Passive Reconnaissance Website Analysis
Assignment: – Reconnaissance Paper
Student Name: – Soumil Deshpande
- Executive Summary
In this assignment, passive reconnaissance was performed on The Weather Channel’s website i.e. www.weather.com and important results have been obtained regarding the organizations online behavior. In this passive reconnaissance attack we have discovered all the domain name and the corresponding IP addresses of the hosts, domain names, servers, reverse DNS, the webhost name and the location of the server. Furthermore, we have also discovered and analyzed many files such as .doc, .pdf, .xls from online public sources which in return gave us valuable information about the organization such as the username of few employees who have created those files, the software that was used to create those files, date of creation, date of edit, what server it was uploaded to, the operating system in use etc. It also provided us with the folder paths where the files were preset on the host servers. This information is very valuable to an attacker who is performing a reconnaissance attack as it gives out a lot of critical information about the internet footprint of the organization and this data was easily available to the attacker via all public sources using passive reconnaissance. To avoid this, we must make sure that we keep a track of all the public information which is readily available on the internet such as DNS lookups, WHOIS information and all the public files hosted and make sure that no valuable information can be extracted by an attacker which in turn could prove harmful for the organization if an attack was conducted on the organization in the future.
- Introduction to the organization
The Weather Channel is an American cable and satellite television channel by NBC Universal. It is also a desktop, mobile app and satellite radio channel. Headquarters of the company is located in Atlanta, Georgia. This organization mainly provides weather related news and analysis which include 24-hour weather forecast and radar imagery.
This company was chosen by me for this assignment because this company has a global presence and a very well wide spread and retrievable online footprint. It has servers all around the world which would give me many different points of opportunities for reconnaissance. And as their main function is far away from security I would assume that not a very high level of resources is spent on information security of all the online assists, domains, hosts and websites.
- Tools and Methods used to obtain data for passive reconnaissance
Following are the tools used for conducting passive reconnaissance with the explanation of their working: –
- FOCA (Fingerprint Organizations with Collected Archives) (FOCA n.d.)
FOCA is an easy to use GUI tool made for windows whose main purpose is to extract metadata from the given website. FOCA automates the process of finding and downloading all the public documents of various format from the website, analyzing them and presenting the analyzed information in a human readable format on the FOCA windows GUI.
The documents which are downloaded from the organizations website are searched by various methods including search engines like Google, Bing, Exalead etc.
We can also add local files which we have acquired from other processes in the FOCA GUI for analysis and metadata extraction. An impressive feature of FOCA is that we can analyze the URL and the file without even downloading it.
FOCA is capable of downloading and analyzing various types of documents ranging from Microsoft Office files to uncommon adobe files or other custom formats.
After all the metadata is extracted from the files, FOCA matches similar information like documents created by the same group, Usernames of the owners of the documents and can even create a network map based on the metadata that was analyzed from all the public sources available on the internet.
FOCA also includes a server discovery mode which automatically searches for the organization servers using recursively interconnected routines.
Techniques such as Web Search, DNS Search, IP resolution, PTR Scanning, Bing IP, Common Names, DNS Prediction and Robtex are used in the process of server discovery in FOCA.
Other features of FOCA include Network Analysis, DNS Spoofing, Search for common files, Proxies search, Technology identification, Fingerprinting, Leaks, Backups search, Error forcing and open directory searches.
- Google Search (Search engines reconnaissance – The magic weapons n.d.)
Search tools are very powerful weapons for an attacker for conducting passive reconnaissance on an organization.
Using Google search as a reconnaissance tools is 100% legal and this process does not involve accessing unauthorized data or files.
Reconnaissance using google is done by using special search queries which are constructed by search modifiers and search operators.
Search modifiers are symbols such as + (Requires to match the term exactly), – (Show all results excluding that match this term), * (Wildcard entry) and “” (Searching for a specific text, word or a phrase).
Search operator includes keywords in the search queries such as:
- Allintext Restricts search to contain all the query terms which you have specified.
- Allintitle Restricts search to contain all the titles which have the specified text
- Allinurl Restricts search to contain all the url specified.
- Filetype Returns the search results which have a file which is specified by the user. For e.g. [document filetype:doc] will return all the documents with the file extension of .doc.
- Site Google will restrict the search to the particular site or domain.
Using the above search modifiers and operators we can construct a special query. For e.g. we can construct a query to get all the doc files from www.example.com as “site:www.example.com filetype:doc”.
From google search alone we can obtain important information like Staff lists and positions, Contact information, Technical skill, helpdesk FAQ’s, Security policies etc.
- DNSDumpster.com
- DNSDumpster is an online service that enables us to scan a particular website to return valuable information like all the DNS records of the website, all the hosts, domains, IP’s, location and reverse DNS addresses.
- It also gives a graphical representation of the network map of the organization by the previously described data.
- We can even export all this information from the website to an excel spreadsheet to further analyze the data.
- WHOIS and TRACEROUTE
WHOIS is a query and response protocol used to retrieve internet resources like domain names, IP address, owner information, webhost contact information etc.
Traceroute is a windows command which records the route through the web space or the internet from your computer to the destination address.
- PassiveRecon Mozilla Add-on (PassiveRecon n.d.)
This very powerful Mozilla add-on combines various passive reconnaissance tools such as IP tracing, WHOIS, google search queries etc. into one single add-on which can use to perform a passive reconnaissance attack with a click of a button.
- Recon-ng (recon-ng n.d.)
Recon-ng is a powerful tool made by the programmer LaNMaSteR53 which is a full-featured web based reconnaissance framework which is written in python.
There is an inbuild module known as “reconnaissance” which is used for conducting all the passive reconnaissance on the website or web server.
It gathers data such as IP information, domain names, hosts, location, related domains and other valuable information about the organization.
It is a Linux tools and works with most of the new Linux distributions such as kali or Ubuntu.
- SamSpade (SamSpade n.d.)
SamSpade is a windows tools which is famously used for passive reconnaissance.
This tools is used to query important functions such as Zone transfer, SMTP relay check, Scan Addresses, Crawl Website, Browse Web, Fast and slow traceroutes, decode URL, parse email headers etc.
- NetCraft (netcraft n.d.)
NetCraft is a United Kingdom based company which tracks almost all websites.
Using this tool, we can obtain all the domains, site report with information like registrar information, location, DNS admin email address, hosting company, netblock owner etc.
It also enables us to look at the hosting history with the name and version of the webserver and display what web technologies have been used on the website.
- Information found after reconnaissance
- DNS Hosts
- By using various reconnaissance tools ass mentioned above, we have gathered over 100 DNS hostnames for the website weather.com with additional information like IP addresses, reverse DNS, Netblock owner, country and webserver.
- The entire table of the gathered information is listed at the bottom of this document in a segregated tabular format for easy understanding.
- A network map has also been created from the above gathered DNS information and has been listed at the end of this document as well.
- We have also obtained the technologies used on the client side of the weather.com website. These technologies include jQuery, Google Hosted libraries, AJAX, Angular JS and Modernizr.
- Extracted Files and Metadata
- Using FOCA as well as google search queries, files were downloaded and analyzed from the weather.com server and host to reveal information about the organization like System Users, System paths, Software used and Clients connected to the server.
- Following are the list of user information which has been extracted from the metadata of the files gathered.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
- Following are the list of software used to create, modify these files or used in the organization in general.
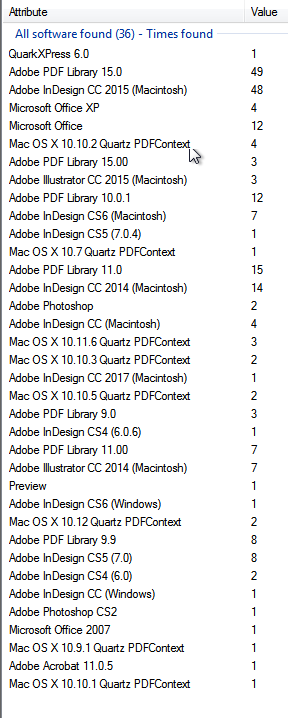
- This data was extracted from over 159 documents which were gathered using FOCA and google search tools.
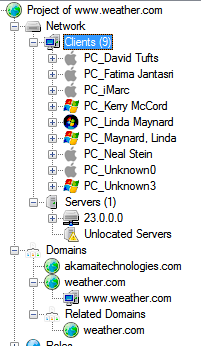
- Following are the Clients, Servers and Domains of weather.com gathered from server searching and analyzing file metadata.
- How the gathered information can be used by the attacker.
The above-mentioned information although publicly available is very useful for an attacker to orchestrate an attack on the website.
With all the information, such as DNS hostname, IP address, Reverse DNS, Hosting server etc. the attacker can further use active reconnaissance techniques on them to gather even more valuable information like the traffic on a particular server, capacity of a particular server, insecure protocols on the domain, SQL injection into form fields, DDoS attack on a particular sever etc.
By recognizing a weak link in the network architecture of the organization, an attacker can find a way to enter into locations which was hidden from the public. By doing this the attacker can gain access to much more valuable information and further construct a stronger attack.
With all the DNS address, available, the attacker can run an active penetration test on these webserver and IP addresses to find out different vulnerabilities which can be exploited in the future.
Serves with a large amount of network loads can be DDoSed to crash the organization website.
User information was also gathered in this passive reconnaissance process which can be used to gain more knowledge about the people working in the organization and can be used for various social engineering attacks.
These particular users can be targeted by email which could in turn compromise the systems they are in charge of.
We now also know the software used in the organization and their version number.
We can find out the vulnerabilities on that particular software and use that with social engineering to exploit a target system on the organization.
By using all the information gathered by this passive reconnaissance process, the attacker is exposed to a lot of avenues on which he can further dive deep into using active reconnaissance or penetration testing methods.
- Suggested Controls
We have to keep in mind that it is essential for a business to release public documents online.
Thus, we have to make sure that these public documents do not give out any valuable information in the form of metadata or even the actual content of the document.
These documents should be analyzed internally by the information security team before uploading them to the public website.
We can even use a tool to locally extract and remove all the metadata from the file before we upload them to the website.
We must also take active actions to harden the perimeter of our network.
We must understand the devices that run on our network and update them with up to date security patches and releases.
We should only release vague and general information to the public regarding domain names and registrar information.
We should also disable and remove all those devices, web servers, users, accounts, domains which are not in use.
We should also conduct penetration testing on our web servers and web sites periodically to further harden our network.
We should also use NAT for as much of the network as possible. This helps to block OS fingerprinting and port scanning issues which are the main part of the active reconnaissance techniques.
We should add a stateful firewall on the network perimeter to prevent any intrusion.
We should also have a IDPS system to monitor the traffic on each web server and log the actions or report the actions.
- Tables and Diagrams
- DNS hostnames, IP addresses, Reverse DNS of weather.com
|
Hostname |
IP Address |
Reverse DNS |
|
dmz.weather.com |
65.212.71.220 |
|
|
dmz.weather.com |
65.212.71.221 |
|
|
weather.com |
23.218.138.47 |
a23-218-138-47.deploy.static.akamaitechnologies.com |
|
adcap0x00.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.199 |
adcap0x00.twc.weather.com |
|
adcap0x01.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.198 |
adcap0x01.twc.weather.com |
|
adserver-es1.weather.com |
96.8.82.170 |
adserver.es1.dc.weather.com |
|
adserver-es2.weather.com |
96.8.83.170 |
adserver.es2.dc.weather.com |
|
adserver-tc1.weather.com |
96.8.84.170 |
adserver.twc1.dc.weather.com |
|
adserver-tc2.weather.com |
96.8.85.170 |
adserver.twc2.dc.weather.com |
|
ash-dc2-named-1.weather.com |
96.8.90.1 |
ash-dc2-named-1.weather.com |
|
attpos.weather.com |
96.8.82.142 |
attpos.weather.com |
|
attpos.weather.com |
96.8.84.142 |
attpos.weather.com |
|
auth.twc1.dc.weather.com |
96.8.84.137 |
auth.twc1.dc.weather.com |
|
b.twc1.dc.weather.com |
96.8.84.144 |
b.twc1.dc.weather.com |
|
b.twc2.dc.weather.com |
96.8.85.144 |
b.twc2.dc.weather.com |
|
backupmediadmz.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.95 |
backupmediadmz.twc.weather.com |
|
betaorigin.weather.com |
96.8.84.147 |
betaorigin.weather.com |
|
betatest2.weather.com |
96.8.85.103 |
betatest2.weather.com |
|
blogs.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.97 |
blogs.twc.weather.com |
|
builddata.weather.com |
96.8.82.54 |
builddata.weather.com |
|
buildds.weather.com |
96.8.82.49 |
builddds.weather.com |
|
buildmap.weather.com |
96.8.82.56 |
buildmap.weather.com |
|
buildmob.weather.com |
96.8.82.50 |
buildmob.weather.com |
|
buildmob2.weather.com |
96.8.82.51 |
buildmob2.weather.com |
|
buildorigin.weather.com |
96.8.82.53 |
buildorigin.weather.com |
|
buildurs.weather.com |
96.8.82.52 |
buildurs.weather.com |
|
buildweb.weather.com |
96.8.82.46 |
buildweb.weather.com |
|
buildweb2.weather.com |
96.8.82.47 |
buildweb2.weather.com |
|
buildwxii.weather.com |
96.8.82.48 |
buildwxii.weather.com |
|
cacheds.twc1.dc.weather.com |
96.8.84.141 |
cacheds.twc1.dc.weather.com |
|
cacheds.twc2.dc.weather.com |
96.8.85.141 |
cacheds.twc2.dc.weather.com |
|
clustsrv1.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.115 |
clustsrv1.twc.weather.com |
|
clustsrv2.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.116 |
clustsrv2.twc.weather.com |
|
clustsrv3.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.117 |
clustsrv3.twc.weather.com |
|
clustsrv4.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.121 |
clustsrv4.twc.weather.com |
|
clustsrv5.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.122 |
clustsrv5.twc.weather.com |
|
connect.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.136 |
connect.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzdc02.dmz.weather.com |
65.212.71.223 |
dmzdc02.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzdc02.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.223 |
dmzdc02.twc.weather.com |
|
dmz.weather.com |
65.212.71.223 |
dmzdc02.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzdc03.dmz.weather.com |
65.212.71.222 |
dmzdc03.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzdc03.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.222 |
dmzdc03.twc.weather.com |
|
dmz.weather.com |
65.212.71.222 |
dmzdc03.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzswitch10.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.10 |
dmzswitch10.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzswitch11.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.11 |
dmzswitch11.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzswitch12.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.12 |
dmzswitch12.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzswitch13.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.13 |
dmzswitch13.twc.weather.com |
|
dmzswitch14.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.14 |
dmzswitch14.twc.weather.com |
|
dns1.weather.com |
96.8.82.15 |
dns2.weather.com |
|
dns2.weather.com |
96.8.82.15 |
dns2.weather.com |
|
dns3.weather.com |
96.8.84.15 |
dns3.weather.com |
|
dsp-db.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.119 |
dsp-db.twc.weather.com |
|
dsq-db.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.99 |
dsq-db.twc.weather.com |
|
dualg.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.100 |
dualg.twc.weather.com |
|
articles.weather.com |
52.200.156.65 |
ec2-52-200-156-65.compute-1.amazonaws.com |
|
chef.dev.web.weather.com |
54.208.182.48 |
ec2-54-208-182-48.compute-1.amazonaws.com |
|
apistatus.weather.com |
54.236.78.100 |
ec2-54-236-78-100.compute-1.amazonaws.com |
|
checkout.developer.weather.com |
54.69.68.23 |
ec2-54-69-68-23.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com |
|
f5.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.140 |
f5.twc.weather.com |
|
f5lab.dmz.weather.com |
65.212.71.66 |
f5lab.dmz.weather.com |
|
f5vpn-lab.dmz.weather.com |
65.212.71.65 |
f5vpn-lab.dmz.weather.com |
|
faspex0b00.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.48 |
faspex0b00.twc.weather.com |
|
faspex0b01.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.49 |
faspex0b01.twc.weather.com |
|
ftp.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.113 |
ftp.twc.weather.com |
|
ftp1.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.108 |
ftp1.twc.weather.com |
|
ftp2.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.109 |
ftp2.twc.weather.com |
|
giporigin.twc1.dc.weather.com |
96.8.84.166 |
giporigin.twc1.dc.weather.com |
|
giporigin.twc2.dc.weather.com |
96.8.85.166 |
giporigin.twc2.dc.weather.com |
|
gwdmz.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.1 |
gwdmz.twc.weather.com |
|
hide135.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.135 |
hide135.twc.weather.com |
|
hide136.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.136 |
hide136.twc.weather.com |
|
hide139.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.139 |
hide139.twc.weather.com |
|
hide166.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.166 |
hide166.twc.weather.com |
|
hide167.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.167 |
hide167.twc.weather.com |
|
hide19.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.19 |
hide19.twc.weather.com |
|
hide20.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.20 |
hide20.twc.weather.com |
|
hide206.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.206 |
hide206.twc.weather.com |
|
hide207.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.207 |
hide207.twc.weather.com |
|
hide208.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.208 |
hide208.twc.weather.com |
|
hide209.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.209 |
hide209.twc.weather.com |
|
hide21.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.21 |
hide21.twc.weather.com |
|
hide22.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.22 |
hide22.twc.weather.com |
|
hide23.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.23 |
hide23.twc.weather.com |
|
hide24.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.24 |
hide24.twc.weather.com |
|
hide25.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.25 |
hide25.twc.weather.com |
|
hide250.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.250 |
hide250.twc.weather.com |
|
hide26.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.26 |
hide26.twc.weather.com |
|
hide27.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.27 |
hide27.twc.weather.com |
|
hide28.twc.weather.com |
96.8.88.28 |
hide28.twc.weather.com |
|
hide29.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.29 |
hide29.twc.weather.com |
|
hide30.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.30 |
hide30.twc.weather.com |
|
hide31.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.31 |
hide31.twc.weather.com |
|
hide35.twc.weather.com |
65.202.103.35 |
hide35.twc.weather.com |
|
iasq-app.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.98 |
iasq-app.twc.weather.com |
|
ibp-db.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.118 |
ibp-db.twc.weather.com |
|
imwxsecure.twc1.dc.weather.com |
96.8.84.159 |
imwxsecure.twc1.dc.weather.com |
|
imwxsecure.twc2.dc.weather.com |
96.8.85.159 |
imwxsecure.twc2.dc.weather.com |
|
careers.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.129 |
przrecruit01.dmz.weather.com |
|
bes.twc.weather.com |
65.212.71.224 |
przsccmdp01.dmz.weather.com |
|
grid.weather.com |
54.231.49.82 |
s3-website-us-east-1.amazonaws.com |
- Network Map for weather.com
n.d. FOCA. https://www.elevenpaths.com/labstools/foca/index.html.
n.d. netcraft. https://www.netcraft.com/.
n.d. PassiveRecon. https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/passiverecon/.
n.d. recon-ng. https://bitbucket.org/LaNMaSteR53/recon-ng.
n.d. SamSpade. https://www.sans.org/reading-room/whitepapers/tools/sam-spade-934.
n.d. Search engines reconnaissance – The magic weapons. http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/19570/hacking/search-engines-reconnaissance-magic-weapons.html.