Project Management and Hemas Holdings
1.1 Introduction on the Project Management and Hemas Holdings – FMCG.
Project Management can be expressed as the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements. Project Management has its long history which was practiced informally and has been officially recognised and emerged in mid of the 20th century in distinctly. The global body for project management which is Project Management Institute USA facilitate the concept and it is comprehensively explained in the Project Management Body of Knowledge (‘PMBOK®’ Guide) further (PIM, 2017).
In meeting successfulness of the project, it is vital to understand and plan the project cycle. Project cycle is the key concept which is discussed massively in the subject of Project Management and it has been acknowledged as the methodical sequence of cohesive set of tasks which are quantified, accomplished in stages, in ensuring the success of the project (Forsberg, 2005).
Hemas Holding PLC, with a renowned history of 65 years, has become a key blue chip company diversified in to five main sectors. The sectors are namely FMCG, Health care, Leisure, Transport (logistic) and other. Hemas FMCG serving the Sri Lankan customer base via its wide range of products and services. The group seized a strategic moving to the next level through the acquisition J.L. Morison Son & Jones (Ceylon) PLC. Also as a move in managed succession plan, Hemas invited Mr Steven Enderby to the Board offering the position of Chief Executive Officer. The flag ship products such as “Baby Cheramy” the Hemas brand has won the Sri Lankan mothers’ loyalty for nearly 60 years (Hemas Annual Report, 2016).

1.2 Project requirements.
The purpose of upgrading SAP 6.0 HANA to SAP S4 HANA at HEMAS FMCG sector was to enhance the Enterprise Resource Planning (referred to as ERP going forward) culture within the organisation. The rapidly growing business which pumps the highest revenues portion which is 38% needs to be fully monitored (Hemas Annual Report, 2016). The controls needs to be well set and deviations need to be reported in a timely manner. Â
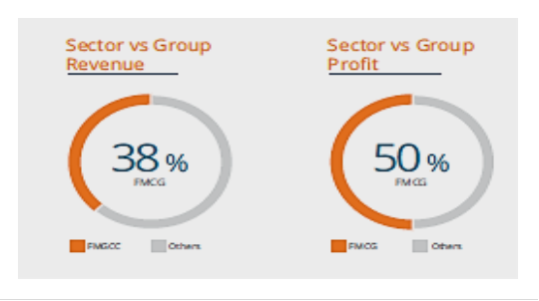
Figure 1 – FMCG Sector Vs. Group performance
1.3 Hemas FMCG strategy and feasibility of the ERP project.
Hemas founded under the vision of “Enriching Lives” and they do focus on it heavily. Hemas history has shaped the ways and means that is se the potential. The consistent effort in generating organic as well as inorganic growth had positively impacted on enriching the value of the Hemas stakeholders today. The ERP project implementation will help the organisation to be well aligned to its ‘Vision 2020’, concept and there five-year strategic plan (Hemas Annual Report, 2016).
The advancement in terms of the SAP 6.0 will allow the HEMAS FMCG sector to cater to the customer requirements and to meet demand. This would decommission most of supporting systems bring all them under one system in an advance tech platform.
1.4 SAP 6.0 to SAP S4 Feasibility study.
The project on HEMAS FMCG, SAP 6.0 HANA upgrade intends further improvements in to the EPR that they operate at the moment and this system upgrade will managed by the global SAP Functional team and the handing over will happen to the Hemas Corporate IT. The creation of blue print copy will be done by this team and also hey will do the pilot run planning and monitoring at FMCG sector offices located in Colombo (Head Office), Dankotuwa (Factory and Walisara (Finish good warehouse). Hence upgrading ERP in Hemas FMCG will be driven by the experienced global SAP team which will be and also will be facilitated by Attune Lanka. Attune is the local consultant for SAP implementation and upgrades.
Attune has shown is positive track records in SAP related projects. The company is very experienced in SAP implementation which is attached to MAS group. Attune with its localized experience they support the implementation and upgrade tasks locally while connecting the procedures with the global consultants and the locally based end users.
The SAP S4 Project needs be sponsored with US $1.5 Mn and this is forecast base on number of operators involved in the Sri Lankan operations. The approximate costing was carried out based on similar projects which were carried out for different agency offices. The Hemas group will be funded the full project which will be repaid to the group by the FMCG sector in 5 years’ time. This is possible as the Revenue growth % is at 20.2% for 2016 (Hemas Annual Report, 2016).
2.1 Statement of work (SOW)
Hemas FMCG sector SAP 6.0 HANA Upgrade to SAP S4 will have the following critical areas as per the Statement of work.
Scope of work
Upgrade of SAP ERP will bring in all the functions such as Demand Planning team, Material Requisition team, Procurement, Stores, Quality Assurance, Finance, Marketing and HR. Currently HR is not integrated within the ERP but with SAP S4 HANA the Hemas FMCG will be fully integrated.
Since the data is currently is the same platform the integration will not be complex and time consuming. Following will be the main functions which will enjoy the facilities of the system upgrade.
- Demand Planning – Material planning
- Procurement – OP (Purchase Ordering) process
- Production – Production planning
- Stores/ Warehouse – GRN (Goods Receive) and stock control
- Quality Assurance – Quality check and release Raw material
- Finance – General Ledger and Financial reporting
- Marketing and distribution- Releasing the Finish goods to the market
Project duration/ Budget
The expected time for the upgrade is 6 months starting form upgrade, pilot run and handing over. This will include the initial test run as well as most critical go live phase. The total SAP S4 upgrade is spitted in to phases for the monitoring and control purpose.
The funds need to be allocated to manage the cost and expenses. Hence a budget is allocated separately which is USD 1.5 Mn.
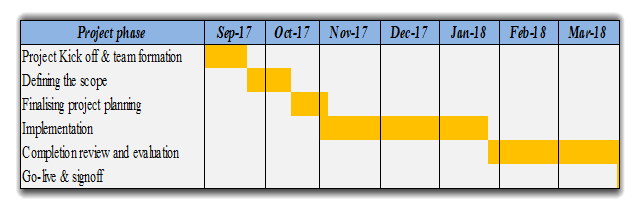
SAP S4 – Project time lines
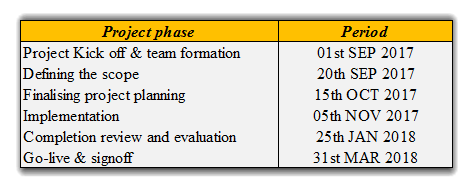
SAP S4 HANA – Gantt chart on Deliverables
Key deliverables of the project
- The key goal is to successfully upgrade the SAP 6.0 HANA in to the SAP S4 HANA. Hemas FMCG Sector intends to integrate the Human Resource (HR) function also to the ERP which in not at present.
- The SAP S4 platform will enhance the integrity and will improve the communication which will be faster and safer in an email based operation.
- Efficiency improvements will occur in the eventuality.
Responsibility and authority
The SAP Upgrade Project team headed by the Hemas FMCG sector Project Manager will be the ultimate responsible party where as all team member of the project team will have an equal portion of the responsibility to deliver the a successful SAP upgrade. Mainly the time lines and the level of success will be monitored and the budget needs to be managed. The SAP Upgrade Project manager will be appointed by the Hemas FMCG Sector management were the member form each functional are will be added to make the presence and brining in ideas to meet the specific expectations of the project. The project manager focus is to monitor the project with the assistance of the functional consultants. Attune Lanka will be responsible for the realizing the project in meeting expected results.
In order to make the project a success the Project manager needs to be provided with Resource in terms of Human Capital as well as knowledge, equipment and funds. Scope will provide necessary guide line which the project team will follow where the excellent level of leadership will drive the team live for its results. According to Laufer, it is clear that comprehensive understanding of the project via clear scope will facilitate the Project Manger to monitor the deadlines and cost factors ensuring no overrun in the two elements (Laufer, 2012).
Project planning, phase monitoring, releasing the resource on time actions on deviation and contingency palling are critical elements. Communication gaps needs to be narrowed down where keeping the entire set of stake holder on the same page with updated information.
2.2 Work Breakdown Structure of the SAP S4 HANA upgrade project.
The project at Hemas FMCG sector on SAP ERP 6.0 HANA upgrade to S4 HANA will flow through 6 months which is starting form the Project Kick off & team formation to Go-live & signoff. The total project can be broadly split in to key 5 areas which are clearly shown within in Project Life Cycle (PLC) as below.
- Scope definition
Understanding the goal of the project is vital which happens in this stage. The GAP analysis will facilitate the stakeholders to understand “Where are we” and “Where we need to go”. The basic planning comes in handy whereas project time lines and resource identification and finalisation occur.
- Project SAP S4 planning
After the resource are finalised the deliverables will be clearly defined and responsibilities of each and every member of the team will be explained recorded and with authority levels to act upon. Planning and Segregation duties will be performed by the Project manager which needs to be rolled out with proper decision making and leadership.
- Execution & control
Monitoring and control of the SAP project is while the project is on the go is a staple action needs to be taken during this stage. Basically implementation, review and control occur ensuring schedules are on track. Deviations needs to be monitored and problem solving and decision making plays a major roll during the session. Also the updated information needs to be reported to key stakeholders at the Hemas FMCG Sector.
- Project evaluation
In terms of evaluation the testing is carried out as in the execution stage the project is on-going and controlled to meet the desired outcomes. The testing is carried out by deriving reports where the Test Data in faded to the system and checked against the previous report whether the output is correct and process is smooth. All testing results and outcomes needs to be kept in documented form and the progress will be reported
- Completion
Focusing on the Project Life Cycle this is the last stage of the project, where an assessment is done against actual and expected outcomes. The delivery of the project results and handing over the project is occurred. The experience and the leanings of the overall project are identified via a post completion audit and the points are recorded to be used in future projects. The explanations for any deviations of the SAP S4 HANA upgrade will be reported with actions taken.
As per Allen, the final user acceptance testing needs to be carried out and performed during completion stage and results needs to be checked and verified against project plan (Allen, 2004).
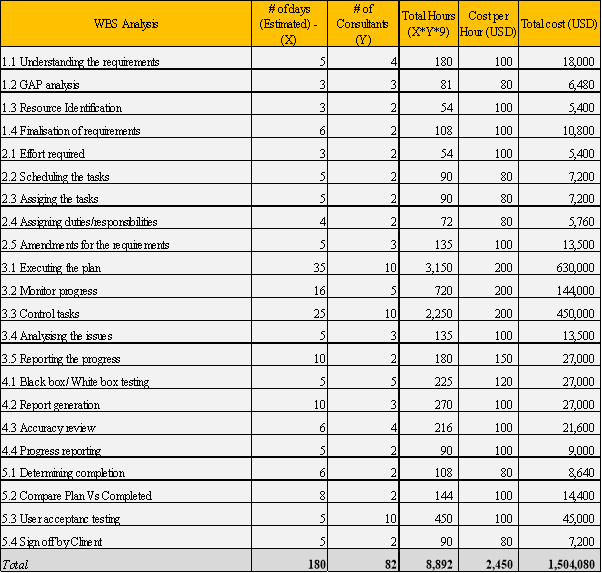
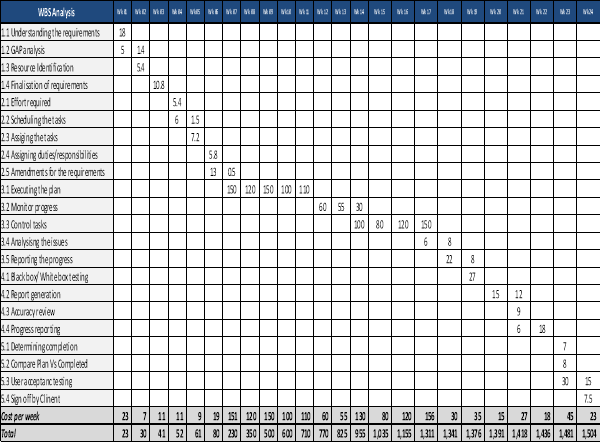
Work Break down structure for the SAP S4 HANA upgrade project can be developed as provided below. The work is divided in to main five phases considering the project life cycle. The sub tasks are the reflector of the main ones.
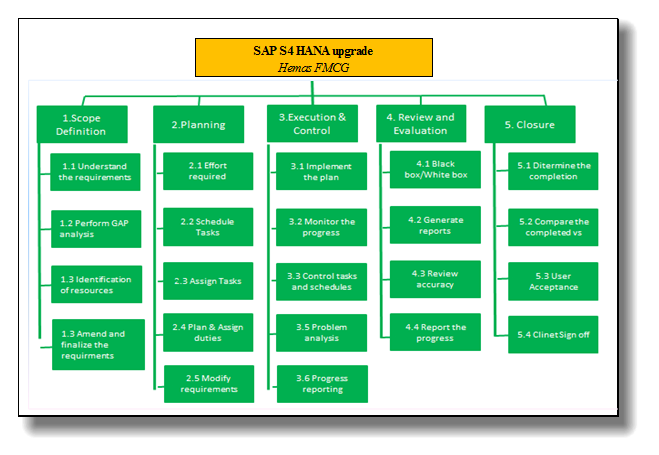
3.1 Network Diagram
The success of the project is what everyone intends. The priorities of each project are different to each other. The Network diagram represents the priorities that need to be in the SAP upgrade project demonstration the sequence of the activities allowing the Project management team to focus on the critical path which project should flow.
Having the network diagram and understanding the critical path of activities create more visibility about the tasks processed and in the same time tasks can be managed in order to assist utmost vital tasks of the entire project which cannot be compromised at any cost (Young, 2000).
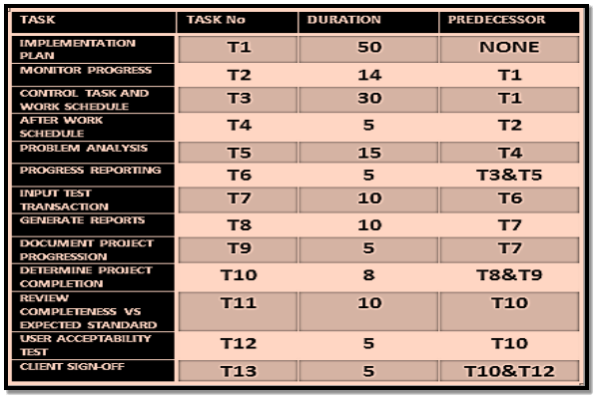
In order to identify the dependencies between the activities the below predecessor table needs to be prepared. Then the Network Diagram will be drawn based on the predecessor table where the Project team will engage in following tasks.
- Gathering necessary resources – the right team
- Identifying each sub tasks which supports the key task
- Putting the tasks in the sequence (along with dependencies)
- Allocating sufficient time for each of the tasks
- Calculating the least possible time for the most time consuming will identified as critical path finally.
- Calculate the earliest completion and latest completion times
- Finalise and review the diagram via a brainstorming session
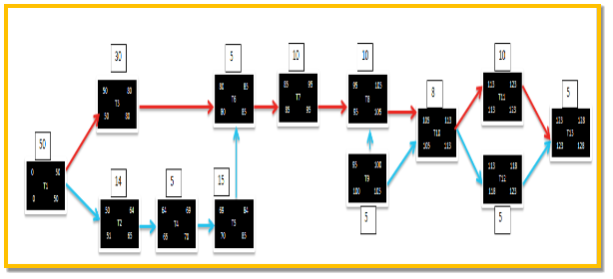
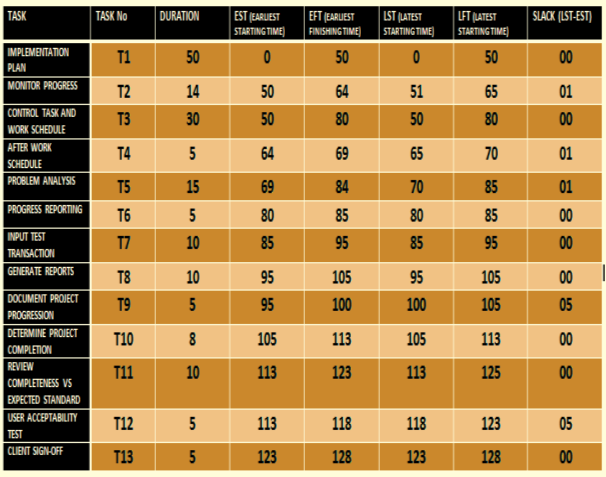
3.2 Network diagram & Critical Path
These two are popular terms discussed in Project management which facilitate the project deadlines demonstrating the time frames in graphical for.
4.1 Proposed budget for the project.
The cost factor is critical for any project as SAP upgrade. The budget needs to be managed by the project management team. When there are low budgets and restriction it will hinder the progress and the success of the SAP project. A well-managed budget helps to manage the funds and to optimal utilisation of resources. Also even the ultimate responsibility is to manage the budget is with the Project manager, the each and every team member needs to make sure that the tasks they are working on are operating and activated on time were the time factor can make a huge effect on the Budget if it gets dragged. Experienced gained form prior project related to implementation or upgrade will help the project manager and his team in ascertaining the spending patterns.
.
This specific project on SAP system upgrade will not be that tough as the SAP ERP 6.0 is already running live at the Hemas FMCG sector from 2005. During the progression of the project if the team decides that resource needs to be enhanced additional resources needs to be allocated which will result in Budget expansions.
4.2 Cost distribution plan – SAP upgrade.
The cost distribution plan demonstrates that the cost or rather the expense level at each stage of the project. This can be broken into weeks. Total spending against the each phase spending can be recognised via the cost distribution plan.
Any deviation in the project which occurs subsequently will require additional funds to be spent. The cost distribution plan ensures that the organization is exactly planning the expenditure and the timing of the cost in the most appropriate manner.
Hemas FMCG sector SAP S4 upgrade can be shown via the Cost distribution plan as below. (Values in USD ‘000’s).
There can be any type of the Project but Project quality management engages with all the controls and monitoring with regard to the quality of the project, as that aspect it expected by all the stakeholder as a key result of the project. The aspect of Quality Management can be discussed as follows.
- Level of Customer Satisfaction
The project goal in to get derive the project goals and to witness the advantages of the project. Mostly a project is carried out to fulfil the customer requirements. When considering the SAP S4 HANA system the upgrade form SAP 6.0 HANA, the end users expect to enjoy the latest facilities in deriving report with more information, processing activities faster, more integration, user friendliness etc. Also since the HR will also get integrated to the Hemas FMCG sector operation via the system upgrade will result in a fully-fledged SAP experience in the eventuality.
- Continuous Enhancement
The competition is at another level as is immense in the modern era. There is no time to relax. An ERP system facilitates the entire operation of the organisation to it will help the continuous improvement in terms of Total Quality Management (TQM) and concepts such as Zero Defects, Six sigma. The Hemas FMCG sector had a growth of 23% against 2015 financial year, and will be growing at a rate. Hence the sector needs more focus in the improving continuously (Hemas Annual Report, 2016).
- Prevention over examination
The cost of quality measurements are considered under this whether it is discussed that precautionary actions will help the organisation to succeed. This can be further discussed as cost of conformance and non-conformance. Basically the system upgrade in to SAP S4 will help Hemas FMCG to further look in to prevention and examinations while to operations grow at a rate.
5.1 Quality Assurance
The topic of Quality Plan describes the identification of quality requirements of the projects and ensures the project is carried out within the quality boundaries. The output of a proper quality plan will be quality management plan, quality metrics and the fact of quality enhancements which is also known as process improvements plan.
Quality Assurance can be broadly defined as the plan and systematic actions executed in a quality system in order to ensure the quality requirements for a specific product or service will be fulfilled. When considering the quality assurance techniques cost benefit analysis, cost of quality, benchmarking, control check lists and Fish borne diagrams are discussed.
- Cost of Quality
The expenses that occur in Quality Management process is discussed in detail where and more focus will be to Prevention cost as that can be managed internally via improvements whereas Appraisal cost in external which the customers of Hemas FMCG get to know.
- Benchmarking
Comparing the SAP 4S at Hemas with another organisation which is already will allows the project team and the stakeholder to identify how the system upgrade is and the success rate. What is to be learnt and how Hemas FMCG could improve the performance of the overall organisation.
- Flow charts
The flow chart represents the sequence of the project progress in a graphic manner. Also this enables the SAP S4 project team to visualize the associated points and processes of the upgrade. Key decision points are identified via the chart and close monitoring can be done based on the identified facts.
5.2 Quality Control
After the completion of the Project the Quality control mechanism takes place focusing on principles of the quality assurance. Quality control check is vital action that needs to be taken to verify whether the output of the project of SAP S4 system upgrade has been executed without any deviations from the original plan. The completed project will not have any advantage of this as this is an audit done upon post completion however the learning point of the upgrade project can be carry forward to make sure the future projects are performed with more care and control (Project Management Institute, 2017).
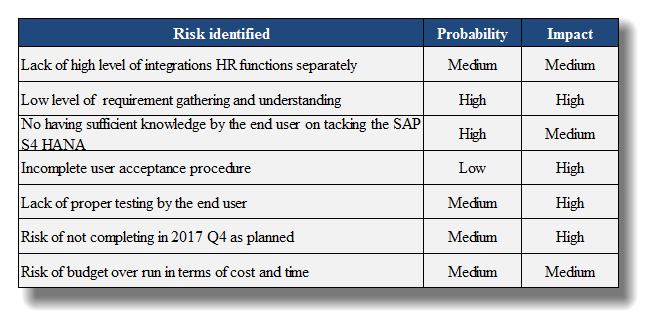
The Risk Management plan is another crucial factor of a project as this facilitates in identification of risk of the specific project, assessing the risk and mitigating the risk. The risk exposure of the Hemas FMCG sector can be identified as follows.
- Lack of high level of integrations HR functions separately
- Low level of requirement gathering and understanding
- No having sufficient knowledge by the end user on tacking the SAP S4 HANA
- Incomplete user acceptance procedure
- Lack of proper testing by the end user
- Risk of not completing in 2017 Q4 as planned
- Risk of budget over run in terms of cost and time
The risk exposures will help the risk assessment. This needs to be done with the comprehensive understanding of rick level and probability of occurrence. The practicality will also need to be counted in assessing the risk. Prior knowledge in SAP 6.0 HANA implementation occurred in 2005 will be useful in upgrading the existing ERP system at Hemas FMCG sector to the next level which is SAP S4 HANA.
Maintenance of a risk register along with the risk assessment is the responsibility of the project team where the information needs to be shared in a frequent manner with the relevant parties in order to eliminate risks as much as possible to ensure the success of the SAP S4 upgrade project. Proper documentation and monitoring is important. SAP S4 HANA upgrade at Hemas FMCG identified risks in the risks identification phase will be utilised in processing the risk assessment as below.
6.3 Risk mitigation plan
Risk mitigation is all about taking action for the per-identified risks and taking prompt action to diminish the negative impact which arises from them based on the priorities identified via the risk assessment.
The Risk identified needs to address as below.
- Lack of high level of integrations HR functions separately
The HR function not being integrated to the system leads to communication gaps. Hence the risk of brining in HR function
- Low level of requirement gathering and understanding
The risk of not gathering important information on the requirements will change the scope and having a reasonable level of braining storming with members form all the function will mitigate the risk.
- No having sufficient knowledge by the end user on tacking the SAP S4 HANA
It is pointless having sophisticated systems if the end users do not know how to use them. Ultimately the investment will be just another useless project. The end users need to be given proper training which motivates them to use the system frequently without any fear.
- Incomplete user acceptance procedure
All the users’ are required to accept the system via proper documentation. This is important is change management as smooth the users needed to get shifted to the new system in an appropriate way.
- Lack of proper testing by the end user
This needs to be mitigated by running several test runs and 100% accuracy test which is the only method to do so.
- Risk of not completing in 2017 Q4 as planned
Project plan execution at its best will remove any risk in delaying the project. The project team needs to coordinate well and execute the actions on time as agreed. Any deviations need to be communicated clearly with prior hand allowing the Project manager to take precautionary actions. Hemas financial year ends by 31st March 2018 and the on time completion will allows the Hemas FMCG to do a parallel run in the SAP S4 HANA.
- Risk of budget over run in terms of cost and time
Budget needs to be managed as that has being agreed after a proper analysis which is USD 1.5 Mn. The perfect execution of project plan will mitigate this risk. Also having a supplementary budget for contingency will always help.
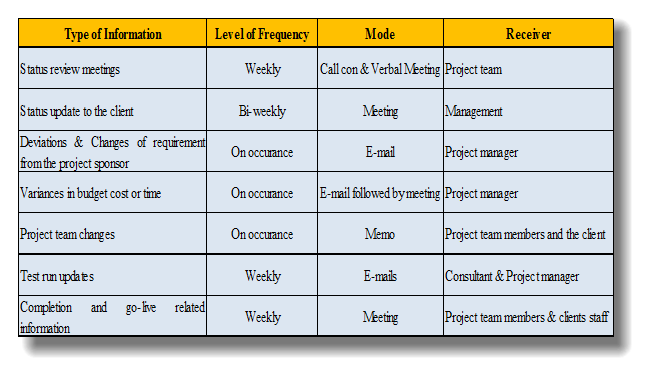
Communication which leads to lot of issues due the gaps is the procedures. There is a paramount importance of proper communication for the success of the project. As per the SAP upgrade in Hemas FMCG sector there are key stake holders including Project team, management of FMCG sector, group IT, group Internal Audit team, shareholders etc. who needs to be managed with proper information. Hence communication plan will help to execute that smoothly. Sound level of communication needs to be handled by the project manager by himself and which will be replicated the project team member in the eventuality (Kliem, 2007).
Communication plan needs to be equipped with,
- Standard format and levels of communication
- The modes which are intended to use – Calls, Meetings, Memos, and Conference Calls etc.
- Responsibility of communication flow
- Frequency of the and the activities which is communicated formally and informally
- How to fulfil the requirements of stakeholders in terms of communication. Timing and controls.
In managing the communication requirements of the SAP S4 upgrade the below communication plan can be utilised.
Hemas FMCG Sector SAP ERP system upgrade will be a challenge as the success of the project has a major impact to the Group as FMCG sector is the key revenue generator with 38% contribution. The challenges and the complexities can be managed via comprehensive understanding and smooth function of the project management methodology. The said project team need to be armed and equipped with necessary resources and skills to ensure a success of the upgrade project.
It is a very critical move that the management decided by cultivating the idea of the SAP system upgrade. The intended results can be achieved as the report emphasise the face of on time quality deliverable in all the tasks of the full project. As mentioned above the leadership of the Project manager and the active participation of the team members are also critical as they are the driving force of the SAP upgrade process in to SAP S4 HANA in Hemas FMCG Sector. Also following proper quality plan, risk management plan and communication plan project team will be more prepared to possible issues that may arise in the project.