Full-Scale Fatigue Testing using the Resonance Method
Welding:
Welding is a process that is employed to join two distinct pieces of the same metal or remove any unwanted material from metals. In other words, the welding can be broadly discussed as the forging of two heated metals by employing electrode which acts as a slag and prevents the atmospheric contamination. The art of welding began when man started forging tools from metals. The first form of welding that was available to mankind was metal forging by pounding a metal until they are fused together. [1]
Types of Welding:
We live in a world where we can fuse a metal and separate a single metal into many components. There are many available methods of welding to achieve this objective. They have all been evolved from the idea of forging and have a high influence in the human survival. Some of the different types of welding that are been used are:
- Oxy-Acetylene gas welding
- Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW)
- Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW)
- Electroslag welding (ESW)
- Gas metal arc welding (GMAW)
- Submerged arc welding (SAW)
- magnetic pulse welding (MPW)
- Electric resistance welding (ERW)
- Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW)
- laser beam welding and
- electron beam welding [2]
Weld Geometry:
Welding two metals depends on a numerous factor such as type of joints, type of welds, groove face, root face, root edge, bevel angle, depth of bevel, groove angle, groove face, groove radius, and root opening. Based on all these factors there are nine categories of welds. They are
- Groove Welds
- Plug or Slot Welds
- Spot or Projection Welds
- Back or Backing Welds
- Flanged Welds
- Fillet Welds
- Stud Welds
- Seam Welds
- Surfacing Welds [3]
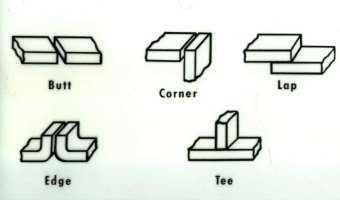
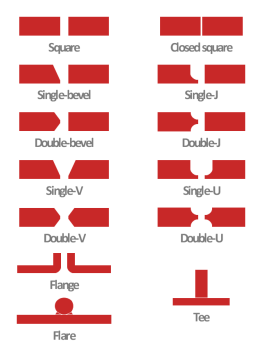
Figure 2: Type of Weld
Figure 1: Type of joint
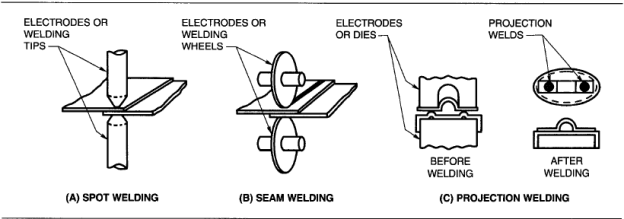
Figure 3: Process of a) Spot Welding b) Seam welding c) Projection Welding
Types of Failure:
A metal component is always subjected to stresses and strain. They have an impact on the total life of the component. A flaw that can cause disruption in the performance of a metal gives us an idea on the integrity of the metal. In case of welding the defect can occur in the area that has been welded. Based on the study, it is identified that most of the failure in the welds occur due to wrong technique, process conditions, bad weld groves, incorrect consumables and operator error. The common types of failures that occurs in welding are due to hydrogen embrittlement and residual stresses. So, the type of welding failure that can affect the life of the metal component are:
- Arc strike cracking
- Undercut
- Cold cracking
- Hot cracking
- Crater crack
- Root and toe cracks
- Hat crack
- Underbead crack
- Lamellar tearing
- Longitudinal crack
- Gas inclusion
- Reheat cracking
- Distortion
- Inclusions
- Transverse crack
- Lack of fusion and incomplete penetration [4]
Fatigue:
Fatigue may be characterized as the weakening of metal caused by the frequent application of cyclic loading and unloading. It causes progressive structural damage to the material. The fatigue strength is defined as the maximum strength a material can exhibit without breaking is an important dimension that is employed to study the life cycle of the metal or the welded structure. The BS 7608 or DNV-RP-C203 gives us an idea about the fatigue strength to the applied load for different weld geometry.
Principle of Fatigue Testing:
Resonance Method Testing is employed for the analysis of fatigue in welds. “The process involves the excitation of the welded metal to be tested to its first mode of vibration by applying rotational radial force at one end.” The rotational force causes a bending moment in its longitudinal axis of the welded metal with two nodal points without any deflection. The welded metal is supported at these points.
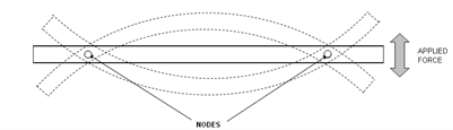
Figure 4: Principle of resonance fatigue testing (in two dimensions).
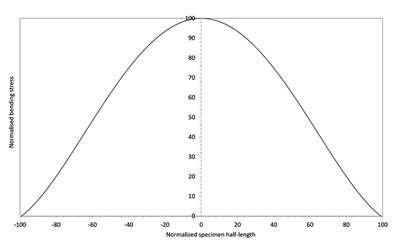
Figure 5: Bending-stress-profile-in-a-resonance-fatigue-test-specimen-with-a-circular-cross-section
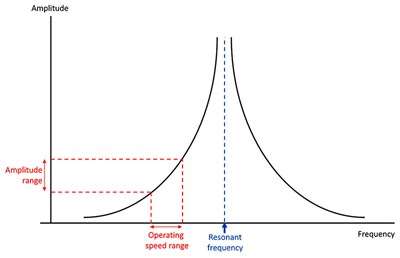 This method is employed to calculate the bending stress in a metal. The resonant frequency depends on the mass and stiffness of the material. Usually the tests are conducted below the resonant frequency to control the stress and thereby regulating the strain and deflection. [5]
This method is employed to calculate the bending stress in a metal. The resonant frequency depends on the mass and stiffness of the material. Usually the tests are conducted below the resonant frequency to control the stress and thereby regulating the strain and deflection. [5]
Figure 6: Resonant-response-of-specimen-deflection-controlled-by-changing-the-speed-of-rotation-of-the-excitation-force.
Industrial Application:
Resonant Testing Machines is the commonly employed fatigue testing machine when compared to its counterpart Servo-hydraulic testing machines due to its advantages such as better efficiency, high frequency, low maintenance and cost. They are used for the fatigue analysis of aerospace and automotive fasteners, engine components, turbine blades, chains etc.
Aerospace Industry:
Resonant test is employed in aerospace industry to study the fatigue strength of the composite materials such as Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP). They are employed to study the fatigue strength of aerospace fasteners such as bolts, screw, studs and rivets. An aircraft uses an utmost 3 million fasteners with bolts taking 25% and the rivets taking the rest. So, fatigue test is done to analyze the reliability of the fasteners to the repeated pressure and temperature cycles, variations in dynamic loads, and high vibration levels. [6]
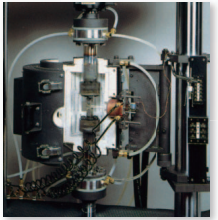
Figure 7: Fatigue Toughness Testing with resistance heating tester.
Automotive Industry:
Resonant tests are being implemented in structural dynamics lab in order to study the fatigue strength of high stiffness components such as the automotive components such as connecting rods, crankshafts, bolts, brackets, gear teeth, knuckle etc. The test duration is controlled by the stiffness of the material and the frequency can go high as up to 100 Hz. [7]
Reference:
- The_Procedure_Handbook_Of_Arc_Welding_742pages_1973.pdf
- Online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Welding
- Online: http://nearyou.imeche.org/docs/default-source/hong-kong-branch/1- 20.pd
- Online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Welding_defect
- Online: http://www.twi-global.com/technical-knowledge/job-knowledge/full-scale-fatigue-testing-using-the-resonance-method-141/
- Online: http://www.fastenerandfixing.com/news/high-cycle-fatigue-evaluation-of-aerospace-fasteners
- Online:https://www.araiindia.com/services_RnD_services_structural_dynamics_engineering_services.asp