Ethics in Data and Web Mining
Higher Diploma in Science in Data Analytics
What is the importance of ethics in Data Mining?
Module Title: Data and Web Mining
Lecturer’s name: Eleni Rozaki
Student:
Liliam Faraon
Student n°: 16108841
Date of Submission: 19th of March 2017
Table of contents
We live in a time when the pursuit of knowledge is indispensable. From the transformations we have witnessed in the past years, we can acknowledge that information assumes a growing importance and a requirement for any sector of human activity. Some authors say that 90% of all data in the world has been generated over the last two years, and more and more devices will be connected to the internet generating data that can be used by companies to predict patterns of consumption and increase specific sales.
The article: “17 ‘Internet of Things’ Facts Everyone Should Read” published by Forbes in October, 2015, brings us an idea of some numbers and the potential market that is available to be exploit:
- Nowadays there are more objects connected to the internet than people;
- By the year of 2020 around 250.000 vehicles will be connected to the internet, (saving time spend in traffic, fuel, improving the performance and protecting the environment and generating data);
- The global wearable device market has grown 223% only in 2015 specially by the launching of Fitbit® and Apple Watches;
- Internet of Things will add $10 to $15 trillion to global GDP by 2036;
But looking at all the facts some questions are raised, such as: how the data we produce is managed and stored? How is it perceived? How businesses are taking advantage from all the that information? And finally, how do we protect our own data and make sure is not being “used” without consent? That’s where web mining poses a threat to ethical values, such as individuality and privacy.
Improvements in IT and storage capacity has enabled companies to develop tools for data collection through many channels. There are a variety of ways individuals generate data, such as: ATM visits, bar-code readers, biometric devices, credit and debit card transactions, loyalty clubs, medical records, online shopping, rentals, scanners, subscriptions, website browsing and use of many Smart devices available. As a result, there is an exponential growth of the amount of data stored and available to be “explored”. This generation of data brought the need of new techniques and technologies that can analyse and convert all this information into useful knowledge and Data Mining becomes a very powerful resource. When all these data are merged and mined, they can infer a person’s associations, credit information, health, income, political interests and tastes.
Liu defines data mining as “The process of discovering useful patterns or knowledge from data sources … The patterns must be valid, potentially useful and understandable.” (Liu, 2011, p. 6).
Data mining based on algorithms are very automated and analytical tools and its use is rapidly increasing. By combining databases, information visualisation, machine learning, mathematical modelling, pattern recognition, statistics and more recently artificial intelligence, very large and complex datasets can be analysed and relationships, patterns, outliers and trends can be revealed.
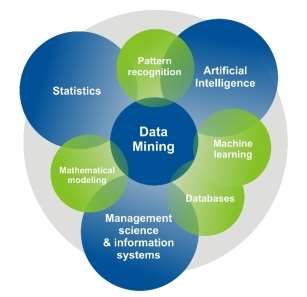
Figure 1: Data Mining
Raw data itself is not useful at all, but the information that can be extracted from the data is where the real value seats. We have endless amounts of data being produced and stored, it makes sense companies and governments have the desire to analyse all this data to uncover patterns potentially useful hidden in there. Data Mining process is basically categorised into two classes:
Descriptive: describes the general properties of information stored in a database
Predictive: draws inferences from the data in order to make predictions.
Witten emphasises: “Data Mining is about solving problems by analysing data already present in databases” (Witten, 2013, p. 4). Decision makers desire the right answers for broad questions and obviously, the more data gathered the more questions raised. Which customers are likely to respond in a positive way to a marketing campaign? What products will have more success when launched? What is the best price range for a new product? How do the competitors tend to react? The response for those questions cannot be reached based on feelings or intuition, they can be answered by analysing customers behaviour and profile using data mining tools.
By collecting and summarizing and making use of data mining companies and organisations can identify insights and obtain competitive advantage, recognize potential competitors, improve customer service relationship, target customer expectations and needs. It also has important uses in social business and science, most recently Government Agencies are using Data and Web mining applications to uncover criminal activities such as terrorist threats.
There are many Data Mining tools are available in the market nowadays, each one with its particularities, the most common are KNIME, NLTK, Orange, RapidMiner (formerly known as YALE), R-Programming and WEKA .
“Ethics must be a condition of the world, like logic.” Ludwig Wittgenstein, 1889-1951.
Giant social media such as LinkedIn, Facebook and Twitter hold billions of user’s data, keeping these data protect and as a secret is a big concern. When an individual creates an account on any of those social media channels a policy agreement is accepted, and it is basically data related.
Data Mining analysts use people personal information collected by organisations all over the world through many different technologies and use them especially for prediction analysis, but practitioners must be very careful when analysing patterns, certain kinds of discrimination are not only unethical but also illegal, gender, religion, race and certain sensitive information is totally unacceptable, in the other hand, anonymizing data is very difficult, for example, over 85% of Americans can be identified from publicity available records using just three pieces of information: zip code, birth date and sex (Witten, 2013, p.33).
When a person shops for a product online, the company has access to customers address, credit card, name, phone number and other information in their database. But how does the company encrypts the information and protects it from misuse or security breach is and ethical and legal issue. Some matters are also raised: Is it ethical and legal to use the user’s information for publicity purposes? How can users protect their right of privacy? Where does the right of a company meets the ethics when sharing its data with another company to comprehend and understand customers and increase profit by selling this information to third party companies is a very important matter and it must be carefully discussed. There is a thin line between of a person’s privacy and company’s right to use it. When a person provides personal information, he or she needs to know how and what it will be used and a few steps must be taken to guarantee confidentiality and integrity.
“The use of data – particularly data about people – for data mining has serious ethical implications and practitioners of data mining techniques must act responsibly by making themselves aware of the ethical issues that surround their particular application.” (Witten, 2013, p. 33).
There is a growing concern regarding to the use of private and sensitive information and the ethical issues of Data Mining must be analysed and understood both from the business and the personal point of view. From a personal point of view, by Data Mining execution respecting consent, privacy and regulations customers might appreciate the fact they are being target with more personalized offers based on circumstances and needs and in return they may be willing to provide more specific data about themselves. From a business point of view by respecting the privacy issues companies will save resources as they will be able to target very specific customers for certain products. It is obvious that as any other powerful technology there are negative consequences of Data Mining, some results can ineffective, misdirected or unregulated, but if used correctly it can be very resourceful.
Some points are very important and organizations making use of data mining techniques should give a thought about them when the use of personal data is planned:
|
|
Connectivity and data sharing |
All the users and people that give consent are connected through the internet and share data |
|
|
Security is essential |
Once all the information traffics through databases, companies worry about the security and privacy, that way all the data will be encrypted, the web services will be hosted in a server with a certificate installed and authentication user |
|
|
The importance of Privacy Policy |
Privacy Policy is a legal statement and regulates the privacy policy related to user’s personal data which is under companies’ responsibility |
|
|
Infrastructure |
The process will not function without an application to analyse, interpret, read and draw patterns from the data |
|
|
Account management: Gathering and leveraging |
Account Management has all the information gathered and leveraged, and elaborate can advertising campaigns. It plays an important role in the profitability of the company |
Information could be released without the consent of the person, it becomes an ethical dilemma, because sometimes the users are unaware of the information gathered and that is being used by companies. It is very important to highlight that the person has the right to know how it will be used and should be able to have the opportunity to consent or not the collection and use. And also when a person becomes part of a group profile and used as a decision making basis, the individuality is threatened, people cannot be judged only as group members, but also as an individual, able to make its own decisions.
It is likely that in the next few years’ an inspection of ethical issues and legal implications will be further required, legislation of digital privacy will be developed and laws will enter force, confidentiality and privacy preservation should be the main points of concern. Unauthorised extraction of data will be considered a crime and companies must be ready for that.
Data Mining algorithms are very important and powerful tools for analysis and predictions, they are expected to become more and more significant in the future, decision based on data will change the way companies base their processes, of course there are no 100% guarantee that they will succeed, but, are more likely to be successful than decisions based on feelings or gut. Once patterns are revealed profiles can be drown and stereotypes can be used for crime prevention, commercial proposes, marketing campaigns, policies development and many others.
Meanwhile Data Mining ethical issues need to be raised and awareness increased, as the world continues to develop, more and more data is likely to be collected and the Data Mining processes will become more sophisticated. People will need to get a clearer idea of privacy and companies will have to become more transparent on its processes of collect, gather and use of data.
Cook, Jack (2005). Ethics of data mining. Available at:
http://scholarworks.rit.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1443&context=article
Ethics in Computing. Available at: https://ethics.csc.ncsu.edu/privacy/mining/study.php [Accessed: 02 March 2017].
Fule, Peter. Detecting Privacy and Ethical Sensitivity in Data Mining Results. Available at: http://crpit.com/confpapers/CRPITV26Fule.pdf
Liu, Bing. (2011). Web Data Mining: Exploring Hyperlinks, Contents, and Usage Data, Springer
MARR, Bernard.17 ‘Internet Of Things’ Facts Everyone Should Read (2015). Available at: http://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2015/10/27/17-mind-blowing-internet-of-things-facts-everyone-should-read/#5e463ad01a7a [Accessed: 01 March 2017].
Wahlstrom, Kirsten (2006). On the Ethical and Legal Implications of Data Mining. Available at: https://csem.flinders.edu.au/research/techreps/SIE06001.pdf
Witten, Ian H (2013). Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, Morgan Kaufmann.
Zhen, “Ethical issues in Web Data Mining”. Available at:http://blog.nus.edu.sg/group208/2012/11/25/ethical-issues-in-web-data-mining/ [Accessed: 01 March 2017].