Reaction Rate of Hydrochloric Concentration
Hydrochloric Intensity
The purpose of the experiment was to gather an understanding for the chemical reactions, depending on the concentration. The rate of reaction is the speed of the chemical reaction. This experiment was to justify if the concentration is high or low will it affect the chemical reaction. ‘Hydrochloric acid constitutes the majority of gastric acid, the human digestive fluid. In a complex process and at a large energetic burden, it is secreted by parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells). These cells contain an extensive secretory network (called canaliculi) from which the HCl is secreted into the lumen of the stomach. They are part of the epithelial fundic glands (also known as oxyntic glands) in the stomach. The chemical compound hydrochloric acid is the aqueous (water-based) solution of hydrogen chloride gas (HCl). It is a strong acid, the major component of gastric acid and of wide industrial use’. (LibreTexts. 2017). It is said from (chem4kids.com. 2017) ‘if a reaction has a low rate, that means the molecules combine at a slower speed than a reaction with a high rate’. The collision theory was used to envisage the rate for a chemical change, collisions don’t always have a chemical reaction. A chemical reaction needs to be equalized for it to have an effective collision. According to (Chemistry LibreTexts. 2017) ‘A collision will be effective in producing chemical change only if the species brought together possess a certain minimum value of internal energy, equal to the activation energy of the reaction. Furthermore, the colliding species must be oriented in a manner favorable to the necessary rearrangement of atoms and electrons’.
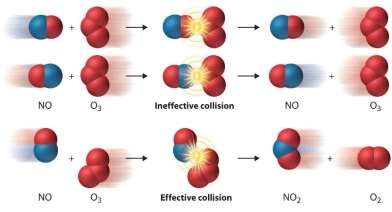
(askllTians. 2017)
The experiment that was used, was all 5 test tubes filled with the same amount of sodium thiosulfate and adding to each different test tube different concentrations of hydrochloric acid and timing how fast the reaction rate is. This experiment was used to find out if you had different concentrations of hydrochloric acid would it affect the rate of reactions.
Na2O3S2 + HCI = SO2
Sodium thiosulfate +Hydrochloric acid = sulfur dioxide
The chemicals in this experiment were Hydrochloric acid and Sodium thiosulfate. Research has shown about hydrochloric acid it is a component found in the human digestive fluid from (Hydrochloric acid. 2017) it says that ‘ Hydrochloric acid constitutes the majority of gastric acid, the human digestive fluid. In a complex process and at a large energetic burden, it is secreted by parietal cells (also known as oxyntic cells). These cells contain an extensive secretory network (called canaliculi) from which the HCl is secreted into the lumen of the stomach. They are part of the epithelial fundic glands (also known as oxyntic glands) in the stomach. The chemical compound hydrochloric acid is the aqueous (water-based) solution of hydrogen chloride gas (HCl). It is a strong acid, the major component of gastric acid and of wide industrial use’. If the human digestive fluid had a low concentration it would take longer to digest food. Concentration is the intensity of an element or substance in an experiment. Concentration is used in everyday life in food, drinks and chemicals added to certain things.
Aim
The Aim for this experiment was if the concentration would affect the rate of reaction.
Hypothesis
The prediction for this experiment was that the reaction time will get faster and slower with each density of hydrochloric acid. Hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulfate will mix together and create a yellow substance of solid Sulphur. The controlled variable in this experiment was the concentration and the independent variable was the rate of reactions.
- 5 test tubes
- 2 measuring cylinders (50ml each)
- 5 different types of hydrochloric acid such as 0.2,0.5,1.0,1.5,2.0 (50ml each)
- 1 sodium thiosulfate 75ml
- 1 test tube rack
- Gloves
- Glasses
- Lab coat
- 3 stop watches
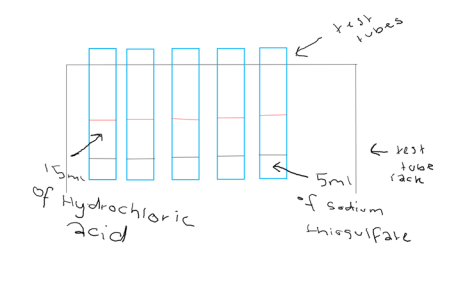
This experiment started by the collection of the resources and safety equipment needed. Followed by the set up of the test tubes in the test tube rack and the measuring of 5ml of Sodium Thiosulfate for each of the test tubes. 15ml of Hydrochloric Acid of different concentrations ranged between 0.2 to 2.0 added to each test tube as soon as the hydrochloric acid is added the timer was stated and the experiment was observed till there weren’t any more changes to the chemicals. When the chemicals first had a change the time from when the hydrochloric acid added to the change was recorded into a results table. Once there was no change to the chemicals, the times was also recorded. The experiment was done three times to make sure there were the best results we could get and incase the results weren’t precise. After the third round of the experiments were finished the equipment used was cleaned up and the area used and all the resources and safety equipment used was returned.
Diagram
Risk assessment
|
Basic steps for experiment |
Risks (low, moderate, high) |
prevention |
|
grabbing equipment from the trolley and placing it out |
It is at a low risk of bumping into people and dropping all the equipment |
To prevent this risk, you will need to walk safely to you working area and be careful with the equipment |
|
When measuring the sodium thiosulfate to put in each test tube |
It is at a low risk of spilling the chemicals |
To prevent this risk, you will need to be aware of people around you and keeping an eye on what you are doing |
|
When measuring the hydrochloric acid to put in each test tube for the first round of experiments |
It is at a low risk of spilling the chemicals |
To prevent this risk, you will need to be aware of people around you and keeping an eye on what you are doing |
|
The combination of the hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulfate into the same test tubes |
It is at a low risk of spilling the chemicals |
To prevent this risk, you will need to be aware of people around you and keeping an eye on what you are doing |
|
Viewing the reaction |
It is at a moderate risk you may be injured by the reaction the chemical pose |
To prevent this risk, make sure you have put in the right amount of chemicals and don’t be so close while viewing the reaction |
|
After repeating the experiment 3 times the area and equipment used will need to be cleaned and washed |
It is at a moderate risk spilling the chemicals on yourself will cause burning or irritation to the skin or dropping the test tubes and breaking them |
To prevent this risk, ware protective gear such as groves, glasses and apron it will protect most of your body at may come in contact with the chemicals |
|
Writing your results |
It is at a low risk the most that can happen is stabbing yourself with a pencil or pen. |
To prevent this risk, be careful |
The health effect the chemicals have:
|
Chemical |
Effects |
|
Hydrochloric acid |
When in contact with skin, your skin will become corrosive, irritant and it will create burns on your skin. Eye contact it will become irritant and corrosive. |
|
Sodium thiosulfate |
Your skin will become irritant. |
results
Experiment 1:
|
Mol |
Before |
after |
reaction |
|
0.2 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
51sec-6.45min |
|
0.5 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
48sec-4.54min |
|
1.0 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
1.10min- 2.28min |
|
1.5 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
1.20min-2min |
|
2.0 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
1.15-2min |
|
Mol |
Before |
after |
reaction |
|
0.2 |
Clear |
change to a creamy white |
51sec-6.45min |
|
0.5 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
33sec-4.53min |
|
1.0 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
26sec- 2.42min |
|
1.5 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
18sec-2.25min |
|
2.0 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
58sec-3.3min |
Experiment 2:
Experiment 3:
|
Mol |
Before |
after |
reaction |
|
0.2 |
Clear |
change to a creamy white |
41sec-3.15min |
|
0.5 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
38sec-2.36min |
|
1.0 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
0.06sec- 1.49min |
|
1.5 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
45sec -1.27min |
|
2.0 |
Clear |
Change to a creamy white |
10sec-2.11min |
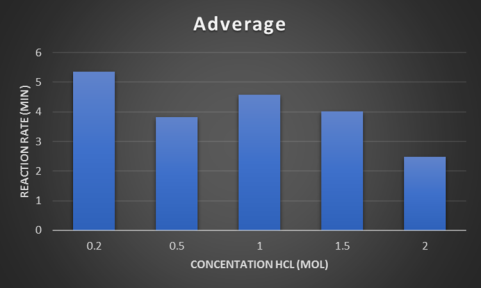
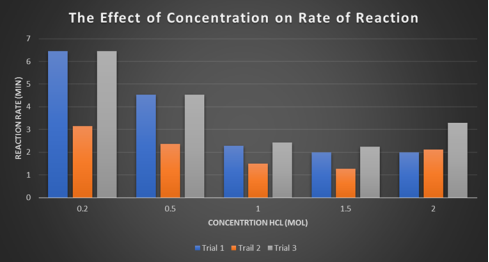
Discussion
In experiment 1, it started with the clear mixed chemicals all with different concentrations of hydrochloric acid. In the experiment for 0.2M the reaction occurred 51 seconds after combining sodium thiosulfate and hydrochloric acid together and the reaction stopped 6.45 minutes after the combining. The hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 0.5M the reaction occurred 33 seconds after the combining and stopped 4.53 minutes after. 1M was 25 seconds and stopped at 2.42 minutes after, 1.5M was 18 seconds and stopped after 2.25 minutes after and finally 2M the reaction started at 58 seconds after it was combined and it stopped 3.37 minutes after the combining. Although all the concentrations of hydrochloric acid, the clear liquid it once was changed to a creamy white.
In experiment 2, it started the same way as experiment 1. Although some of the results were different to experiment 1. O.2M it started at 51 seconds and stopped at 6.45 minutes after, it was the same as in experiment 1. The chemical reaction started at 33 seconds and it stopped 4.53 minutes whereas 1M started at 26 seconds and it stilled at 2.42 minutes after it was added. 1.5M was started at 18 seconds whereas 2M started at 58 seconds but 1.5M stopped at 2.25 minutes and 2M stopped at 3.3minutes. However, all the concentrations in the end change to the same color in experiment 1.
Experiment 3, just like all the other experiment it was started the same way with the clear mixed chemicals however, the chemical reaction happened when the sodium thiosulfate was being measured because it was accidently measured in the hydrochloric acid measuring cylinder so that effected the results for this experiment, so it was measured when it got to a darker shade of creamy white. 0.2M was affected 41 seconds after and it stopped 3.15 minutes after. 0.5 changed 38 seconds after and it stopped at 2.36 minutes. 1M was the one that was most effected when measuring the sodium thiosulfate occurred it was recorded in the results that it started at 0.06 seconds and stopped at 1.49 minutes. 1.5M started at 45 seconds and finished 1.27 minutes after finally 2M started at 10 seconds and stopped 2.11 minutes.
The Average, when the recording was happening there wasn’t someone all the time watching the experiment so it may not be quite accurate. The average for 0.2M was 5.35 minutes, 0.5M was 3.81 minutes, 1M was 4.58 minutes, 1.5M was 4.02 minutes and finally 2M was 2.47 minutes. This average was only recorded by when the chemical changed stopped.
The research collected helped understand what was going on with the experiment it was known if it had a low concentration is would go slower and it would go faster if it had a high concentration. The Hypothesis was supported it did get faster and slower with each density of hydrochloric acid. Although it didn’t create a solid yellow substance, the experiment only created a liquid substance. This experiment has created a understanding of what would happen if the human digestive fluid has a much higher concentration it would help digest quicker but it would also eat the lining of your stomach.
Evaluation
This experiment worked well but there were many mistakes that occurred such as the results were not recorded properly because you needed to keep an eye on the experiment at all times to get the most accurate answer. The other mistake was with the measuring cylinders needed to make sure that this experiment used one for sodium thiosulfate and a another for hydrochloric acid otherwise it will be an inaccurate answer because the chemicals will already mix when your measuring how much you will needwith one of the chemicals. To improve this experiment, it would have been better if one person is always watching the tests so this experiment would have made the results more accurate and if the measuring cylinders were easier to tell apart so there was a clear distinction of which on was used for that certain chemical.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the experiment was used to have a better understanding of chemical reactions depending of the concentration. The collision theory was used to rate the chemical change, hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulfate make a yellow liquid substance. Concentration is also used every single day without most people’s knowledge. The concentration did effect the reaction rate because it either had a high or low reaction rate. The hypothesis was supported except for the concentration of 2M more information was needed to understand why.
Bibliography
- Chemistry LibreTexts. (2017). Reaction Rate. [online] Available at: https://chem.libretexts.org/Core/Physical_and_Theoretical_Chemistry/Kinetics/Reaction_Rates/Reaction_Rate [Accessed 9 Feb. 2017].
- Encyclopedia Britannica. (2017) | chemistry. [online] Available at: https://www.britannica.com/science/collision-theory-chemistry [Accessed 5 Mar. 2017].
- Mar. 2017].
Studios, A. (2017). Chem4Kids.com: Reactions: Rates of Reactions. [online] Chem4Kids.com. Available at: http://www.chem4kids.com/files/react_rates.html [Accessed 5 Mar. 2017].
- Pubchem.ncbi.nlm.gov. (2017) | HCI – Pubchem. [online] Available at: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/hydrochloric_acid [Accessed 9 Feb. 2017].
- Pubchem.ncbi.nlm.gov. (2017). SODIUM THIOSULFATE | Na203S2 – Pubchem. [online] https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Sodium_thiosulphate#section=Top [Accessed 5]