Plan for Outsourcing Payroll
This report is aimed at the MD and all stakeholders referencing a proposal for a research project in relation to payroll being outsourced or to bring in house for B & W Plant Hire and Sales Ltd
- A description of the project under research, analysis of good practice in relation to this issue.
- The identification of key stakeholders.
- Why the stakeholders would be interested or effected by the study.
- The key sources from the secondary research
- The evaluation of the contribution to the study
- To outline the present findings and inform the stakeholders to act on the results
Overview of this research
In 2005 there was only 35 people on the payroll, as the company has grown over the years there are now 75 employees, the payroll is outsourced to a local company at a cost of £4500.00 per annum.
In 2010 it was decided to outsource the payroll to save time and money, as there was only one person qualified in payroll. To take the responsibility from the only one person qualified it was decided any person in the accounts office could gather the weekly hours from depot and email to the outsource company. When the reports came back it was checked against the information sent. The correct reports were returned and processed by the office manager. The cost was lower than the company was paying for in house payroll. The software cost was £1500.00 per annum, the time it took was 2 hours, so it was decided by the MD and the accountants to outsource payroll.
In 2014 the payroll was moved to a different outsource at a cheaper rate, as the payroll has grown the cost is now £5600.00 and growing.
The administration of the payroll has become difficult to manage collating the average holiday pay by spreadsheet of the growing number of employees along with the pension information. Correct information is not communicated correctly i.e. national minimum wage increase, apprenticeship wage P32 reports not being sent to the company on time, basically a lack of communication.
To start the process of developing a business case to recommend whether to outsource or bring payroll back in house the researcher will conduct a situational analysis to collect information the current system in use, how it works, any overlaps or shortfalls will be noted. When this is completed the investigation of the product ranges and functions available within the budget settings can this begin.
The research of the investigation will perceive the benefits and gain evidence of the potential benefits to the company along with the potential costs and show the realistic advantages of outsourcing or in house payroll.
There are 4 depots within the company, each depot has a clocking in machine. All weekly paid employees are to clocking and out each day. If an employee goes to a job from home they are to inform the depot manager and have their clock card signed, this is also checked by the tracker information on the vehicle. (It logs the time the vehicle was started)
Every Monday morning each depot scans a copy of the clock cards to the Office Manager.
As the depot managers, do not check the clock cards for anomalies it falls back on the Office manager to find the relevant information to complete the spreadsheet (appendix 1)
As the spreadsheet is keyed it is prone to human error, the depot managers now must add the hours on the clock cards and sign them, they are then checked again by the office manager who then keys them into the spreadsheet. It is again checked by the finance manager. When all the above is complete it is then forwarded to the outsource company by email to collate. Manual tracking in this way is time consuming and prone to human error, resulting in over pay or underpay and time theft.
There are deadlines to meet for the weekly payroll, if the correct information is not sent through, there is an element of pressure on the administrator to request the information on time.
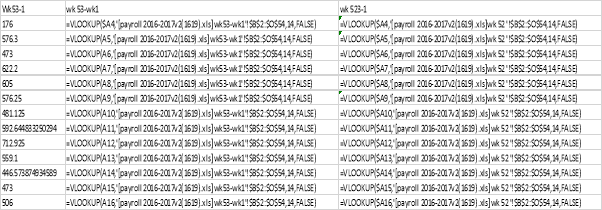
An image of the formulas used for recording the 12 week average
Good practice
Employee costs are the single greatest expense of most Companies. Payroll one of the most important business functions. Payroll is unusually complex. It must be accurate. It must be efficient. It must comply with all the regulations imposed on it at local, national, and international levels. Employee morale and retention is so critical, payroll must do these things while keeping employees satisfied that they will receive their wage with minimal disruption of their workdays. No one-size-fits-all payroll solution exists that solves the very real challenges of managing payroll in today’s fast-paced and highly regulated global environment.
Establish Discipline and Manage Expectations
Ensure that all stakeholders know what to expect from the payroll department. When do, timesheets need to be submitted? Who approves them? Who is notified if an employee goes on leave? When are the monies in the employee`s bank account.
Enforce Accountability
Make sure all stakeholders are appropriately accountable. Employees need to know what they are responsible for doing; managers likewise. For example, if an employee forgets to clock in the timecard at the beginning of the day, or clock out  at the end of the day, who is responsible for making sure that employee is paid equitably for their time? What are the consequences of failing to be accountable for meeting payroll’s requirements? Who absorbs the cost of having to cut a check in midcycle? Alongside this accountability must come transparency-all steps in the process must be visible to the payroll staff.
Perform Rigorous Balances and Audits
The demand for accuracy in payroll is rigorous. Balancing, auditing, and segregating of duties is critical. These steps are to ensure minimized error rates, this can also help avoid off-cycle payments.
There should be separate duties so the person entering timecard data is not the person who balances the number of timecards with the payments going out. (Due diligence) Then yet another person should audit the data to make sure it is correct. Rethink Control and Compliance in the Age of Outsourcing. Both the importance and complexity of payroll, many Companies are outsourcing either part or all the function.
How much-or how little-is outsourced varies tremendously from company to company. The issue is control: how much of it does company need over its payroll data? When payroll is done in-house, it’s easy to integrate the data into other systems, to slice and dice it different ways, and otherwise make it work to provide value to the business. Given that Employee costs are the single greatest expense of most companies, having this kind of flexibility can be enormously helpful when making decisions about labouring sourcing, for example, deciding where and when to open a new depot.
Advantages and disadvantages – appendix 2
The researcher should be aware or data protection issues surrounding the implementation of outsourcing payroll. The principles of the Data Protection 1998 Act concerning the processing of personal data, the key rights that the Data Protection Act gives to data subjects, the consequences for companies of breaching the Data Protection Act and the key issues that arise in outsourcing transactions because of the Data Protection Act’s requirements. The DPA gives comprehensive rights to data subjects in relation to their data. In relation to outsourcing transactions, the most important rights include:
- Access to personal data.
- Prevention of certain kinds of processing.
- By way of court order, rectification, blocking, deletion and destruction.
These rights are generally enforceable against the outsourcing company as data controller rather than against the data processor. Where the outsourcing provider handles personal data on its client’s behalf, the client as the data controller should include appropriate provisions in the outsourcing contract to ensure the outsourcing provider’s collaboration. This includes obligations to:
- Amend, transfer or delete the data as requested by the client.
Notify the client of data access requests or complaints that it receives in relation to the client’s data and provide the client with full co-operation in relation to such requests or complaints. The outsourcing company should also include an obligation on the data processor to be notified immediately if any of the following occur:
- Data gets accidentally deleted or corrupted.
- Data becomes lost.
- The outsourcing provider becomes aware that the data is processed unlawfully.
This is to ensure that the client can take the necessary steps to address the issue, including notification to the ICO and/or the data subjects if required. (Andrew Dunlop and Uwe Nimscheck, Burges Salmon LLP)
Stakeholder Analysis
The stakeholders are anyone with an interest in the business. Stakeholders are individuals, groups or organisations that are affected by the activity of the business. Consideration for powerful and supportive stakeholders i.e. Payroll, HR and Finance with high levels of interest must be updated on this project. If the project has a good team and consists of highly regarded and motivated people who enjoy change on board it can then by brought to the attention of other stakeholders with enthusiasm this is turn can overcome obstructions from individuals when engaging in research. This adds trust and the belief, into the smooth running of the project, a bonus for when asking for funding. For this research this is who is affected indirectly or directly.
They include:
Directors
Managers
Staff/Employee
Payroll
Finance
Shareholders
HMRC
The researcher should be aware of the drivers for the introduction of the payroll outsourcing/ in house process.
Operational Driver- cost effectiveness through time efficiency
Logical Driver – improved performance for demanding employees and managers.
Transform Driver- key strategic drivers addressed in the company – net profit
During the analysis, it is essential that the stakeholders are fully informed or involved and understand the current process and the impact of change it will have on their role.
The opportunities and threats for each stakeholder should be identified and managed during the process.
Do they need to be informed or are they involved – see appendix 3
The finance team are key stakeholders along with payroll and HR. finance need to be aware for budgeting and forecasting purposes and the costs involved evaluated correctly and if it is a viable project to implement. Payroll dept. will be collating the data regardless of payroll being outsourced or not, it must be carried out.
HR need to be involved for change management. They understand the importance of strategy, culture and values, this would be advantageous throughout the planning and implementation process.
The ethics must be considered when exchanging information especially when using emails, confidentially is a must, along with free and informed consent. Stakeholder should remain committed and not alienated from the project.
Methods of research
Literature defining Primary data
This date should be Qualitative and Quantative
For companies dealing with employees’ sensitive personal information for payroll purposes, whether internally or through a third party, it is essential to ensure the right processes and procedures are in place to safeguard the data. See appendix 4
Literature defining Secondary data
Secondary data is the data that have been already collected by and readily available from other sources. Such data are cheaper and more quickly obtainable than the primary data and may be available when primary data cannot be obtained at all. The credibility of the method and data must be accessed these factors have a direct influence on the accuracy of the data. The data collected for this research paper is (The International Journal of Human Resource Management, Vol. 24, No. 4, February 2013, 704-720). (Payroll and HR outsourcing, I.J.Maise march 2001). (Payroll Outsourcing: A New Paradigm. Princy Thomas and P K Thomas) CIPD factsheet on HR outsourcing 2016)
This is referenced at the bottom of the report
Meetings with the payroll administrator and the project leader and stakeholders are to be held to discuss the current situation and any issues or ideas for improvement. These meetings are important to establish different perspectives and build commitment to the project. Within these meetings, the researcher can interview the relevant people for their input on the project, this making qualative data.
Benchmarking similar size companies outsourcing payroll would also be benefitable.
The researcher should investigate the benefits following the implementation of outsourcing payroll before during and after.
The researcher should seek advice from providers for insight into current trends available updates and support with reports.
All information obtained should be equal and fair to make a fair comparison. Information on Return on investment should also be carried out. If the company chooses to outsource / bring in house this information is extremely important for signing off the project and setting scoring matrix for use when having structured interviews with the providers.
Present Findings
Different stakeholders will benefit from data being presented in different ways.
Directors need detailed reports with a full breakdown on the project including costs and anticipated outcomes.
The business case report should be presented as follows
Executive summary –
- The key reasons for doing the project
- The current service provision
- The key future requirements
- A summary of the full list of options
- A summary of the options selection procedure and the options chosen for detailed examination
- A summary of the comparative findings and justification for the preferred option
- Highlights of the Implementation Plan
- A statement to seek approval.
Analysis of requirements.
The Strategic Overview and Context-Provide an overview of the service or project, including strategic aims, policies and outcomes.
Project Objectives-State the policy objectives that the project is required to meet.
The Current Service Provision-Analyse the status and the issues with the current service.
Options selection and evaluation
Evaluation Criteria-State criteria for evaluating the benefits of the various options. Define these criteria in advance of identifying the options to avoid undue influence of the options.
Identifying Available Options-State the available options and describe how the various options were identified, what methodology was used and why some options were discarded early (if any).
Initial Evaluation and Consolidation-Explain how the shortlisted options were chosen and what options were shortlisted.
Detailed Options Analysis-Provide an overview of the evaluation methodology.
Benefits Evaluation-Quantitative as well as qualitative benefits for each option should be considered.
Cost Evaluation-Discuss the various costing elements that were evaluated. Details regarding the assumptions used and the outcome of the evaluation should be presented. Cost elements typically include the following:
Non-recurrent Costs-Describe the non-recurrent costs (or one off cost to establish the option) elements, including the transition cost, and the basis for deriving these costs.
Recurrent Costs-Provide a description of costs that will be incurred throughout the life of the project. These costs may either be fixed or variable.
Opportunity Cost- Opportunity cost is the cost of the next best foregone alternative to deliver a given option.
Whole of Life Costs-Describe and include costs that will be incurred over the life of the project to ensure that the assets originally procured can continue to be delivered to a level of service that provides the required outcomes. The whole of life costs may include activities such as replacement of assets, refurbishing or upgrading specific asset elements.
Strengths and Weaknesses Evaluation-Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the options considered.
Risk Analysis-Describe the process used for risk identification, risk quantification as well as key observations from this aspect. Detail any findings in a risk register.
Sensitivity Analysis-Discuss the findings of any sensitivity analysis carried out to determine how sensitive the outcome of the analysis is to variations in the assumptions.
Implementation planning
Describe how the chosen option will be delivered and rolled out and the various issues that must be considered.
Project Structure and Governance-Detail how the project will be managed and governed.
Governance-Describe the chosen governance structure for the project, include information on individuals or positions that are already identified.
Project Management-Describe the project management methodologies that will be used in delivering the project, including where available, a high level description of the organisational structure (could be graphical).
Implementation Detail-Detail the programme and transition arrangements.
Implementation Timing-Include a high-level implementation programme. This could cover single-stage or multi-stage delivery of the project. Present as a Gantt chart. – see appendix 8
Transition Planning-Describe the activities and temporary arrangements required during the transitional phase.
Constraints, Assumptions, Sourcing and Funding Requirements-Document identified constraints and the major assumptions made which affect the implementation.
Sourcing and Procurement Strategy-Describe the chosen sourcing models with reasons why they were chosen and how goods and services will be procured and tracked.
Funding Requirements-Describe what funding requirements are required, the timing, source and application/approval arrangements of the funds.
Approach to Manage Risk, Communications and Resources
Risk Management-Describe the risk management plan with detailed responsibilities and actions.
Communications Strategy-Describe the required communications strategy together with what to communicate, to whom and when.
Staff Resources-Detail what are the key issues, particularly from a human resources management point of view. This could include both staffing requirements for the project together with any impact caused by the project such as staff re-deployment or reductions/increases.
Technical Considerations
Describe any technical considerations, which could range from ICT requirements to general or specific engineering requirements.
Regulatory Impact Assessment / Business Impact Assessment-Any impact on any regulatory bodies or regulated or third party businesses which could be adversely or positively affected by the introduction of the project should be included.
Legislative Considerations-Detail any legislative aspects to the project that could require legislative changes or issue of new guidelines/codes of practice.
The Post Implementation Review Process
Explain how and when reviews will be carried out to check that the expected benefits have been realised and delivered. Also, describe how to track the benefits and report on them versus the original analysis.
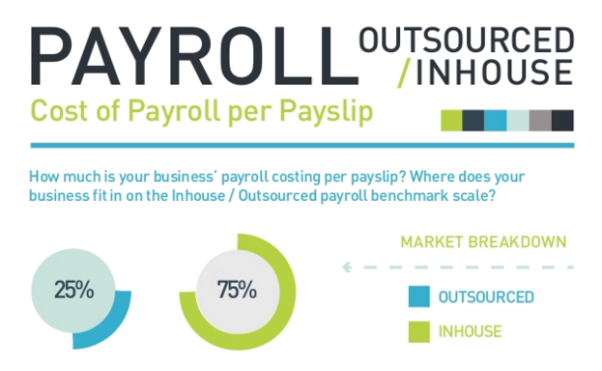
Within a company, Payroll is the main area outsourced – per Statistics – see appendix 5
“Large competition and challenging environment has forced companies to focus more on added value and revenue generating core business activities rather than the routine of regular HR practices i.e. payroll” most companies outsource payroll for various reasons according including reducing coat and controlling them”. according to (Princy Thomas and P K Thomas).
According to a study conducted in the US by PMR’s payroll outsourcing satisfaction survey, it was found that out of the 215 respondent companies, 119 companies outsource payroll processing to a third party for activities such as tax filing, human resources, time and attendance, benefits administration, workers’ compensation administration and unemployment compensation administration (PMR, 2003) (appendix 6)
“Large competition and challenging environment has forced companies to focus more on added value and revenue generating core business activities rather than the routine of regular HR practices i.e. payroll” most companies outsource payroll for various reasons according including reducing coat and controlling them. according to (Princy Thomas and P K Thomas).
Benchmarking
As per the office of national statistic, the government outsource the payroll
The following information has been provided in relation to Payroll;
- We use the Logica payroll system, provided by CGI IT UK Limited.
- At the last count, in January 2017, there were 3,967 employees supported on the above system.
- The contract value when last purchased was £840,000.
- The contract renewal date is 31/05/2022
- We do not provide individual employee contact names to preserve Commercial confidentiality. Please contact us at [email protected]
- Not applicable
16th Feb 2016 It’s official.
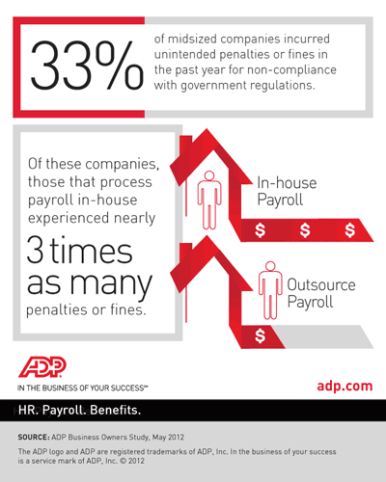
New Research on the outsourcing market 2016-2020 has revealed that payroll outsourcing is the fastest-growing segment of the global human resource outsourcing (HRO) market. The report from Infiniti Research see appendix 5 indicates that organisations are rapidly adopting payroll services to achieve cost reduction. The in-depth market analysis used inputs from industry experts and covers the market landscape and its growth prospects over the coming years, and findings revealed a growth in either an outsourced single process or the entire payroll service to enhance the existing function. Managing payroll in-house involves high costs. The research revealed that organisations that maintain an in-house team for tasks such as payroll, time and attendance, workforce administration, and benefits administration spend 20% more than organisations that outsource the same functions.(Global payroll outsourcing market 2016-2020 2016 by Infiniti Research)
Employee Confidentiality and Ethics Mellewigt et al. (2007) explained the importance of trust and its influence on outsourcing relationship. Protection of payroll information is very crucial. Strict internal control measures should be in place to prevent payroll confidentiality breaches, as it will have disastrous effects on any organization.
The business case reports accurately the information and informs how the company will function weather in house payroll or outsourced payroll. The information should provide consistent information to all audiences. The strategy to support the business objectives need to be highlighted along with the direct cost of savings benefit. Indirect benefits are often intangible this must be explained in the report, with the relevant case studies and reports to add credibility. I.e. payroll errors have an impact on the trust and morale of the employee by being under/ overpaid this can lead employees feeling less engaged and less motivated along with feeling undervalued. It can have an impact on the payroll administrator by increasing the pressure of mistrust.
Employees would benefit by receiving information in an informal way by having a presentation with their managers who would also distribute the newsletter with the information. The newsletter would contain the relevant information which effects the individual. The project manager would also be present at the presentation so as the employees can ask questions without feeling intimidated.
The Report for the finance team would consist of figures for cashflow purposes. The information would outline the initial costs, terms of payment, operating expenses, return on investment and budget. The information is to conduct an affordability assessment and prepare for budget and cashflow forecasts.
Payroll outsourcing is the fastest-growing segment of the global human resource outsourcing (HRO) market. Organizations are rapidly adopting payroll services to achieve cost reduction. They either outsource a single process or the entire services to enhance the existing function. Managing payroll in-house involves high costs. Organizations that maintain an in-house team for tasks such as payroll, time and attendance, workforce administration, and benefits administration spend 20% more than organizations that outsource the same functions.
The majority of payroll outsourcing functions are related to finance and accounting (F&A), human capital management (HCM), and shared service centers. The HR department uses outsourcing services more commonly than any other departments.
Technavio’s analysts forecast the global payroll outsourcing market to grow at a CAGR of 4.4% during the period 2016-2020.Payroll outsourcing is the fastest-growing segment of the global human resource outsourcing (HRO) market. Organizations are rapidly adopting payroll services to achieve cost reduction. They either outsource a single process or the entire services to enhance the existing function. Managing payroll in-house involves high costs. Organizations that maintain an in-house team for tasks such as payroll, time and attendance, workforce administration, and benefits administration spend 20% more than organizations that outsource the same functions.
The majority of payroll outsourcing functions are related to finance and accounting (F&A), human capital management (HCM), and shared service centers. The HR department uses outsourcing services more commonly than any other departments.
Technavio’s analysts forecast the global payroll outsourcing market to grow at a CAGR of 4.4% during the period 2016-2020.
Payroll outsourcing is the fastest-growing segment of the global human resource outsourcing (HRO) market. Organizations are rapidly adopting payroll services to achieve cost reduction. They either outsource a single process or the entire services to enhance the existing function. Managing payroll in-house involves high costs. Organizations that maintain an in-house team for tasks such as payroll, time and attendance, workforce administration, and benefits administration spend 20% more than organizations that outsource the same functions.
The majority of payroll outsourcing functions are related to finance and accounting (F&A), human capital management (HCM), and shared service centers. The HR department uses outsourcing services more commonly than any other departments.
Technavio’s analysts forecast the global payroll outsourcing market to grow at a CAGR of 4.4% during the period 2016-2020.Payroll outsourcing is the fastest-growing segment of the global human resource outsourcing (HRO) market. Organizations are rapidly adopting payroll services to achieve cost reduction. They either outsource a single process or the entire services to enhance the existing function. Managing payroll in-house involves high costs. Organizations that maintain an in-house team for tasks such as payroll, time and attendance, workforce administration, and benefits administration spend 20% more than organizations that outsource the same functions.
The majority of payroll outsourcing functions are related to finance and accounting (F&A), human capital management (HCM), and shared service centers. The HR department uses outsourcing services more commonly than any other departments.
Technavio’s analysts forecast the global payroll outsourcing market to grow at a CAGR of 4.4% during the period 2016-2020.
Payroll outsourcing is the fastest-growing segment of the global human resource outsourcing (HRO) market. Organizations are rapidly adopting payroll services to achieve cost reduction. They either outsource a single process or the entire services to enhance the existing function. Managing payroll in-house involves high costs. Organizations that maintain an in-house team for tasks such as payroll, time and attendance, workforce administration, and benefits administration spend 20% more than organizations that outsource the same functions.
The majority of payroll outsourcing functions are related to finance and accounting (F&A), human capital management (HCM), and shared service centers. The HR department uses outsourcing services more commonly than any other departments.
Technavio’s analysts forecast the global payroll outsourcing market to grow at a CAGR of 4.4% during the period 2016-2020.The evaluation of the contribution to the study.
The HR Function has been trying to reposition itself, the aim is to encourage the function to be more strategic and have less administration tasks and to be more of a business support function and a facilitator of change rather than a guardian of the traditional function of employee welfare. HR are becoming high profile contributors at a strategic level they are well intergraded with the business and demonstrating they are adding value.
Although extensive research has taken place globally, there is limited information Three common reasons for outsourcing were: to acquire specialised HR capabilities, improve quality and efï¬ciency and concentrate on the strategic HR role.
The outsourcing of strategically important resources or services typically requires intensive communication and coordination among the personnel of both the outsourcing firm as well as the supplier (Borys and Jemison, 1989; Bello et al., 1999; and Mellewigt et al., 2007). Payroll outsourcing is one of the innovative practices in HR which helps to avoid unnecessary risk and effort to meet various objectives of the organization. The propensity to outsource payroll is the highest, resulting in a huge opportunity. When the size of an organization is small, the accounting firms are the preferred payroll service providers. When the organization is mid-sized, payroll is normally processed by their in-house team. And in the third stage, as the organization grows larger, they either look at an onsite processing option
or outsource to a payroll service provider.
According to Swartz (2007) security and private risk is greater when outsourcing takes place. The supplier’s inability to maintain confidentiality is a question. Costs of outsourcing payroll can be high, especially for a young business. There is a certain degree of risk if communication lapses – for example, if you don’t advise the payroll specialist of a staff member starting or leaving.
Outsourcing will also mean losing control of some of the key elements of your business, e.g.:
- you may not have instant access to payroll if it has been outsourced
- you won’t always be able to check it when you want to, or add anything that’s missing
- you must hand over confidential and sensitive staff information
Andrew Dunlop and Uwe Nimscheck, B. S. L., 2011. outsourcinghandbook.. Data protection in outsourcing transactions: the UK experience.
Brown, P. S. A., 2013. Motivations for HR outsourcing in Australia. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 04 Feb, Volume 24, p. 704-720.
CIPD, 2016. HR outsourcing, s.l.: CIPD.
Gantt, 2012. http://www.ganttchart.com/BasicGanttExample.html. [Online]
Available at: http://www.ganttchart.com/Chart/BasicGantt.pdf
[Accessed 24 March 2017].
HCM, O., 2013. Mordern HR in the cloud , s.l.: Oracle HCM.
Maise, I. J., 2001. Payroll and HR outsourcing, s.l.: CMA.
Research, I., 2016. .Global payroll outsourcing market 2016-2020, s.l.: s.n.
statistics, O. o. n., 2017. Current systems and suppliers for payroll, HR and training, s.l.: s.n.
Thomas, P. T. a. P. K., 2011. Payroll Outsourcing: A New Paradigm. The IUP Journal of Business Strategy,, Volume Vol. VIII, No. 4,, pp. 46-54.
Andrew Dunlop and Uwe Nimscheck, B. S. L., 2011. outsourcinghandbook.. Data protection in outsourcing transactions: the UK experience.
Brown, P. S. A., 2013. Motivations for HR outsourcing in Australia. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 04 Feb, Volume 24, p. 704-720.
CIPD, 2016. HR outsourcing, s.l.: CIPD.
Gantt, 2012. http://www.ganttchart.com/BasicGanttExample.html. [Online]
Available at: http://www.ganttchart.com/Chart/BasicGantt.pdf
[Accessed 24 March 2017].
HCM, O., 2013. Mordern HR in the cloud , s.l.: Oracle HCM.
Maise, I. J., 2001. Payroll and HR outsourcing, s.l.: CMA.
Research, I., 2016. .Global payroll outsourcing market 2016-2020, s.l.: s.n.
statistics, O. o. n., 2017. Current systems and suppliers for payroll, HR and training, s.l.: s.n.
Thomas, P. T. a. P. K., 2011. Payroll Outsourcing: A New Paradigm. The IUP Journal of Business Strategy,, Volume Vol. VIII, No. 4,, pp. 46-54.