Organisational Culture Analysis of BP
Title: What is the role of Organisational Culture in British Petroleum at Lancashire County?
Contents:
- Literature Review
- Research Aims, Objectives and Limitations
- Research Methodology
- Research Methods Analysis
- Results
- Recommendations and Conclusions
Introduction
Organizational culture is the set of shared values, beliefs, and norms that influence the way employees think, feel, and behave in the workplace (Schein, 2011). The purpose of this dissertation is to explicate the impact of organizational culture in British Petroleum towards achieving the business objectives and capabilities of employees’ roles and subsequent role behaviours. I propose that four types of cultures (clan, entrepreneurial, market and hierarchy) exert different and at times competing pressures, thus, creating distinct role schemas regarding the range of expected employee behaviours, which in turn, guide distinct forms of employee role behaviour (e.g. helping, innovation, achievement and compliance).

Organizational culture has the potential to enhance organizational performance, employee job satisfaction, and the sense of certainty about problem solving (Kotter, 2012). Organizational culture has received ample attention both in the popular and scholarly press as an important factor predicting organizational effectiveness by inducing employees to behave effectively (Cooke & Rousseau, 1988; Schein, 1985, 1990). Knowing the culture of an organization allows employees to understand both the organization’s history and current methods of operation. Organizations can achieve effectiveness only when employees share values.
For instance,Eliot Jaques provides the following description of the culture of a factory:
“The culture of the factory is its customary and traditional way of thinking and of doing things, which is shared to a greater or lesser extent by all its members, and which new members must learn, and at least partially accept… Culture is part of the second nature of those who have been with the firm for a long time.” (1951: 251). Organizational culture, through its norms, serves as a control mechanism to channel behaviours toward desired behaviors and away from undesired behaviours. This can also be accomplished by recruiting, selecting, and retaining employees whose values best fit the values of the organization.
The aim of the study was to present and discuss the preliminary culture model to indicate the culture performance within the British Petroleum and proposing a model for assessing organisational culture towards achieving business objectives.
Objectives
Approach of organisational culture allows access to the dynamics of the social system in all its complexity, and then it leads to the concept of corporate identity (Strategor, 1995. The main objectives of organisational cultural and capabilities to achieve the aim are,
- Analysing the present and future Business plan
- Staff employment and their internal relationship
- Knowledge sharing and Decision making
- Plans for business process and implementation
Rational of the research
An Organisation’s culture determines the organisation’s ability to complete projects successfully that can encourage a culture in their business that aligns with their objectives and makes employees more likely to succeed in reaching their objectives. Even though two businesses have similar structures, the impact of effectiveness can be different because of differences in their cultures. So the research about comparing the present model of organisational culture of the selected organisation with the competitors provides ample of knowledge and new understanding about employing staff, kind of work assignment, communication plans and their in-house relationship provides understanding which enhances the knowledge for assessing organisational culture towards achieving business objectives.
Scope
The scope of the study will contribute to the extant research on organizational learning, culture, and identification, the literature on these constructs remains mostly prepositional. There is a wide scope for continued quantitative and qualitative research on each one of the latent variables included in this study individually and collectively. This research studies could be applied for the findings of research to multiple organisation at various geographic locations, in order to determine commonalities and differences across various business sectors and localities.
Different combinations of culture and learning variables influence organizational identification at different levels like low, medium and high.
Limitations
Money and Time Costs: When the basic data are subjected to frequent changes, incorporating them into the Organisational research models is a costly affair. Moreover, a fairly good solution at present may be more desirable than a perfect solution available after sometime.
Implementation: Implementation of decisions is a delicate task. It must take into account the complexities of human relations and behaviour internally.
Data collection and analysis methodology is to be carried out throughout this research which should be chosen to match the particular evaluation in terms of its key evaluation questions (KEQs) and the resources available. Impact evaluations should make maximum use of existing data and then fill gaps with new data.
Some common data collection methods include observations, interviews, focus groups, surveys, and the use of secondary data such as test scores.
I have choose to carry out Qualitative data methods and analysis which is allows to find out the reasons. This may be beneficial to an organization in bringing out the required changes to create a culture that can facilitate better learning opportunities.
The research will be both deductive and inductive in nature and will be anchored in grounded theory.
Methodological problems predicted which may arise while carrying out this research are
- Voluntary participation, because in most cases, permission is needed from people before involving them in any primary research.
- Confidentiality and anonymity – as participants may reveal embarrassing or potentially damaging information such as racist comments, unconventional behaviour and
- Researcher bias.
I will be using both primary and secondary sources for this research such as primary sources like questionnaire, personal and group interviews and observations and secondary sources like internet, journals, articles, magazines and books.
The validity of the proposed model will be tested by a few case studies. In order to measure current and expected organisational culture capabilities, it will adopt the maturity-level techniques which is being able to measure the organisational readiness (Galliers & Sutherland, 2003; Salleh & Alshawi, 2006). The gap between the current and expected levels could be identified which also is known as the “Readiness Gap”(Salleh & Alshawi, 2006).
TASK 1 part 2: Plan and procedures for the agreed research specification (AC1.5);
|
Research objective |
By when |
Resources to be used (2.1) |
Milestones (when do you know this objective is achieved) |
Review dates (which is after the “by when to ensure that you have actually achieve the objective “) |
How will you monitor this objective is being achieved? – method of monitoring |
|
Analysing the present and future Business plan |
21/12/16 |
Gathering information on good make better sense of your market research. |
5/1/17 |
8/1/17 |
By constant evaluation after gathering the required resources |
|
Staff employment and their internal relationship |
25/12/16 |
Online survey, questionnaires, Journals, |
28/12/16 |
31/12/16 |
By gathering data in regular basis about the employee culture in the organisation |
|
Knowledge sharing and Decision making |
5/1/17 |
Articles about franchise buyers, books and related web link |
11/1/17 |
14/1/17 |
By getting answer to the questions – How much knowledge does the average employee has in terms of decision making |
|
Plans for business process and implementation |
7/1/17 |
The proper and effectively business plan and implementation |
11/1/17 |
13/1/17 |
Employee works in a happy atmosphere and the productivity will more and growth of the company |
2.1 Match resources efficiently to the research question or hypothesis
I focused on the effects and implications of the conceptualisation and operationalization of organization culture and formulation of the research problem of a grounded theory study. The research formulation implications discussed above are the research design considerations that I reflect on analysing the present and future Business plan, internal relationship of staff, decision making, business process plan and implementation. I used methodology of direct survey questionnaire as a main instrument, observation ad interviews.
Each of these methods were unique and useful in their own way. By the end of the research, the results from one method were more useful than from the other, and some of these methods did not even work
2.2 Undertake the proposed research investigation in accordance with the agreed specification and procedures
Data Collection and Analysis
I use observation, documentation review, surveying and questionnaire method of data collection which I believed effective and the research was conducted by means of a direct survey. Questionnaire was the instrument of data collection which consists of 20 to 25 questions with a mixture of Likert-scale and closed-ended questions with one answer was developed. A five-point Likert scale was employed to gather responses, 5 indicating “maximum agreement” and 1 “no agreement”. The survey was sample-based. Non-random sampling was applied and advantages and disadvantages specific to this method of sampling were considered. A small group of those surveyed does not authorize to make generalizations, but allows the identification of the specific mechanisms and formulation of questions and conclusions. Tested on a larger sample, they will make it possible to formulate more documented and certain, useful theses on a larger scale. Analysis method I used here is predictive analytics and machine learning to anticipate important events and continuous tuning of analytic platform using feedback.
Advantages
- I could see see directly what people is relying on rather than what they say they do.
- With Questionnaire method covered large geographical area.
- Capable of collecting data from a large number of respondents
- I found to ask numerous questions about a subject, giving extensive flexibility in data analysis
- With survey software, advanced statistical techniques can be utilized to analyze survey data to determine validity, reliability, and statistical significance, including the ability to analyze multiple variables
- A broad range of data was collected (e.g., attitudes, opinions, beliefs, values, behavior, factual).
Disadvantages
The challenges I faced in data collection methods are, its much time consuming, information is often incomplete, couldn’t get a proper and careful feedback as the wordings biasing the responses. Also I felt couldn’t get the full story and surveys are in need of sampling expert.
2.3 Record and collate relevant data where appropriate.
I used questionnaire surveys and semi-structured interview schedules, gathering of observational data and analysis of documentary data method because of the limited number of senior staff, it may not be possible to conduct pilot semi-structured interviews with them, as this will preclude them from the final data collection.
According to the model based on the basic underlying assumptions the description of the current culture was made. The questionnaire was used because of its advantages (little time required and low costs) and because the team wanted to get a general impression of the mood in the company as quickly as possible. The questionnaires were distributed personally by the heads of the departments, and a very good return ratio from approximately 40% was reached.
In 2011 BP a 10-point plan had been put forward that outlined what could be expected from BP over the next three years. During 2012 work had been done towards the milestones that had set out for 2014. Their plans are refined and communicated further information on our longer-term strategic objectives beyond 2014(BP.com, 2012).
Bp has been identified as an organization that adopts differentiation strategy over the years due to the proper utilization of the company’s competences or capabilities. It has different brands such as BP, Ampm, Arco, Castrol, Aral and Wild bean cafe (www.bp.com), and also diversification into development and production of alternative sources of energy(BP.com, 2011).
With the collected relevant data I found if BP wants a safety culture, it must implement massive changes throughout every aspect in their organization that are guided by that safety focus. More than re-structuring or changing incentives and rewards it must do more because, so many problems are due to a focus on profits over safety? Repeatedly, a focus on growth at the expense of safety or quality leads companies on a dangerous path that affects human lives.
The causes are described as systemic issues. Examples include:
- Flaws in BP’s management and design procedures
- Failures to appreciate risks
- Lack of communication and training about lessons learned from prior problems
- Government regulators lacking the authority, necessary resources and technical expertise
- Using time-saving and cost-saving measures
When major quality or safety issues are exposed to the public, by either a disaster or a recall, the changes in the culture are often systemic-it’s not an isolated error but a change in values. The changes must start at the heart of the culture at its core, where employees stop for a moment to reflect on the values that are important and together create a shared view. If safety is what’s valued over profits, then employees should not be over-worked, and faulty equipment and poor maintenance should not be allowed.
Employees should be hired not only for competency but also because they personally value safety. It should be the role of each employee to enhance the safety culture.
Administration of the questionnaire and analysis of questionnaire data are done to provide material for the interviews and interviews are conducted concurrently. Numerical data were analyzed, which was also enabled the responses from sub-groups of the organization which was separated for analysis. Qualitative data was analyzed using protocols of content analysis.
TASK 3: Be able to evaluate the research outcomes
3.1 Use appropriate research evaluation techniques
For the study conducted, there was a requirement of the resources which would assist to identify key constituents that have been undertaken for the purpose. In order to achieve this target, the focus of the study was on the various types of strategies of management that undertaken by British Petroleum. The British Petroleum operates worldwide and in diverse population. For example, the European market, people can be divided into various sub-cultures and consumer behavior is also different (Ford & Jeffrey, 2009, 105).
The outcome of the research shows the true analysis of BP’s organisational plan, leadership, staff relationships and organizational decision making of sources of internal information collection and organising the duration of data project and sources of usage of collected data for business process implementation and development.
The research finding has a valid and reliable data to achieve the aim and objectives of the research. Depending on factors like the goals of the data collection project, the organization’s size, resources and time, data may be gathered about many sub-sets within a broader group of interest (e.g. youth service users who cannot read and who speak English as a second language).
According to Dr. Mustafa Ozkan Karatay (2013) the benefits of the research conducted includes data collection about a group of interest that shares characteristics and the Leadership enhancements that are essential to avert comparable occurrences in BP which consist of:
- A solo overall project leader.
- Clear communications to every individual functioning on the project.
- Greater safety trainings linking past experiences and crisis analysis.
- 4.Hiring employees with the essential skills to complete tasks competently and securely
It is also important to recognize that based on their unique combination of identities, people exposed to particular forms of discrimination.
Bp has under gone major restructuring under the new management of the new CEO Robert Dudley, Dudley said that BP was to re-structure its upstream segment from a single business into three separate functional divisions; exploration, development and production, which would carryout a detailed review of how the group managed third-party contractors in order to reinforce accountability for risk management. The company is doing this because of the findings of an internal report; it stated that the breakdown in communication was one of the contributing factors to the BP disaster.
3.2 Interpret and analyse the results in terms of the original research specification.
The following chart represents the BP’s Organisational structure from the top level management from where different business models are distributed throughout the different geographical area in the globe.
Organization Structure
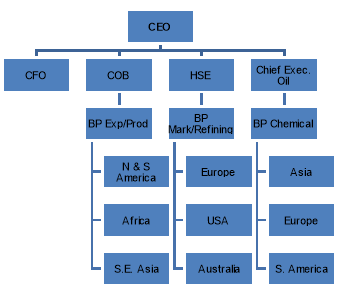
The political influences made a notable difference in BP’s strategy which has been changed in general possible to observe two main tendencies. First, BP attempts to hedge political risks in the oil producing countries by means of partnership and deals with the governments. For instance, BP signed a contract with the Russian state-run oil company. It is reported that the company started producing solar panels after the acquisitions of Lucas Energy Systems (1980) and Amoco (1998)(Saud M. Al-Fattah, 2013). Furthermore, it is reported that BP invested more than $6 billion in wind and bio-fuel energy projects during the period from 2005 to 2010 (BP.com, 2011)
BP also runs a series of development programmes notably known as Managing Essentials to help managers apply the leadership framework in their own teams. I t also runs three specialist development programmes designed to build excellence in the 3 important functional areas of operations, finance and human resources. The Operations Academy, set up in partnership with MIT, provides BP’s senior managers with a systematic and rigorous approach to managing safe and efficient operations.
The overall statistics of British Petroleum’s business and turnover is found below.
|
Countries of operation |
:Over 80 |
|
Number of employees |
:85,900 |
|
Sales and other operating revenues |
:$375,765 million |
|
Cash flow |
:$20.5 billion |
|
Replacement cost profit |
:$11.4 billion |
|
Proved reserves |
:17,000 million barrels of oil equivalent |
|
Retail sites |
:20,700 |
|
Refineries (wholly or partly owned) |
:15 |
|
Refining throughputs |
:2,354 thousand barrels per day |
Detailed and structured questionnaire was designed where the survey was undergone with a sample of 50 employees in BP. The methodology developed was Primary and Secondary research. The questionnaire was designed to get information from staffs about their satisfaction and overall opinion about organizations and its structure. Some sample of the questionnaire is showcased below. Here most of them gave multi answers for questions.
- In what way are individual positions, units and so on clustered within your organization unit?
a) By Function c) By product e) By place
b) By target group d) By service f) By project
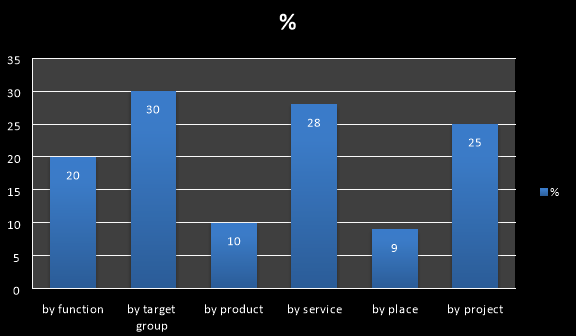
The graph shows the way how individuals position is clustered within the organization. It shows like it depends mostly on the project individual involved with and the service given by them along with the target group.
2. Is the content of job changed for the employees during last two years?
a) Work autonomy c) Co-operation with management
b) Specialization d) Multi-tasking e)Weight upon technical qualifications
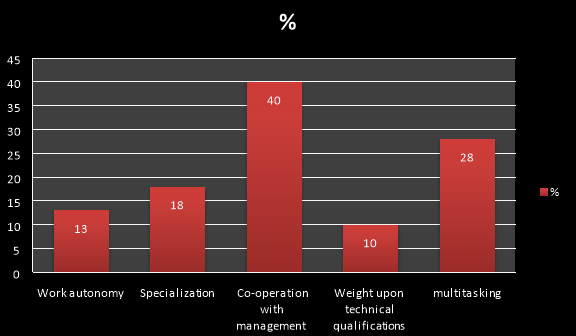
According to the answers of staffs the above graph shows that the content of the job has been changed in past two years with the cooperation with management and also for the individuals who do multi tasking.
3. Does your company use any of the following ways of organizing work?
a) Quality circles / groups
b) Delegation of responsibility
c)Planned job rotation
d) As per resource availability
e) Integration of functions
f)Specialization
g) Incentives based upon quality of results
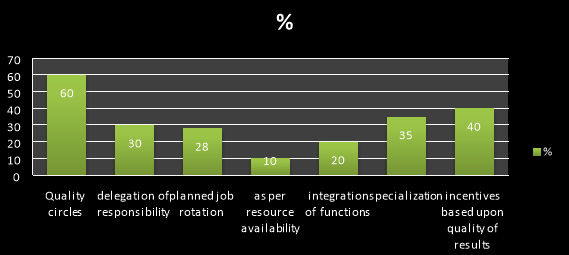
It shows that the company is preferably using the quality circles as more than 50% answered such for organizing the work and 40% said that the incentives are based upon the quality of results they obtain.
4. How the Knowledge management has been benefiting your company
- Contemporary technologies & processes
b) Efficient management of information
c) Increasing customer satisfaction
d) Fosters innovation
e) Increasing productivity
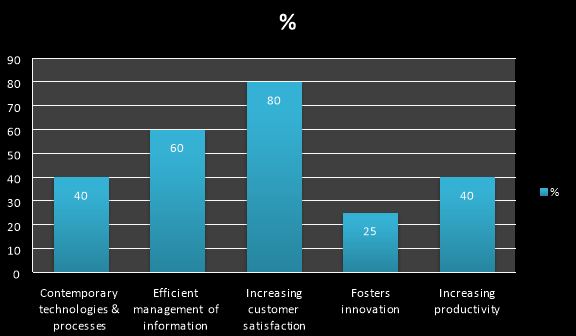
It clearly shows with the above graph that the most of them answered(80%) as the company use knowledge management which increases the customer satisfaction and 60% answered as efficient management of information. Upto 40% answered that contemporary technologies and processes and increase in productivity.
5. How much freedom of action has, in your opinion, an executive within the organization to vary his leadership with regard to directing and collaboration?
a)None c)Complete e)Much
b)Little d)Not much
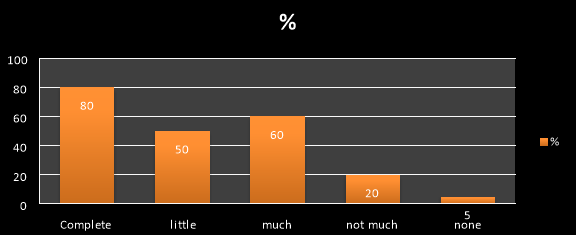
For the question arised about the freedom of action for an executive within organization to vary his leadership most(80%)of them answered as complete freedom has been given and very less percentage(5%) said as no. So it shows a positive sign for employees to execute their ideas and work in a hassle free environment.
6. People here try to make friends and to keep their relationships strong.
- Low
- Medium
- High
|
LOW |
MEDIUM |
HIGH |
|
2 |
3 |
45 |
|
4% |
6% |
90% |
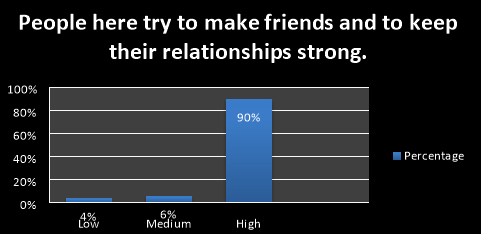
The above graph shows that 90% of the people say, they make friends and to keep their relationships strong.
7. People here do favours for others because they like one anther
- Low
- Medium
- High
|
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
4 |
4 |
42 |
|
8% |
8% |
84% |
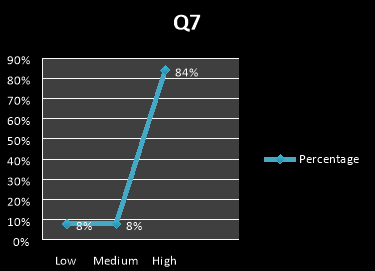
The above graph shows that 84% of the people say, they do favours for others because they like one anther.
8. People in our group often socialize outside the office
- Low
- Medium
- High
|
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
8 |
3 |
39 |
|
16% |
6% |
78% |
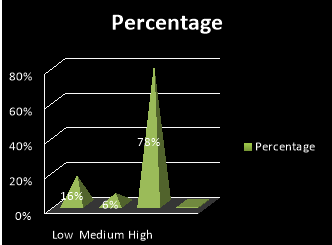
The above graph shows that 78% of the people say, they often socialize outside the office
9. When people leave your group, stay in touch one another
- Low
- Medium
- High
|
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
7 |
6 |
37 |
|
14% |
12% |
74% |
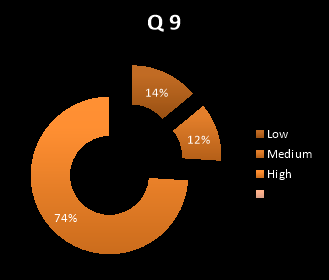
The above graph shows that 74% of the people say, they stay in touch one another when they leave their group.
10. People here often confide in one another about personal matters
- Low
- Medium
- High
|
Low |
Medium |
High |
|
1 |
3 |
46 |
|
2% |
6% |
92% |
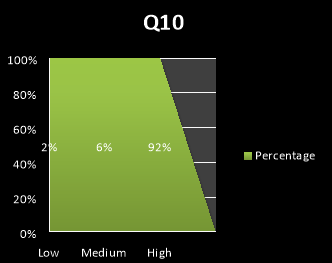
3.3 Make recommendations and justify areas for further consideration.
BP Company’s project, is a significant step toward the growth of the company, but the Chief Executive officer should ensure that the established Centralized Developments organization enhance the integrity in the project implementation process. While considering their present, future business plan and implementations they should establish a body of expertise in greenhouse gases in order to reduce emissions that may hinder the attainment of the project goal. The other recommendation I am keen to insist is that BP should invest much on renewable energy sources like wind power, solar panel and bio-fuels which is because they present little or fewer risks on people health and environment. There is also a need for the BP Company to consider reorganize its 4 P’s of marketing viz. product, price, promotion and placement so as to secure a competitive advantage over the other six competitors in the industry.
BP’s weaknesses led it to engage in excessive cost-cutting and to take disproportionate risks with respect to the environment, worker safety, national security and its own profitability. I analysed also about BP’s problematic ethics which despite being hailed by the financial media for its corporate citizenship, its rhetoric and deeds about social and environmental responsibility were diametrically opposed.
Furthermore I recommend that the company should increase expenditures on infrastructure maintenance and employee safety. It should also conduct employee training. It is recommended that BP should use the diversification strategy as a future strategic option in order to continue responding to the environmental challenges. The company should diversify its product range associated with the production of solar and wind energy for individual and corporate customers. It is expected that these products will be popular in the emerging markets such as India and China where incomes are not high, but energy consumption patterns are growing very fast. Together with alternative energy production, this will positively influence corporate reputation after the recent safety scandals and ‘green washing’. Finally, it is recommended that BP should continue popularizing efficient use of energy by individual consumers and industrial enterprises.
Conclusion:
Organizational culture includes the values, beliefs, behaviours, norms and artefacts that connect the members of an organization. As in all other cultures, organizational culture develops over a long period of time with the participation of the members. Through studying or analyzing the culture of an organization, we can able to come up with various conclusions. These include conclusions about the resistance of culture, organizational performance, communication, leadership styles. These conclusions can be helpful for managers and consultants seeking to encourage better organizational cultures.
References
- BP.com (2011). Annual Report and form 20-F. Available: https://www.zonebourse.com/BP-PLC-9590188/pdf/292392/BP%20plc_SEC-Filing-20-F.pdf. Accessed: 2nd January 2017]
- Ford, Jeffrey D., Ford, Laurie W. & McNamara, Randall T. 2009. Resistance and the background conversations of change. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 15 (2): 105-121.
- BP annual report (2012). BP Summary review 2012. Available: http://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/pdf/investors/bp-summary-review-2012.pdf. [Accessed: 02nd January 2017]
- Mustafa Ozkan Karatay (2013) What Change Management Strategies Can Be Undertaken By British Petroleum after Undertaking Strategic Analysis to Help Them Gain Competitive Advantage. Available: https://era.library.ualberta.ca/files/d791sg676/Thesis_Karatay.pdf. [Accessed:3rd January 2017]
- Saud M. Al-Fattah (2013). National Oil Companies: Business Models Challenges and Emerging Trends.Available: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Saud_Al-Fattah/publication/261696989_National_Oil_Companies_Business_Models_Challenges_and_Emerging_Trends/links/00463534fe986b81d1000000.pdf. [Accessed: 03rd January 2017]
- Cooke R A., & Rousseau, D M 1988. Behavioral norms and expectations: A quantitative approach to the assessment of organizational culture. Group and Organization Studies, 13: 245-273
- Schein E , 1984. Coming to a new awareness of organizational culture. Sloan Management Review, Winter: 3-14
- Kotter J.P. & Heskett J.L. 1992.Corporate culture and performance
- New York: Free Press.
- Galliers R. and Sutherland A (2003). The Evolving Information Systems Strategy-Information systems management and strategy formulation: applying and extending the ‘stages of growth’ concept In Strategic Information Management-Challenges and Strategies in Managing Information Systems.R. Galliers and D. Leidner. Oxford, Butterworth-Heinemann: 33-63.
- Salleh H and Alshawi M(2006) Measuring the Readiness of an Organisation Prior IS/IT Implementation . Proceedings of the 6th International Postgraduate Research Conference. April 6-7, 2006, Delft University of Technology, Netherlands, pp.293-305
- Strategor (1995), ZarzÄ…dzanie firmÄ…: Strategie, struktury, decyzje, tozsamosc. WE, Warszawa.