an idealized abstraction. All economies are located somewhere in the middle, someone is less controlled by the state, and some more. The degree of economic freedom of a country is assessed index of economic freedom. As we see from table 1, only few countries in 2016 have an indicator above 80%. The leadership is by small countries Hong Kong and Singapore, that long period of time were in shadow, but now are the main suppliers for the world economy (Economic Freedom 2016).
For weak countries and free market – it is big checkup and competition. In each competition there are winners and losers. Losers will be bankrupt companies, winners’ mostly big monopoly companies. Thousand unemployed workers and uncontrollable prices as the result, high risk of inflation and recession processes, showing that the market regulation system is not always stable due to the number of factors (Agarwal, 2016):
- each company is willing to decrease expenses and increase efficiency. With the innovation progress, owners are trying to substitute the manual work with machines. As a result – the raise of the unemployment rate;
Table 1: Index of Economic Freedom 2016
- free market economy is leading to enrich rich and to make poor poorer. The market mechanism is not able to provide social guarantees, help and donations for the society. For the corrupted system this is a chance to gain more (Grigg 2012);
- the person from the lower class without material base does not have chance to run away from this style of life. As a market economy is tough competition. The person is not able to receive good education, qualified medicine help, to give good education to children, as a result kids also are not able to get a high paid job. The social adversity inherited from one generation to another. All this mechanism shatter family, which stop existing as an Institute;
- market only tends to gain profit and do not care much about ecology, natural sources and health. The companies are not interested to save the natural environment;
- market economy does not preview the valid expenses for the army and defense, which is highly needed in the modern situation. The resources are not allocated wisely (Hanks 2015);
- media & marketing hypnosis – companies are trying to sell their goods by any cost. Here coming marketing and advertisement. They are showing goods and services to us in their best shape and look, to convince that buyers really need and want them. Though, most of the time the information provided is faulty. In addition, manufacturing one product, companies making a lot of adds to make the product work. Like a printer and not refillable cartridges, phones and chargers, cases, headphones etc.
The good example of inefficient allocation of resource he result of absence of government regulation it is bulb that appeared on US market. In order to grow US economy needed to increase consuming. How to increase it, if the income of population was the same? The solution was as following: to take loans and consume them, as like an income. Low interest rates and weak real estate market regulators provoked a crisis. It appeared that tree quarter of US economy was connected to the real estate market. When the bulb exploded and incredibly high prices for the estate fall down, owners of real estate properties became bankrupts. They lost their houses, savings, and hopes for future – education for their kids, comfortable life and pensions (Stiglitz 2010).
The free market system is not able to exist on its own. The government needs to regulate the supply in order to exclude the monopoly, to assure fair market mechanism; to provide the social standards for the society, to have working army, to take care of the environment. The free market system is possible only in a society free from greediness, corrupts, envies and lies, – but nowadays it is utopia.
Question 2
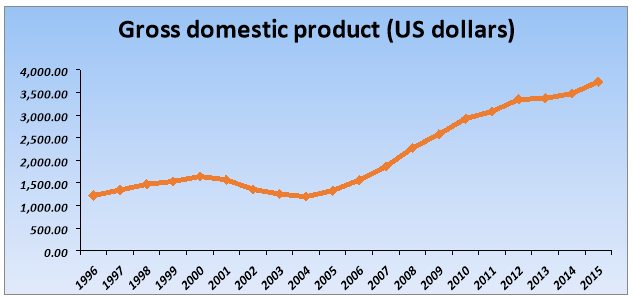
Egypt is considered as the country of the third world. Struggling after two revolutions and passing through the deep descent, during the 2015-2016 country could regain it power again, as it is visible from the table 2 (IMF 2016).
Table 2: Trend of GDP per capita in Egypt
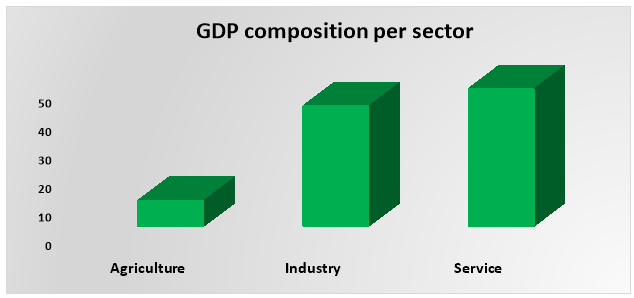
Currently Egypt features the second largest consumer market in the Middle East and Africa region, behind Nigeria. Egypt’s economic structure counts as one of the most diversified in Middle East and Africa (Economy Watch 2010). The advantageous location near Nile and the sea built the agriculture vector in the Egyptian economy. Quickly understood that the agriculture orientation demanding more expenses and the income is not significant, it share has been rapidly reduced with the quick industrialization, as it is shown in the table 3 (IMF 2016). Egypt has a range of industries, such as steel, electricity, oil extraction and refinery, chemicals, domestic goods and automobiles. The IT industry is also gradually expanding in the region (Maher 2015). Sure, sophisticated location near the sea, warm climate, heritage from pharos – making Egypt one of the most attractive countries for tourism.
Table 3: GDP composition per sector 2015
The distribution of resources depends on the basic economic foundations: supply and demand. According to the population growth, wealth of the society, tastes, style of living depends the general distribution.
Egyptian market is mixed, entrepreneurs have freedom to manufacture required goods and services; however government has a solid influence on the infrastructure, price and supply. Egypt is one of the countries were the important influence has an army. Army with the government are the main competitors for the private companies. It is separated Institution that building roads, compounds, manufacturing goods and food. Ready products are sold with the lower prices, as the production cost is much lower due to the government donations. In such case, private sector is not able to manipulate with the price.
But taking care of defense system, government and society caused gap in education and cultural growing. Lack of free schools, social upbringings followed by the dirty streets are followed by the descending of writing skills level, ambitious and comprehensive development (Hall & Lieberman 2008).
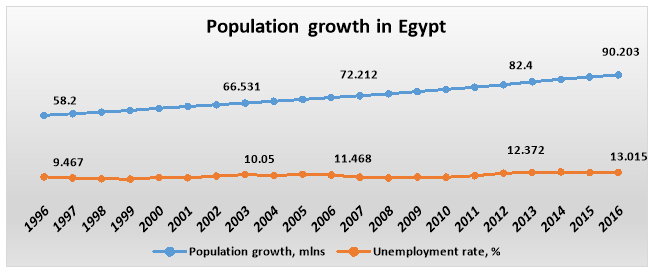
The demand in Egypt has been formed by culture and traditions. Egypt is one of the most attractive markets nowadays, due to the growth of population and the birth rate, as shown in the table 4 (IMF 2016). It is common to find families with 4-5 kids. In addition, Egyptians are fans of home comfort and family gathering. The furniture is always in demand, the same as food. For sure the population growth will create need in Egyptian cotton for dressing; heavy machinery and materials to build houses. Hectic life and high population will always make a demand for the automotive industry. Pharmaceutical area does not have any issues:Â Arabs taking care of themselves and visiting doctor once per month obligatory, as Islam it is religion of purity (Maher 2015).
Table 4: Population growth in Egypt 1996 – 2016
The way of production of goods and services in Egypt is more labor intensive. Egyptian got used to trust to their own hands, than to machines. The benefit differs from the one industry to another. In the patchwork, weaving, leather making, household furniture is considered more precious and unique. While in the heavy machinery and building there is need for the capital intensive process. Moreover, we are living in the hi-tech century, where machines are making part of the human job more accurate, secure and faster. This is time for Egypt to invest to become the hi-tech developed country (Sexton 2008).
Due to the last events: the “embargo” on tourism from Russia and some of the European countries – Egyptian resorts felt the consequences heavily. This situation, proves again that Egyptian economy well diversified, controlled, regulated and supported by the government. As Egypt could face the same bulb with the tourism, like US with the real estate market in 2007.
Question 3
The original definition of the efficient market has been given by Fama “A market in which prices always fully reflect available information is called efficient” (Jarrow & Larsoon 2011). On the Efficient market price is anunbiased estimate of the true value of the investment. According to the Efficient Markets Hypothesis” (EMH) prices reflect information. Efficient market will reflect quickly into market prices and vise-versa (Bloomfield 2002).
Overall, the efficient market is a market with the resources that have been wisely allocated, to satisfy needs and changes and advantageous for all the participants in the market. The participants produced the right products and in the right way (Scott 2003).
There are two main types of efficiency that we might be concerned with: allocative and productive efficiency. Allocative efficiency is when the right type of goods and service produced in society. This type of efficiency occurs when consumers pay the price that reflects the marginal cost of production P = MC. The adjustments will take place, when changes in a supply, demand, technology or innovations going to happen. This kind of efficiency can be achieved in the perfect competitive environment. Since there is no interaction from aside, the market system will be regulated by “invisible hand” (Economics Online 2016).
Productive efficiency is when the market produce goods and services for the lowest cost possible P = minATC. (Heakal 2014). The firm should combine the sources in an efficient way, to use least-cost technology to get at the end the lowest cost possible in order to survive.
To reach productive efficiency on the market, all the firms must have the same marginal cost of production. If one firm or company has a lower cost, than it will be more efficient for the current industry, considered the lower cost producer. (Economic growth 2009).
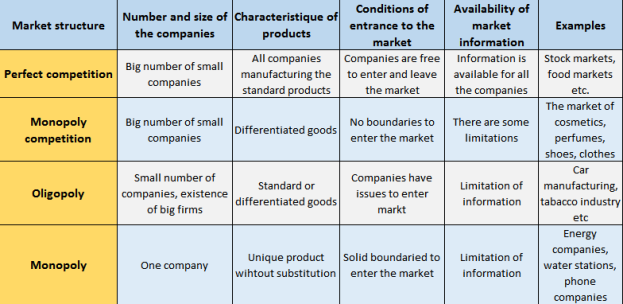
Market competition – this is competition between the companies for the most advantageous conditions of manufacturing and supply of goods and services, in order to receive the maximum income. Competitiveness – this is the way of effective allocation of limited sources. It plays the stimulating role. There are few types of market structures, as shown in the table 5 (combined by author based on Heakal 2014):
- Perfect competition;
- Monopoly;
- Oligopoly;
- Monopolistic competition.
Perfect competition is the most advantageous market environment for all the participants:
- The solid number of sellers and buyers. That is why a certain seller is not able to influence on the market price. Participants fully depend on the market environment.
- There is no a bid variety of products on the market. The goods sold are standard, in this case buyers do not have any preferences to one sellers in comparison to another, as an example of standard product we can take wheat, corn, fish etc.
- One firm is not able to influence on the market price, because there are numerous companies and they all selling standard product.
- Buyers are well informed about the price, if someone from the manufactures will raise up a price, they can lose buyers. In addition, the sellers are not able to negotiate a price.
- The companies do not have any issues to enter and leave a market (Tucker 2014).
Contrast to the perfect competition is a monopoly – the market where exist and operating only one firm and could influence the price. Monopoly is the best example of imperfect competition:
- The manufacture of goods is controlled by one seller;
- The goods and services produced by monopoly are unique and do not have close substitutes, in this case the price on the good is not elastic, and the demand is descending with the time;
- The other firms are not able to enter the market, there is no competition on the monopoly market (Harford 2010).
The current conditions help to make a conclusion, that the firm monopoly has full market influence and able control and change the price. In comparison with the perfect competition market, where each company should accept the market price.
Monopoly competition – the market structure, where combining the features of perfect competition and some elements from the monopoly structure. The main parameters of monopoly competition. There are many medium companies on the market, but less than in perfect competition market structure. Firms producing similar, but not the same product, so a result:
- Each firm has a small part of the market for manufactured good, the control of the price is limited, but the companies are independent in their decisions and do not pay much attentions on the competitors;
- The goods produced are differentiated. In the conditions of monopoly competition, companies on the market can produce goods, different from the competitors: different by quality, the quality of services, difference is location and availability for selling products, usage of advertisement, pack to highlight product among others (Richards 2014).
The good example is cosmetics, perfumes, medicines, home suppliers. This kinds of products are differentiating between each other, but still the same. The demand on goods decrease with the time, but not as rapid as in the conditions of monopoly.
The same as in conditions of the perfect competition, the companies are free to enter and leave a market. But in the conditions of the competitive monopoly companies should spend extra for advertisement: to manipulate with the difference in design, safety of exploitation, ecological usage, esthetic qualities etc.
Oligopoly market system – one of the most widely spread structure in the modern economy:
- There are few competitive firms on the market (from 2-3, 10-12), so it cannot be considered as the pure monopoly. Each company has a separate part of the market, so it gives the possibility for the participants to influence the market.
- The demand on the suggested product is decreasing with the time, so the system cannot be considered as the perfect competition
- In the market there is at least one big company. It actions will find the reflection from the side of competitors, this is the main difference from the monopoly market system. Of the main specification of oligopoly, is that the companies should consider not only the reaction and behavior of consumers, but also the reactions and behavior of competitors.
- The product can be produced as standard (oil, aluminum) – pure oligopoly, as differentiated (for example, cars) – differentiated oligopoly. So the companies have a certain power on the market (Heakal 2014).
Basically, in order to achieve market efficiency, two main criteria’s should be achieved – productive efficiency and allocative. Specifically in the conditions of perfect competition, these two requirements can be achieved, what makes the perfect competition the most effective type of the market. All the rest market systems are not able to achieve mentioned features – the minimum range of costs, effective allocation of resources, the lack of deficit and product surplus, the lack of economic gain and losses. For Customers perfect competition is the most advantageous type of the market: price is stable, goods and services are always available, information is not hidden and the advertisement does not influence on mind (Jarrow & Larson 2011).
In comparison to the perfect competition – monopoly cannot achieve neither productive, not allocative efficiency. Monopoly realizing the product with the higher price, with the surplus of product and additional expenses to maintain the monopoly status (buying of patents and license).
One more important aspect that influence on the efficiency of pure monopoly and perfect competition – innovation and technological progress. The competitive environment stimulating companies to innovate and develop, but there is no long-lasting effect. The lack of competition in the monopoly market system does not stimulate companies to innovate, however, on the other side slight innovations help monopoly to solid their positions on the market. Monopoly is less receptive for innovations.
Monopoly stimulating inequality of the income contribution. Monopoly companies set the higher price than the other industries, practically it imposes the Customers with the private taxes. Customers they do not have any other choice, than to follow rules on the monopoly market. This type of market is advantages only for owners of monopoly companies (Harford 2010).
While the rest monopoly competition is a mix between perfect competition and monopoly, still it does not tend to satisfy interests of buyers. Consumers will be always in loss: due to the manipulation with the advertisement and variety line of products.
Table 5: Characteristics of the market structures
There is no agreed point of view regarding the economic efficiency of oligopoly. Often the oligopoly companies co-operating together, what leads to the monopoly. The volume of production goods in oligopoly is less, and the prices higher, in comparison to the perfect competitive market. In addition, only big oligopoly companies can allow to innovate. And the boundaries to enter the market guarantee the long term income from innovations (Belen 2010).
Oligopoly is not advantageous market system for the consumers, as the price is not stable and often higher, than it could be in conditions of the perfect competition, though it is better than a pure monopoly, where consumers do not have a choice, as shown at the figure 1.

Figure 1: Example of the companies according to the market structure (Edbus 2016).
In our imperfect world everyone has an aim to gain to provide the better future and live according to the modern standards. But where a gain of one, there is a loss of another. There is no balance, neither in life, nor in economics. There is only way: to adapt, work and think differently – not to be as a general mass.
Think different.
Steve Jobs (Forbes 2011).
Bibliography
Agarwal, P. (2016). Free market: advantages and disadvantages. Intelligent Economist. Available at: https://www.intelligenteconomist.com/free-market/ [Accessed 11 September. 2016].
Belen, R. (2010). Market structure. [online]. Available at: http://www.slideshare.net/reyzter/market-structure-5246029 [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
Bloomfield, R. J. (2002) The “Incomplete Revelation Hypothesis” and Financial Reporting. Accounting Horizons, [online]. Available at: http://www.aaajournals.org/doi/abs/10.2308/acch.2002.16.3.233 [Accessed September 13. 2016].
Brunnermeier, M. K. Market Efficiency, [online]. Princeton University. Available at: https://scholar.princeton.edu/sites/default/files/13lecture.pdf [Accessed 12 September.2016].
Business Dictionary, (2015). Free market [online] Available at: http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/free-market.html [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
Damodaran, A. Market Efficiency: Definitions and Tests. Available at:http://people.stern.nyu.edu/adamodar/pdfiles/invphiloh/mktefficiency.pdf [Accessed 13 September. 2016].
Dimson, E. and Mussavian, M., (2000). Market efficiency. [pdf] London: Spellbound Publications. Available at: http://e-m-h.org/DiMu00.pdf [Accessed 13 September. 2016].
Dwight, R. L. (2001). Economic Efficiency. Foundation for economic education, [online]. Available at: https://fee.org/articles/economic-efficiency/ [Accessed 11 September. 2016].
Economy Watch. (2010). Egypt Economic Structure. Economy Watch. Follow the money, [online]. Available at: http://www.economywatch.com/world_economy/egypt/structure-of-economy.html [Accessed 13 September. 2016].
Edbus. Alex’s Econ InNotebook . Available at: http://edbus.saschina.wikispaces.net/Alex%27s+Econ+InNotebook [Accessed 14 September. 2016].
Economic Freedom (2016). Index of Economic Freedom, [online]. Available at: http://www.heritage.org/index/ [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
Economic growth, (2009). Productive and Allocative Efficiency for different market structure, [online]. Available at: http://economicgrowthanalysis.blogspot.com.eg/2009/11/we-know-that-there-are-4-different.html [Accessed 13 September. 2016].
Economics Online, (2016). Efficiency [online] Available at: http://www.economicsonline.co.uk/Business_economics/Efficiency.html [Accessed 13 September. 2016].
Grigg, C. (2012). Characteristics of a Market Economy. [pdf]. Available at: https://mrsarudi.wikispaces.com/file/view/characteristics+of+a+market+economy.pdf [Accessed 11 September, 2016].
Hall, P. (2005). Economic Efficiency. Western Washington University.
Hall, R. and Lieberman, M. (2008). Microeconomics: Principles and Applications. 4th ed. [ebook] Thomson: Thomson Learning Inc. Available at: https://books.google.com.eg/books?id=5mhPgLq-t4YC&pg=PA40&lpg=PA40&dq=how+society+answer+a+question+what+goods+and+services+will+be+produced&source=bl&ots=90tIbmhfNQ&sig=omhMFKITXLFz8kuw4OpjcaTIes4&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjSj6_r7ozPAhVhDsAKHZ9ZDgYQ6AEIOTAG#v=onepage&q=how%20society%20answer%20a%20question%20what%20goods%20and%20services%20will%20be%20produced&f=false [Accessed 11 September. 2016]
Hanks, G. (2015). Explain the Advantages & Disadvantages of Free Market Economies. Chron, [online]. Available at: http://smallbusiness.chron.com/explain-advantages-disadvantages-market-economies-70553.html [Accessed 10 September. 2016].
Harford, T. (2010). Perfect Competition, Monopoly, and Monopolistic Competition. [pdf]. Available at: http://www.econ.jku.at/members/WinterEbmer/files/Teaching/managerial/lecture4.pdf [Accessed 14 September. 2016].
Heakal, R., (2014). Economics Basics: Monopolies, Oligopolies and Perfect Competition. [online]. Investopedia. Available at: http://www.investopedia.com/university/economics/economics6.asp [Accessed 13 September 2016].
Heakal, R., (2014). What Is Market Efficiency? [online] Investopedia. Available at: http://www.investopedia.com/articles/02/101502.asp [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
International Monetary Fund (2016). [online]. Available at: http://www.imf.org/external/index.htm [Accessed 11 September. 2016].
Investopedia, (2016). Invisible hand [online] Available at: http://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/invisiblehand.asp [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
Jarrow, R. and Larsson, J. (2011). The Meaning of Market Efficiency. [pdf]. Available at: https://www.bauer.uh.edu/departments/finance/documents/RJarrow%20MarketEfficiency6.pdf [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
Maher, M. (2015). 9 leading industries in Egypt. Feed, [online]. Available at: http://yallafeed.com/%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B9%D8%A7%D9%84%D9%85/%D8%A8%D8%B2%D9%86%D8%B3/9-%D9%85%D9%86-%D8%A3%D8%A8%D8%B1%D8%B2-%D8%A7%D9%84%D8%B5%D9%86%D8%A7%D8%B9%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D9%81%D9%8A-%D9%85%D8%B5%D8%B1/ [Accessed 10 September. 2016].
Moffatt, M., (2016). What Is a Free-Market Economy? [online] About Education. Available at:http://economics.about.com/cs/economicsglossary/g/free_market_e.htm [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
Murray, N. (2008). Free Market. The concise Encyclopedia of Economics. [online]. Library of Economics and Liberty. Available at: http://www.econlib.org/library/Enc/FreeMarket.html [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
Ollman, B. (2014). Market Economy: Advantages and Disadvantages. Dialectical Marxism, [online]. Available at: https://www.nyu.edu/projects/ollman/docs/china_speech2.php [Accessed 12 September. 2016].
On Marketing (2011). The Real Story Behind Apple’s ‘Think Different’ Campaign. Forbes, [online]. Available at: http://www.forbes.com/sites/onmarketing/2011/12/14/the-real-story-behind-apples-think-different-campaign/#59dcca3e55c2 [Accessed 15 September. 2016].
Richards, L. (2014). 5 Different Types of Market Systems. Chron, [online]. Available at: http://smallbusiness.chron.com/5-different-types-market-systems-25818.html [Accessed 14 September, 2016].
Scott, D. (2003). Efficient market. Wall Street Words: An A to Z Guide to Investment Terms for Today’s Investor. Available at: http://financial-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Efficient+market [Accessed 13 September. 2016].
Sexton, R. (2008). Exploring Economics. 4th ed. [ebook] Thomson: Thomson Learning Inc. Available at: https://books.google.com.eg/books?id=95wGaI7KQSEC&pg=PA64&lpg=PA64&dq=how+society+answer+a+question+what+goods+and+services+will+be+produced&source=bl&ots=RbrzGCn5h0&sig=HI0FKHoWsINVELQyb_U5qS0tKyU&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjSj6_r7ozPAhVhDsAKHZ9ZDgYQ6AEINjAF#v=onepage&q=how%20society%20answer%20a%20question%20what%20goods%20and%20services%20will%20be%20produced&f=false [Accessed 11 September. 2016].
Stiglitz, J. E. (2010). Free Fall. America, free markets, and the sinking of the world economy. [pdf] New York: W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Available at: http://urbanartiphax.com/ebooks/files/Freefall-Joseph-E-Stiglitz.pdf [Accessed 9 September. 2016].
Summary of efficiency. (2015). [lecture]
Tucker, Ch. (2014). Market Structure. [pdf]. Available at: http://www.swlearning.com/ibc/tucker3e/pdf/Tucker_ch08.pdf [Accessed 14 September. 2016].