Integrated Development Environment (IDE) Components
A. For P3.4 – Make effective use of an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) including code and screen templates.
B. For D2 – Furthermore to A discuss all the components and their properties used inside the IDE for this implementation.
.NET is a product created by Microsoft, to compete against SUN’s Java. Sometime ago, Microsoft was only realigning on VC++ and VB against Java, but Java attracting the market rapidly. With universal demand for Internet/Web and java based tools, becoming the best choice for the web applications, Microsoft seemed to be losing the battle. Developers where moving to java and away from VC++ and VB. This was a major issue for Microsoft and many of the Microsoft users started becoming anxious And Microsoft had answered by the introduction of .NET.
But Microsoft has a wonderful history of starting late but catching up quickly. This is true in case of .NET too. Microsoft put their best men at work for a secret project called Next Generation Windows Services (NGWS)., under the direct supervision of Mr. Bill Gates. The outcome of the project is what we now know as .NET. Even though .NET has borrowed most of it’s ideas from Sun’s J2EE, it has really outperformed their competitors.
Microsoft’s VC++ was a powerful tool. But it was too complex. It has too many datatypes, and developers had to learn many libraries including WIndows SDK, MFC, ATL, COM etc. There were many datatype compatibility issues while exchanging data between different layers. Visual Basic was too easy, and many serious programmers hated it just for that reason. Even though Visual basic was very easy to use, it was not very flexible to develop serious applications. SUN’s Java became a very good choice for these reasons. It had the flexibility and power of C++ and at the same time easy enough to catch the attention of VB programmers.
Microsoft recognised these factors and they introduced the .NET considering all these factors. All unwanted complexities are eliminated and a pure object oriented programming model was introduced. This makes programmer’s life very easy.
.NET framework comes with a single class library. And thats all programmers need to learn!! Whether they write the code in C# or VB.NET or J#, it doesn’t matter, you just use the .NET class library. There is no classes specific to any language. There is nothing more you can do in a language, which you can’t do in any other .NET language. You can write code in C# or VB.NET with the same number of lines of code, same performance and same efficiency, because eveyone uses same .NET class library.
What is .NET ?
• It is a platform neutral framework.
• Is a layer between the operating system and the programming language.
• It supports many programming languages, including VB.NET, C# etc.
• .NET provides a common set of class libraries, which can be accessed from any .NET based programming language. There will not be separate set of classes and libraries for each language. If you know any one .NET language, you can write code in any .NET language!!
• In future versions of Windows, .NET will be freely distributed as part of operating system and users will never have to install .NET separately.
What is Not ?
• .NET is not an operating system.
• .NET is not a programming language.
“.NET is a framework”
Are you confused by this definition? Well, that is OK. It is really confusing!
We cannot define .NET as a ‘single thing’. It is a new, easy, and extensive programming platform. It is not a programming language, but it supports several programming languages. By default .NET comes with few programming languages including C# (C Sharp), VB.NET, J# and managed C++. .NET is a common platform for all the supported languages. It gives a common class library, which can be called from any of the supported languages. So, developers need not learn many libraries when they switch to a different language. Only the syntax is different for each language.
When you write code in any language and compile, it will be converted to an ‘Intermediate Language’ (Microsoft Intermediate Language – MSIL). So, your compiled executable contains the IL and not really executable machine language. When the .NET application runs, the .NET framework in the target computer take care of the execution. (To run a .NET application, the target computer should have .NET framework installed.) The .NET framework converts the calls to .NET class libraries to the corresponding APIs of the Operating system.
Whether you write code in C# or VB.NET, you are calling methods in the same .NET class libraries. The same .NET framework executes the C# and VB.NET applications. So, there won’t be any performance difference based on the language you write code.
What is Visual Studio.NET ?
Many people always get confused with Visual Studio .NET (VS.NET) and .NET technology. VS.NET is just an editor, provided by Microsoft to help developers write .NET programs easily. VS.NET editor automatically generates lot of code, allows developers to drag and drop controls to a form, provide short cuts to compile and build the application etc.
VS.NET is not a required thing to do .NET programming. You can simply use a notepad or any other simple editor to write your .NET code!!! And you can compile your .NET programs from the command prompt.
Well, what I said is true theoretically.. but if you decide to use notepad for .NET programming, by the time you develop few sample applications, Microsoft would have introduced some other new technology and .NET would be outdated. You may not want that. So, let us go by VS.NET, just like every other .NET guys.
You can read more about VisualStudio.NET in the next
article.
.NET supported languages
Currently .NET supports the following languages:
• C#
• VB.NET
• C++
• J#
The above languages are from Microsoft. Many third parties are writing compilers for other languages with .NET support.Difference between VB and VB.NETBelieve us, there is not much in common between VB and VB.NET other than the name. VB.NET is a totally new programming language. It just retains the syntax of old VB. So, if you are a vb programmer, probably you may like VB.NET than C# just because of the syntax.
In addition to this, VB.NET still support many of the old VB functions just for backward compatibility. But if you are a serious .NET programmer, we strongly suggest never use old VB functions in VB.NET. So, switching from VB to VB.NET is just like learning a new programming language, with very small similarities between them.
C# or VB.NET ? Which one to choose ?
There is no difference. Whether you write code in VB.NET or C#, as you compile, code will change to MSIL (Microsoft Intermediate language). It is this MSIL that is delivered to the end in the format of DLL and/or EXE. The MSIL is executed by the .NET framework, whether is written in C# or VB.NET.
The MSIL generated by C# and VB.NET is almost identical many assume that C# has the functions of C++ and VB.NET has the UI of VB. This is wrong.
VB.NET includes backward compatibility with the legacy Visual basic. So, it supports legacy VB functions. C# is a new modern language. So it supports C# instead of the VB.NET just for this new compiler.
Many old VB guys usually like to stick with VB.NET and are kind of scared of C#. We are sure that you will not take more than few days to get familiar with C# syntax. This online tutorial is based on C# and all samples will be provided in C#.
Is it platform independent ?
Many people ask this question “Java is platform independent, what about .NET ?”.
The answer is “Yes” and “No” !
The code you write is platform independent, because whatever you write is getting compiled into MSIL. There is no native code, which depends on your operating system or CPU. But when you execute the MSIL, the .NET framework in the target system will convert the MSIL into native platform code.
So, if you run your .NET exe in a WIndows machine, the .NET framework for Windows will convert it into Windows native code and execute. If you run your .NET application in Unix or Linux, the .NET framework for Unix/Linux will convert your code into Unix/Linux native code and execute. So, your code is purely platform independent and runs anywhere!
But wait, we said it wrong… there is no .NET framework for Unix or Linux available now. Microsoft has written the .NET framework only for Windows. If you or some one else write a .NET framework for other platforms in future, your code will run there too. So, let us wait until someone write .NET framework for Linux before you run your .NET code in Linux.
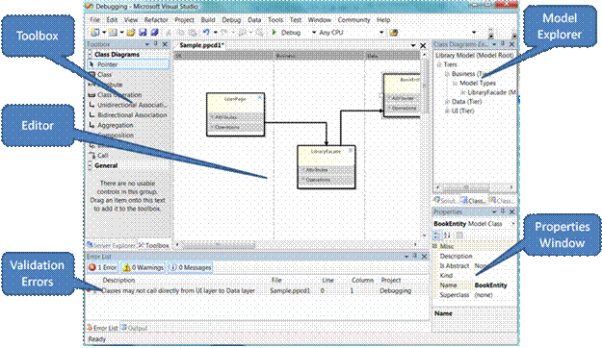
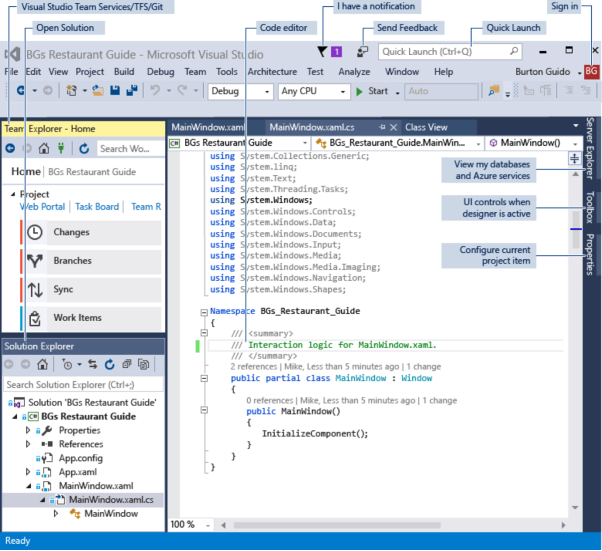
integrated development environment elements
In the beginning of a Visual Studio project , you will experience the following Main Page which incorporates a list of links to a set of resources, including the newest updates in Visual Basic and information with regards advanced programming topics.
Menu Bar
You can make your VB projects in a better way by including menus to your applications. You select the Main Menu control from the toolbox an draw it anywhere on the form. You must also set the form property ‘MenuName’ to MainMenu, so the menu is displayed when the program runs.
ALT + letter shortcuts:
Enter an & in front of the word that you would like the shortcut for . For example, if you want ALT & f in the file menu simply input &File in the caption part of tmenu options
Code:
To include code to the menu option simply double click on the menu item in the project window and the code window with the sub/end sub for that menu item will be displayed. Add you code.
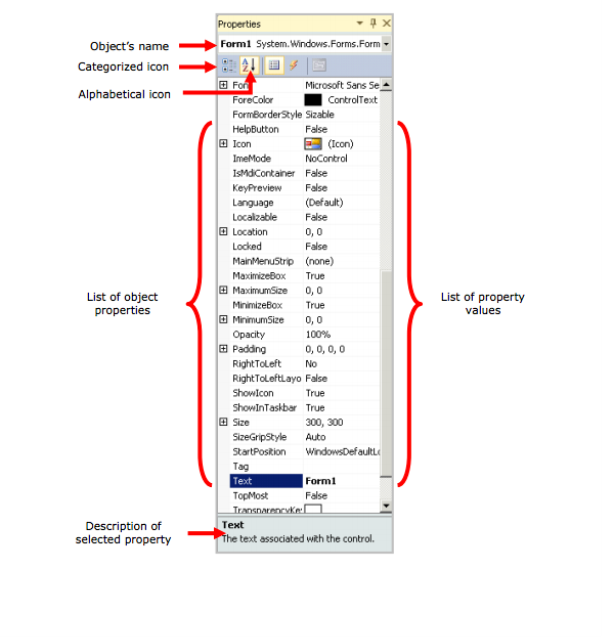
PROPERTIES WINDOW
Properties Window shows properties for Form and control objects. Properties define the object’s attributes, example size, color and location. The Properties window enables the user to set an object
properties visually without writing code.
SOLUTION EXPLORER
Solution Explorer window supplies access to the solution files and enables user to edit files visually.

FORM DESIGNER
The Form shows the main window of the Windows Application that user is constructing . They can be modified by including extra controls, such Buttons, Labels, the TextBoxes, etc. User can include controls onto the Form by allowing the Toolbox.
To allow the Toolbox a user need to click on the Toolbox function at the left side of the program IDE.
Toolbox’s groups prebuilt controls into categories. When you click a group name, the Toolbox displays all the controls in that group.
