Information and Administration Report: Irish Tax and Customs
Â

The Mission Statement of The Revenue is:
“To serve the community by fairly and efficiently collecting taxes and duties and implementing Customs controls.”
Â
Table of Contents
| Â | Â | |
|
Michael Collins was a soldier and politician who was a leading figure and fighting for Irish Independence in the early 20th Century. He was assassinated on 22 August 1922. |
||
|
Six months after Michael Collins’ death, 21 February 1923, his wish was expressed in his last known letter. On that date his objective of an organised body was to collect the State’s revenues which got the final approval when Government Order 2/23 became law. When setting up the Office for the Revenue Commissioners, it consisted of three Commissioners: |
||
|
||
|
The Order 2/23 stated the Revenue Commissioners’ duty was to obey all instructions issued them by the Minister of Finance. On 13 March 1923, the Minister of Finance clarified the role of the Revenue Commissioners, as follows: |
||
|
||
|
Before the new Office of the Revenue of Commissioners could operate, large scale adaptations of UK revenue legislation had to be carried out. The War of Independence followed by the Civil Ware had put havoc with the country’s finances. Survival of Saorstát Éireann was dependant on the collection of taxes and duties on the Exchequer. |
||
|
The main areas of revenue collection in the fledgling State were, as follows: |
||
|
||
1.1 |
Core Business of the Revenue |
|
|
The collection of all taxes and duties derives from obligations imposed by statute and by Government and of Ireland’s membership of the European Union. |
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
1.2 |
Size and Location of the Revenue |
|
|
At present, Revenue currently employ 5,876 full-time staff. These staff are located in around 70 Revenue offices across the country. |
||
1.3 |
The Structure of the Revenue |
|
|
The structure is designed around the customer base. The Revenue Regions are responsible for their customers within their geographical area, except for large corporates and high wealth individuals who are dealt with by the Large Cases Division. |
||
|
There are 16 Divisions with Revenue, as follows: |
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
1.4 |
Services of the Revenue |
|
|
The Revenue administers all taxes which are collected from the State, some of which are: |
||
|
Customs Division |
||
|
This department is responsible for ensuring that no illegal goods have entered or leave the country. The Custom Officer’s duties are checking for all illegal food; drink, drugs, animals; and vehicles. Any imports or exports coming into or leaving the country are stopped at all the airports, ports; and road checkpoints. For example, if a car has a foreign number plate, the Custom Officer has the authority to stop the driver and ask the driver for all the relevant paperwork. |
||
Â
|
Revenue Solicitors Division |
||
|
The Revenue’s solicitor’s job is to ensure that the finance laws are carried out legally. They act on an advisory capacity if any of the divisions of Revenue have any legal queries. In relation to Debt Management, Revenue’s solicitors would act on behalf of Revenue to pursue non-compliant tax payers. |
||
|
Corporate Services / AGs Division |
||
|
This department administers Human Resource for staff. They make sure that all staffs’ paperwork is forwarded to relevant administration departments throughout the region. If any queries, they advise who to contact within the organisation. |
||
|
The AGs do spot audits and arranged audits on a tax payer or businesses to check they are compliant with all taxes. |
||
|
Collector General (CGs) |
||
|
The responsibility of CGs are to collect taxes for the running state. The money is used to fund the public services eg. Health service, education system, and Councils. |
||
|
There are various forms of taxation: |
||
|
– |
PAYE: employees pay direct from their wages. |
|
|
– |
Income Tax (IT): tax on self-employed business / tax payer. It is a self-assessed tax, which must be filed every year. |
|
|
– |
Corporation Tax (CT): charged on all profits from companies / residents within the state. |
|
|
– |
Capital Gains Tax (CGT): chargeable on all gains from disposable assets eg. sale of a property or inheritance. |
|
|
– |
Vehicle Registration Tax (VRT): chargeable on vehicles brought into the country from outside the state. |
|
|
– |
Professional Services withholding Tax (PSWT): this is a tax professionals must pay when providing their services eg. Solicitors. |
|
|
– |
E-Levy: a minor tax (environmental) for the usage of plastic bags. |
|
|
From the foundation of the Revenue, all business was conducted on hardcopies; in recent years the Revenue has moved with the times. An electronic system of reporting and paying your taxes online has been developed ie. which is a secure and user-friendly way of paying taxes. |
||
Â
| Â | Â |
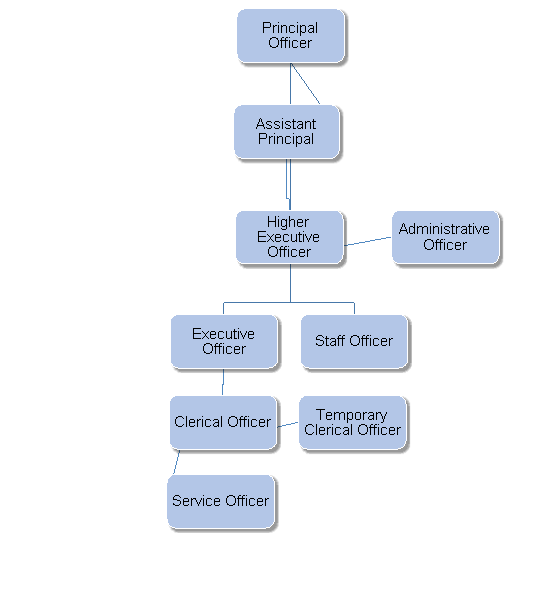
2.1 |
Clerical Officer’s Duties |
|
A Clerical Officer also known as a Case Officer, deals with the taxpayer’s queries. Their duties are to help the tax payer with any queries they have on their taxes; check all the history of their taxes; and check there a no outstanding Returns which need to be filed and paid to date. Also advise accordingly with setting-up payment arrangements. |
Â
2.2 |
Staff Officer’s Duties |
|
A Staff Officer is responsible for a team of Clerical Officers and oversees that procedures are carried out accordingly. They maintain weekly stats from their team’s performance. If a Clerical Officer has any queries with their casework or personal matters, they can go directly to their Staff Officer who will advise accordingly. A Staff Officer attends weekly meetings with their colleagues from other departments to go over any new regulations / issues which have arisen and keep all Clerical Officers informed of such changes. |
|
| Â | Â |
|
The functions of an office is to receive and sort information accurately and to distribute the information securely and efficiently to the relevant people / businesses. |
|
3.1 |
Computer |
|
Computers have helped improve the efficiency and accuracy of office administration by providing various software and communication functions to help execute work tasks. Computers today are now part of the every office and most offices cannot function without the use of them. |
|
|
Before computers were introduced in the office, it was a very loud environment to work in, as sometimes there were more than one typewriter in the office going full tilt. |

Â
3.2 |
Multi-functional Photocopier |
|
A photocopier helps produce copies of paperwork and takes numerous copies of documents within minutes which saves time and money for the administrator and the company. |
|
|
A lot of photocopiers have many functions these days eg. a number of paper draws which allows for letterhead and continuation paper to be used; automatic paper feed on top; digital screen; sorting documents into batches; manual feed tray so that sheets of labels can be fed through manually. These functions help save time for an administrator if distributing a large volume paperwork such as minutes, newsletter and reports. |

3.3 |
Telephone |
|
A telephone call is the best way to get a personal response. If the administrator calls and the client is available, they can take care of business on the spot. Other forms of communication such as texting or email, you have to leave a message and hope for a quick response. The telephone call, which connects a caller with a human voice, is still an important business component. |

| Â | Â |
4.1 |
Eight Rules of Data Protection |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
Protection of Employees (part time work) Acts 2001-2007 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.3 |
Employee Welfare Legislation |
|
|
|
|
|
Amanda Mulcahy 24 November 2016
Amanda Mulcahy 24 November 2016
Amanda Mulcahy 24 November 2016
Amanda Mulcahy 30 November 2016
https://ucpcentralmn.org/computers/ Amanda Mulcahy 28 November 2016
Amanda Mulcahy 28 November 2016
Amanda Mulcahy 30 November 2016
Amanda Mulcahy 28 November 2016