Impact of Natural Disaster on Infrastructure
We humans cannot envision when a regular calamity happens, and more often than not, when a natural disaster happens it brings a lot of wreckage and demise. Recent events show that a significant increase in number of natural calamities for natural and human made reasons which could have potentially very huge consequences on infrastructure. If those infrastructures fall the chain of accidents could lead to a catastrophic situation, and can affect the environment, the economy and people. This paper will focus on the study of the impact of natural disaster on infrastructure. This paper will analyze the methodology of assessing the risk regarding natural Calamity on critical infrastructure through the analysis of cascade effect. This paper will analyze a series of proposals to reduce the risk of such events.
Rationale of the Study
The significant increase in natural disasters has serious consequences on the population, environment and economy of the world. This consequence has been extended because of the development of Transport networks industrial plans and infrastructures. According to Rahman (2005), during the year of 1980 to 1990, the major catastrophic natural disasters was caused by a earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, lightning and violent winds. They have also analyzed the contributing factors regarding those natural disasters and its impacts on the infrastructure. Now critical infrastructure is a complex system of components that includes production, Transportation, communication, health, safety and activities that is necessary for social needs. So naturally if the infrastructure or Falls then sodas their communication system as well as the economy of the word. That is why there is a very significant impact of natural disasters on the infrastructure and economy of the world. And because of that this is a very important problem to study.
Research Objectives
Major objectives of this research are given below.
- To investigate the importance of infrastructure in modern economy
- To investigate the contributing factors of natural calamities
- To investigate the impact of natural calamities on infrastructure
- To recommend proposed ways to minimize the risks on natural calamities.
According to Chen and Mark (2010), critical infrastructure is a series of complex system that involves production, Transportation, health, communication, safety and all the teams that is society needs to run. Now any destruction of this complex system or affect the overall economy as well as the working structure of the word. The potential sources of affecting the infrastructure can come from natural causes, technological causes or human origin causes. The disaster can also be triggered by a simple mistake which has a big consequence over the environment. And those risks can combine with each other to lead to an event complex situations where the consequences are even bigger. Natural reasons involve earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions and other natural emissions including floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, storms and climate change. On the other hand, the technological list on infrastructure involves fire, explosion, pick toxic chemicals release and other mechanical explosions that can affect infrastructure. And finally, the human cause two reasons involve human error, defect in design, carbon emission by human civilization that can lead to Natural disasters and many other (Showalter and Myers, 1994).
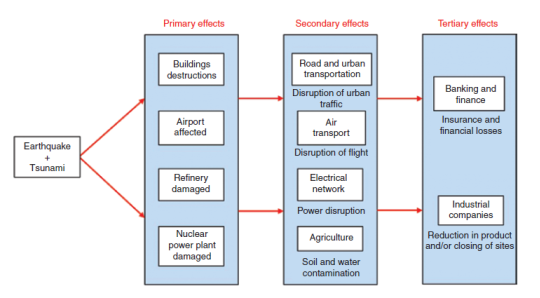
Figure: Infrastructures Damaged by the Effects of the Earthquake.
According to Birregah, Muller and Châtelet (2011), earthquakes are one of the main reasons that do more harm to infrastructure than any other natural events. But earthquakes don’t kill people, buildings do. They describe the effects of the 7.9 magnitude earthquake in 2008 in China where the main cause of death and injury was because of the collapse of a building due to earthquake. During this event, a lot of industrial facilities, where houses and buildings have destroyed and because of the destruction of those infrastructure a lot of people died and injured. On the other hand, a 9.0 magnitude earthquake occurred in Japan in 2011 who is causes a powerful aftershock that gave rise to a huge tsunami who treats several miles in Japan. The earthquake and tsunami destroyed the overall infrastructure in the country including roads, Bridges, ports, railways, buildings and other infrastructures. And because of the earthquake more than 28,000 people were dead or missing which created a havoc. Because of the earthquake and tsunami, the nuclear plant in Fukushima, Japan was destroyed the creating more disaster because of nuclear radiation. These also created a total blackout in many regions in Japan during the time (Krausmann and Cruz, 2013). This example shows how the combination of natural disasters and technological event can occur simultaneously and affect a whole country’s Industrial infrastructure thus leading to social crisis.
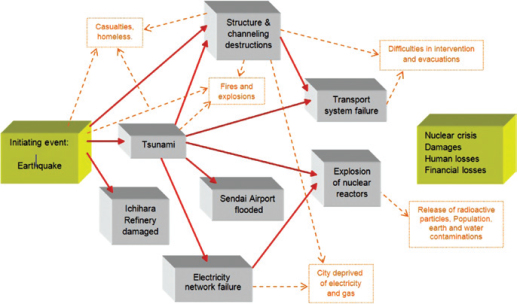
Figure: The Accident Sequences Generated by the Earthquake.
A natural event can also cause a chain of events that can lead to a complete destruction of a country’s infrastructure. The figure above shows how an earthquake give birth to a series of events that can completely destroy the critical infrastructure of a country. For example, if we consider the destruction of supply because of the chain event caused by an earthquake it can be found that the earthquake can produces a huge shock wave that create a tsunami and that can destroy the Nuclear Power Plant which produce energy. And because of the destruction of the nuclear power plant the whole country can face a complete blackout. And it takes a lot of time and money to rebuild the infrastructure destroyed by the natural disasters.
This research will provide several recommendations to reduce the destructions and costs offered by natural disasters. Some proposed recommendations are given below.
- Dampers, also known as shock absorbers can be a very useful tool to absorb the shock wave during an earthquake while designing an earthquake resistant building.
- As concrete are able to withstand wind, hurricane, flowers and Fire; powerful concrete’s can be used to build earthquake resistant buildings.
- When designing a house or building, hipped roof or with stands can be used instead of flat or gable shaped roof. The reason is because hip shaped roofs are more stable than gable type roof.
This paper will present proper methodology of carrying out risk assessments on infrastructure because of natural disaster. As natural disasters have a significant economic, social, environmental and political impact on the country, these disasters can cause a huge loss for a country. And that is why it is very important to always be prepared because natural disasters are very hard to predict. But by taking precautions it is possible to reduce disease done by natural disasters. Aldo tropical cyclones, floods, storms are predictable but severe natural disasters such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunami are very hard to predict. Their examples where a single disaster led to a whole destruction of a country’s infrastructure. Besides, because of the difficulty of measuring the actual impact of natural disaster on the, economy continues to be a major challenge, it is not always possible to asses the proper loss caused by those disasters. So, the challenges are always big when it comes to natural disasters part by taking precautions it is possible to reduce the loss caused by those natural events.
References
Birregah, B., A. Muller and E. Châtelet (2011) “Interdependency-based Approach of Complex Events in Critical Infrastructure under Crisis: A First Step toward a Global Framework.” In: (C. Soares, ed.) Advances in Safety, Reliability and Risk Management. London: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis, pp. 149-155.
Campedel, M., V. Cozzani, E. Crausmann and A. M. Cruz Naranjo (2008) “Analysis of Natech Accidents Recorded in Major Accident Databases.” In: Proceedings of PSAM9 International Conference on Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management, IAPSAM – Int. Association for Probabilistic Safety Assessment and Management, Hong Kong, China, May 18-23, pp. 1-8.
Chen, Z. W. and H. Mark (2010) “Impact Analysis of Natural Disasters Using Interrelation of Infrastructure and Associated Industries,” Journal of Shanghai University (English ed.), 14(6):424-429.
Kadri, F., P. Lallement and E. Châtelet (2012) The Quantitative Risk Assessment of Domino Effect on Industrial Plants Using Colored Stochastic Petri Nets. Presented at PSAM11 and ESRELConference, Helsinki, Finland.
Krausmann, E. and A. M. Cruz (2013) “Impact of the 11 March 2011, Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami on the Chemical Industry,” Natural Hazards, 67(2):811-828.
Krausmann, E. and F. Mushtaq (2008) “A Qualitative Natech Damage Scale for the Impact of Floods on Selected Industrial Facilities,” Natural Hazards, 46(2):179-197.
Krausmann, E., A. M. Cruz and B. Affeltranger (2010) “The Impact of the 12 May 2008 Wenchuan Earthquake on Industrial Facilities,” Journal of Loss Prevention in Process Industries, 23(2):242-248.
Rahman, S. (2005) “Impact of Natural Disasters on Critical Infrastructures.” In The 1st Bangladesh Earthquake Symposium. Dhaka, Bangladesh, December 14-15.
Showalter, P. S. and M. F. Myers (1994) “Natural Disasters in the United States as Release Agents of Oil, Chemicals, or Radiological Materials between 1980-1989: Analysis and Recommendations,” Risk Analysis, 14(2):169-182.