Organizational Behavior Concepts: Self-Analysis
Organizational Behavior Concepts: Self-Analysis and Team Assessments with Recommendations and Analysis
Submitted by
Vineesh Nambiar
MGT 621A – Winter 2017
Instructor: Dr. Joseph Ofori-Dankwa
Date: February 22, 2017
Table of Contents
The makings of a successful organization can generally be traced back to its ability to define itself from day one; very few organizations succeed if top level management doesn’t lay down the rule of the land as far as expected Organizational Behavior is concerned. What exactly is Organizational Behavior? It basically relates to the study of the structurally set-up social system in an enterprise. In laymen’s terms, Organizational Behavior is a deeper look at the relationship employees (as individuals as well as in groups) have with a firm. The purpose of this paper is to examine different aspects of Organizational Behavior at various levels while simultaneously identifying managerial skills sets and attitudes that are beneficial at aiding in the successful fulfillment of objectives as it pertains to employee management. Using the CROAPI model, this paper looks to delve deeper into the following:
- Human Process
- Individual in the Organization
- Group Dynamics
- Influencing Others
- Organizational Processes
Primarily this paper looks to shed light on self and critical evaluation of the concept of the ‘team’; mainly concerning itself with the important and practical guidelines associated with the facets that traditionally fall under the larger umbrella of ‘Organizational Behavior’. Starting with ‘team cohesion’, the aforementioned facets are as follows:
Team Cohesion
Aristotle once said that “The whole is greater than the sum of its parts” and there can be no quote in existence that better summarizes the underlying relevance of team cohesion. Cohesiveness among teammates in any organization is essential for the maximization of effectiveness and efficiency when it comes to a firm. The similarity among members, the size of a team, the interaction between members and the overall penchant that a team shows for actively and aggressively pursuing success are some of the factors looked into when it comes to ‘team cohesion’.
Social Loafing
The next section deals with the phenomenon known as ‘social loafing’. A term devised to reflect the inability of some members in an organization to contribute a relatively acceptable level of performance when it comes to group tasks, potential and existing ‘social loafers’ must always be on the radar of managers. There are a myriad of ways in which this issue can be dealt with: emphasizing the importance attached to a task, highlighting the work contribution of an employee and reducing the size of a task group are some of these.
Motivation
A manager has to put up with numerous expectations that sound easy on paper but nigh impossible in practice; keeping an employee or a set of employees at a constant level of high motivation falls under this category. This section of the report examines different theories that are associated with employee ‘motivation’ as a unique, separate concept. These theories include Maslow’s Theory of Motivation, the Equity Theory of Motivation and the Expectancy Theory of Motivation.
Personality
Using the Five-Factor Model, this report aims at outlining different personality traits and establishes relevant relationships between these and employee performance. The parameters used under this model are ‘Conscientiousness, Agreeableness, Neuroticism, Openness to experience and Extraversion’ (CANOE for short). Gauging personalities is often an underrated aspect of managerial expertise and hence, this paper looks to expand on the topic in an analytical manner.
Perception
The perception can arise in an organization as the process of receiving information about, and making sense of, the world around us. This can lead to different problems within an organization or team. Creating Self-Fulfilling Prophecies and Minimization of Stereotyping, Attribution Errors, Halo Effect it can be managed in an organization.
Values across Cultures
Cultural values are very often overlooked when managerial decisions are undertaken. The prevalence of a ‘one-size-fits-all’ mentality is generally found to be the culprit beyond this sort of dodgy decision making. Via the use of Hostfede’s data on Germany and the United Arab Emirates, an analysis has been carried out in this report with emphasis on the differences between collectivism and individualism as well as ‘power distance’ as it relates to potential managerial techniques that need to be employed.
This paper ultimately aims at not just critical self-evaluation of the team but also the analytical formulation of recommendations that can aid in systematically and logically dealing with any plausible problems that can arise under the gamut of ‘Organizational Behavior’. Using conceptually-approved managerial measures of evaluation, the following pages seek to ask questions and deliver answers to many different aspects of ‘Organizational Behavior’. The paper will cover the following individual sections
- Self and Team analysis
- Team Cohesion
- Social Loafing
- Motivation
- Personality
- Perception
- Values Across Culture
I have done a self-analysis and have posted a picture of myself in the analysis and also I have interviewed my team members Madison Rase, Duo Wang and Zui Tao on their educational qualifications, professional and career aspirations and the professional achievement that they are proud of.
|
TEAM MEMBER |
QUALIFICATION AND OBJECTIVE |
|
SELF- Vineesh Nambiar |
I am an international student from India and hold a Bachelor’s in Computer Science Engineering from Anna University, India. I am currently Pursuing my MBA at SVSU and my interests are in Web Application Development and Cloud Computing. I have 2 years of experience in developing applications using Java and web Applications. My career objective is to pursue a dynamic and challenging career with an organization of repute, which will give value addition to the organization as well as opportunity to enhance professional skills while getting high level of satisfaction and recognition. |
|
Madison Rase |
Madison is currently pursuing a Bachelor’s degree in chemistry with an anticipated graduation date of May 2017 and simultaneously pursuing an MBA with an anticipated graduation date of May 2018. She is an experienced Lab Technician at the Dow Corning Corporation where she has created and evaluated formulations for customer standards and has also helped in correcting production issues. Her career objective is to have her own business working with the design and production of cars. |
|
Duo Wang |
Duo Wang is an international student from China who holds a Bachelor’s degree in animation design from Guilin University of Electronic Technology, China. She is currently pursuing her MBA at SVSU. She has an aspiration to work for an animation company. While she was doing her undergraduate degree, she was a member of the student’s association for three years and, also served as the head of the association for a year. This experience gave her an insight on how to work in a team and what teamwork is all about |
|
Zui Tao (Chris) |
Chris is an international student from China. He earned his Bachelor’s degree in General Business from SVSU. His aspiration is to have a successful management career in the U.S.A and more specifically in Human Resource Management. He has two years volunteering experience and used to run a department in the association. He is looking forward to reflecting on his personal values with and his abilities. |
Team cohesion (Appendix A- Figure 2).refers to the degree of attraction people feel toward the team and their motivation to remain members. It is a characteristic of the team, and includes the extent to which its members are attracted to the team, are committed to the team’s goals or tasks, and feel a collective sense of team pride. Thus, team cohesion is an emotional experience, not just a calculation of whether to stay or leave the team. It exists when team members make the team part of their social identity. Team development tends to improve cohesion because members strengthen their identity to the team during the development process.
Following where the factors that lead to high cohesion of our group where these factors reflect an individual’s social identity within the group and beliefs about how team membership will fulfill her or his personal needs.
- Member Similarity: This was very applicable to our team as all of us are pursuing an MBA degree in SVSU and has definitive objectives after completing the course.
- Team Size: This is also very relevant to our team as we are at the right number of team members.
- Member Interaction: we periodically communicate or interact with the team members using E-mails, Text, and group meetings.
- Team Success: This is the first project we are doing as a team and we expect to perform well and will be willing to work as the same team should we all be together in another course at SVSU.
Social Loafing happens when a group member exerts less individual effort when doing an addictive task in groups than when working alone (McShane and Von Glinow, 2015, p. 224). This occurs when a large group is formed, the lower will be the impact of force on any of the one member in it. Thus, more the people who might be contributing for the group production, the less pressure each person faces and will result less responsible for behaving appropriately and social loafing occurs.
Following are the ways by which social loafing can be overwhelmed.
- Emphasize the importance of the work: People are unlikely to go for free rides when they believe that the tasks that they are performing are vital to the organization. To help this I would explain to my team members the nature of contribution of work they need to do towards the team project.
- Making the team member’s identifiable: Social loafing occurs when people feels that they can get away by taking it easy, under conditions in which each individual’s contribution cannot be determined. It can only be overcome when one’s contribution to an additive task are identifiable. It is that potential loafers are unlikely to loaf if they have the fear of getting caught.
- Rewarding individuals for the contribution to their team’s performance: The employee must be given with a bonus or some sort of recognition when they succeed in their task. In such situations, each member would benefit from the team success which encourages the individuals to contribute for their team’s performance. In our team, we appreciate the good work done by each team member in an attempt to motivate each other.
- Reduced Group size: It will be very easy to track the performance of the individuals in a small group where as in large groups judging of the individuals cannot be done. The members of a team will be cautious about the responsibility when they are in a small group. Our group stated as a small team of 4 which was ideal to manage without issues.
“Motivation refers to the forces within a person that affect the direction, intensity, and persistence of voluntary behavior” (McShane and Von Glinow, 2015, p. 124). It is one of the several determinants of job performances but not equivalent. People are motivated with the work ethics as they seek interesting and challenging jobs. Managers are the key peoples to motivate the team to reach the organizational goals.
Ways of motivating a team:
- MASLOW’s Theory of Motivation: Maslow’s needs hierarch theory Developed by psychologist Abraham Maslow in the 1940s, the model (Appendix A- Figure 3). condenses and integrates the long list of drives and needs that had been previously studied into a hierarchy of five basic categories (from lowest to highest): physiological (need for food, air, water, shelter, etc.), safety (need for security and stability), belongingness/love (need for interaction with and affection from others), esteem (need for self-esteem and social esteem/status), and self-actualization (need for self-fulfillment, realization of one’s potential) (McShane and Von Glinow, 2015, p. 127). Maslow suggested that we are motivated simultaneously by several primary needs (drives), but the strongest source of motivation is the lowest unsatisfied need at the time. As the person satisfies a lower-level need, the next higher need in the hierarchy becomes the primary motivator and remains so even if never satisfied.
We adopted some of the techniques that come under the different categories of the theory to motivate the team members.
Physiological Needs
- Provide input for employee salaries and bonuses.
Safety Needs
- Ensure the correct tools for the job are available.
- Create an environment where individuals are comfortable challenging requests that are dangerous.
Social Needs
- Schedule weekly project team meetings. (Adopted)
- Get the team together to celebrate project milestones. (Adopted)
Esteem Needs
- Recognize team members for excellent contributions to the project. (Adopted)
- Ensure each team member understands how important they are to the project. (Adopted)
Self-Actualization Needs
- Consider each team member’s tasks goals when assigning tasks. (Adopted)
- Empower team members so that they can develop and grow. (Adopted)
- EQUITY Theory of Motivation: Equity theory (Appendix A- Figure 4) claims that people desire to attain an equitable balance between the ratios of their outcomes and inputs and the corresponding ratios of comparison to other (Jerald Greenberg, 2011, p. 224). Inequitable states of overpayment inequity and underpayment inequity are undesirable, motivating people to try to attain equitable conditions. Responses to inequity may be either behavioral like raising or lowering one’s performance or thinking differently about work contribution, a psychological way. To avoid negative reaction such as strikes, reduced work, resignation overpayment and underpayment inequity must be avoided.
In our team, we made sure that the tasks were equally allocated or distributed so that no one team member is overwhelmed with their assigned tasks.
- Employee engagement: It is described as an emotional involvement in, commitment to, and satisfaction with work (McShane and Von Glinow, 2015, p.124).
In our team after assigning the tasks we made sure that members were in agreement with their assignments so that they have 100% involvement, committed and enjoyed working on their assignments/ tasks.
- EXPECTANCY Theory of Motivation: A motivation theory based on the ideas that work effort is directed toward behaviors that people believe will lead to desired outcomes (McShane and Von Glinow, 2015, P.133).
Three components of expectancy theory are:
- Effort-to-Performance expectancy:Â It is one’s belief that his or he effort towards the task will result in a particular level of performance.
- Performance-to-Outcome expectancy: This theory is based on the principle that a particular result will be obtained if one displays a specific behavior or performance level.
- Outcome valences: valence is the expected or desired satisfaction or dissatisfaction an individual feel towards the results.
Personality can be defined as the outline of thoughts, emotions and behaviors that characterize a person along with the psychological process associated with those characteristics. Personality have five dimensions which comes under Five-Factor Model (FFM) and they are (CANOE) Conscientiousness, Agreeableness, Neuroticism, Openness to experience and Extraversion (Appendix A- Figure 1).
- Conscientiousness: It is the predisposition of an individual or a person to do what is right, especially to do one’s duty well and thoroughly.
- Agreeableness: Nature of an individual to be compassionate towards others.
- Neuroticism: It is the tendency of an individual to experience unpleasant emotions such as anxiety, anger, envy, guilt etc. easily.
- Openness to experience: The tendency of an individual to enjoy new ideas and experiences.
- Extraversion: It is the characteristics of an individual to seek recreation and to enjoy he company of other people.
Following table was used to assess the personality of myself and my team members. Used a scaling factor of 1 through 5 (1-Strongly disagree, 2-Disagree, 3-Neutral, 4-Agree, 5-Strongly agree) to gauge the personality of each team member using Five-Factor Model.
|
FFM |
Madison Rase |
Duo Wang |
Vineesh Nambiar |
Zui Tao (Chris) |
|
Conscientiousness |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
Agreeableness |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
Neuroticism |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
Openness to Experience |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
|
Extraversion |
5 |
5 |
5 |
5 |
Except for neuroticism all members scored high on the other factors in Five Factor Model (FFM).
Job performance can be measured in employee evaluation. This provides the evaluation regarding the employer’s quality in their work. In order to determine an employee’s skill set is appropriately matched to the employee’s job it is important to conduct or perform employee evaluations. The four reasons why assessments are important are:
- Employee Training and Development: Strength and weakness are the first step steps for evaluating the type of training the employee needs. An evaluation helps understand the type of development programs required to benefit employee and eventually the employer.
- Employee Performance Goal: Evaluation stipulates the performances standards against the job. Or in other words it is the expected level of performance of job duties of an employee. Performances can be evaluated on a periodic basis as determined by the leadership of the organization.
- Conflict Management Among Employees: Conflicts arise from the differences in personalities. A personality assessment will help evaluating the root cause for conflicts which needs to be corrected so that the team can perform well.
- Employee Reward and Recognition: Most organization compensation structure is based on performance measurement through employee evaluations. It gives the upper leadership of an organization to recognize employees’ hard work, dedication and commitment.
Perception (Appendix A- Figure 5). can be defined as “the process of receiving information about, and making sense of, the world around us” (McShane and Von Glinow, 2015, p. 72). The process begins with the stimuli received through our senses of which some are retained and most screened out after bombarding with our senses. The retained information then gets organized and interpreted. So the process of only attending to some information while ignoring the other is called selective attention and is greatly influenced by the characteristic of the person or object being perceived. Additionally, the characteristics of the perceiver also influence selective attention. So, this can lead to different problems within an organization or team one of which is called confirmation bias. The process of readily accepting confirming information and screening out that are contrary to our values and assumptions is called Confirmation bias.
Below are some of the perception related issues an organization or a manager should consider when dealing with team members.
- Minimization of Stereotyping:Â stereotyping is something that is existent in all organizations and teams. People engage in stereotyping because it is a natural and mostly nonconscious process. Stereotyping lays the foundation for discriminatory attitudes and behavior. It can be minimized by providing appropriate trainings to team members and by efforts from managers in educating them.
- Minimization of Attribution Errors: It is the tendency of an individual to explain someone’s behavior based on the internal factors such as personality or disposition and intern underestimate the influence of external factors have on another person’s behavior. One of the major causes for the conflicts between the teams is when attribution error exists so, manager or upper leadership make efforts to cultivate good understanding within the team member thus, reducing conflicts.
- Creating Self-Fulfilling Prophecies: A self-fulfilling prophecies is a prediction that directly or indirectly causes itself to become true as a result of the positive feedback between belief and behavior or in other words it is a belief that comes true because we are acting as if it is already true. For example, if one believes that his or her project is strong and feel confident about it the person will most likely write a strong confident letter. This faith in the project and oneself will also serve well when it comes to for example, marketing the project. So, promoting self-fulfilling prophesies will lead to team success.
- Minimizing Halo Effect: it is a tendency for an impression created in one area to influence opinion in other area. In an organization halo effect occurs when a supervisor gives an employee a rating in all areas of performances based on a general impression of that person. Is also has an impact on employees sees themselves. They tend to develop their own insights about their performances and the company’s overall performances based on the management feedback. Halo effect can be reduced by developing a training plan to build the capacity of the managers along with including information on how evaluations can be done more accurately.
An Individualism can be defined as a value described to a degree in which the people with a culture emphasize personal uniqueness and independence. Where when it comes for a group with a harmony it becomes collectivisms. Power Distance is the value describing the degree by which people in a culture who accepts power in the society which is unequal.
U.A.E from Asia and Germany from Europe where the countries where selected for evaluating Individualism/collectivism and Power distance.
|
VALUE |
SAMPLE COUNTRY |
ANALYSIS |
|
Individualism/Collectivism |
High: Germany Low: United Arab Emirates |
In Germany, small families with a focus on the parent-children relationship rather than aunts and uncles are most common. There is a strong belief in the ideal of self-actualization. Loyalty is based on personal preferences for people as well as a sense of duty and responsibility. United Arab Emirates scored a low for individualism/collectivism. Loyalty in a collectivist culture is dominant, and supersedes most other societal rules and regulations. The society fosters strong relationships where everyone takes responsibility for fellow members of their group. In collectivist societies offence leads to shame and loss of face, employer/employee relationships are perceived in moral terms (like a family link), hiring and promotion decisions take account of the employee’s in-group, management is the management of groups. |
|
Power Distance |
High: United Arab Emirates Low: Germany |
In United Arab Emirates people accept a hierarchical order in which everybody has a place and which needs no further justification. Hierarchy in an organization is seen as reflecting inherent inequalities, centralization is popular, subordinates expect to be told what to do and the ideal boss is a benevolent autocrat Germany is highly decentralized and supported by a strong middle class. Co-determination rights are comparatively extensive and hence have to be taken into account by the management. A direct and participative communication and meeting style is common, control is disliked and leadership is challenged to show expertise and best accepted when it’s based on it. |
 From Vince Lombardi’s quote “Individual commitment to a group effort–that is what makes a team work, a company work, a society work, a civilization work”. It was a great experience working with the team and we did not find much difficulty in completing the work together. We did follow the basic guidelines upon the team cohesion, personality, controlling social loafing and perception. We put conscious efforts to control any conflicts by establishing a good leadership in the team and also built a team culture among us. Adopting these strategies would eventually lead to a good team and will contribute to a successful organization.
McShane, S. L., & Von Glinow, M. A. Y. (2015). Organizational behavior. New York: Irwin/McGraw-Hill
Greenberg, Jerald. Behaviour in Organization. Tenth ed. New Jersey: Pearson Education, 2011.
Plant, L. (2012). Motivation and feedback influencing change in the goal-setting process (Order No. MR84417). Available from ProQuest Business Collection. (1115315275). Retrieved from https://0-search.proquest.com.library.svsu.edu/docview/1115315275?accountid=960
Lee, S. (1998). The relationship of personality type to self-perceived and faculty-perceived managerial effectiveness among college and university sport/physical education administrators in the republic of korea (Order No. 9820638). Available from ProQuest Business Collection. (304482798). Retrieved from https://0-search.proquest.com.library.svsu.edu/docview/304482798?accountid=960
Townsend, W. (2013). INNOVATION AND THE PERCEPTION OF RISK IN THE PUBLIC SECTOR. International Journal of Organizational Innovation (Online), 5(3), 21-34. Retrieved from https://0-search.proquest.com.library.svsu.edu/docview/1419395542?accountid=960
Alonso, A. (2003). The attribution of motives to organizational citizenship behaviors: The influence of personality, gender and ethnicity (Order No. 3085811). Available from Psychology Database. (305233252). Retrieved from https://0-search.proquest.com.library.svsu.edu/docview/305233252?accountid=960
Yu, C. (2005). An I -P -O model of team goal, leader goal orientation, team cohesiveness, and team effectiveness (Order No. 3202366). Available from ProQuest Business Collection. (305360282). Retrieved from https://0-search.proquest.com.library.svsu.edu/docview/305360282?accountid=960
Suleiman, J., & Watson, R. T. (2008). Social loafing in technology-supported teams. Computer Supported Cooperative Work (CSCW), 17(4), 291-309. Retrieved from https://0-search.proquest.com.library.svsu.edu/docview/622218484?accountid=960
Mortenson, S. T. (2002). Sex, communication values, and cultural values: Individualism-collectivism as a mediator of sex differences in communication values in two cultures. Communication Reports, 15(1), 57-70. Retrieved from https://0-search.proquest.com.library.svsu.edu/docview/203808136?accountid=960
APPENDIX A: DIAGRAMS
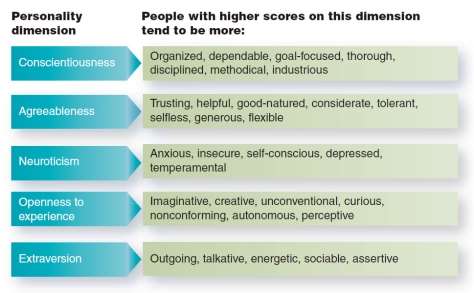
Figure 1. CANOE
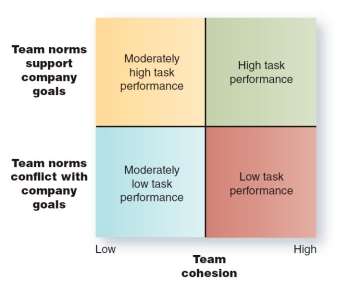
Figure 2. TEAM COHESION
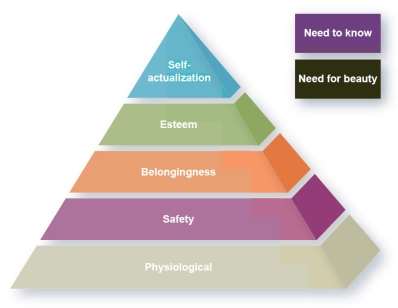
Figure 3. MASLOW THEORY OF MOTIVATION
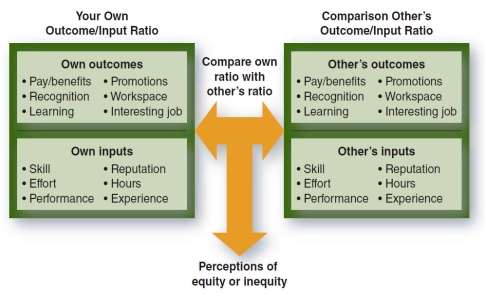
Figure 4. EQUITY THEORY OF MOTIVATION
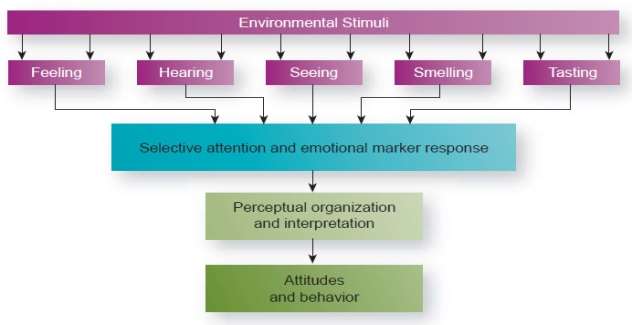
Figure 5. PRECEPTION