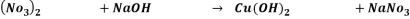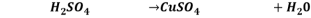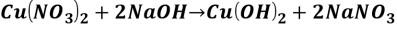Reactions of Copper and Percent Yield
Purpose-The purpose of this experiment is to examine the chemistry of copper and with the concept of percent yield. /2
Procedure- CHEM16882, Applied Chemistry1 Laboratory Manual Experiment no.6 posted on slate/Sheridan college, Brampton (accessed on 20.feb.2017) (1). /2
Observations
- Create your own data table for quantitative data. The table must include all the measurements you recorded in the laboratory; it must have a table number and title.
Answer- Table for quantitative data measured while conducting the experiment.
|
Compound |
Mass(+ /- 0.0001g) |
|
Initial weight of copper |
0.5189g |
|
Final weight of copper |
0.5651g |
|
Weight of 250 ml empty beaker |
117.29g |
|
Evaporating dish |
56.2529g |
|
Final weight of copper + evaporating dish |
56.8180g |
/4
- In table format record qualitative observations for each of the five reactions. All observations must be written in complete sentences. The table(s) must have a table number and title.
Answer-Table 1.
|
Reaction 1. Cu + |
|||||
|
Physical state |
The physical state of copper is solid. |
The physical state of Nitric acid is liquid. |
Copper2 nitrate is liquid in nature. |
Nitrogen dioxide is a gas. |
Water i.e. dihydrogen monoxide |
|
Color |
The color of copper is brown |
Nitric acid is clear. |
Copper 2 nitrate is in Blue green color. |
Nitrogen dioxide is in brownish shade |
Dihydrogen monoxide is Clear. |
|
ADDITIONAL OBSERVATION-Heat is generated during this experiment. |
|||||
Table 2.
|
Reaction 2. Cu |
||||
|
Physical state |
The physical state of copper nitrate is Liquid. |
The physical state of sodium hydroxide is Liquid. |
Copper hydroxide is Solid in nature. |
Sodium nitrate is in Liquid form. |
|
Color |
It is in Blue green color. |
It is Clear. |
It is Black in color. |
It is in Dark blue color. |
|
ADDITIONAL OBSERVATION-Blue precipitates are formed when NaOH is added. |
||||
Table 3.
|
Reaction3. Cu |
||||
|
Physical state |
The physical state of copper hydroxide is Solid. |
– |
Copper hydroxide is Solid. |
The physical state of dihydrogen monoxide is Solid. |
|
Color |
It is Dark blue in color. |
– |
It is in Black color. |
– |
Table 4.
|
Reaction 4. CuO + |
||||
|
Physical state |
The physical state of copper hydroxide is solid. |
Sulphur acid is in Liquid form. |
Copper hydroxide is liquid. |
The physical state of dihydrogen monoxide is Solid. |
|
Color |
It is in Blackish tone. |
It is Colorless. |
It is Light blue in color. |
– |
Table 5.
|
Reaction 5. Cu |
||||
|
Physical state |
The physical state of copper sulphate is Liquid. |
Zinc is a Solid. |
Zinc sulphate is solid in nature. |
Copper is in Solid form. |
|
Color |
It is Black in color. |
It is Silver in color. |
It is Colorless. |
It is Reddish/brown in color. |
|
ADDITIONAL OBSERVATION-Heat is generated during this reaction. |
||||
- Write balanced chemical equations for each of the five reactions. Identify and name the product(s) for each reaction. State whether the product is a solid, liquid or gas.
Answer-Reaction 1
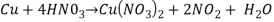
Reaction 2
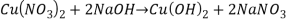
Reaction 3
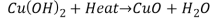
Reaction 4
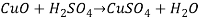
Reaction 5
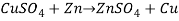
/5
- For each of the five reactions, identify the type(s) of reaction each is. Your choices are: decomposition reaction, oxidation-reduction reaction, acid-base reaction, combustion reaction, single displacement reaction, double displacement reaction and synthesis reaction.
Answer-
Reaction 1.
It is a decomposition reaction.
Reaction 2.
It is a double displacement reaction.
Reaction 3.
It is single displacement reaction.
Reaction 4.
It is Acid Base Reaction.
Reaction 5.
It is a Redox Reaction i.e. oxidation reduction reaction because zinc loses 2 of its electrons and copper gains 2 electrons.
/3
Calculations
All calculations must show the equation used (typed with equation editor), units must be present with all numbers and the final answer must be recorded with the correct number of significant figures.
1. Calculate the % yield of Cu at the end of the five reaction steps. (This could also be referred to as the % recovery of Cu.) Show ALL calculations.
Answer- Actual mass of copper=0.5189g
Final mass of copper obtained=
Mass of evaporating dish and copper (g) – Mass of empty flat evaporating dish(g)
=56.8180g-56.2529g=0.5651g=0.56g
Percentage yield %= 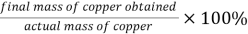
=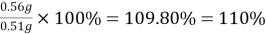
/3
2. For Reaction 1 between Cu and HNO3, calculate the theoretical yield of Cu(NO3)2 in grams.
Answer-
Reaction 1. 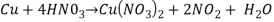
Molecular mass of Cu =63.546g/mol
Molecular mass of HN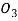 =63.01284g/mol
=63.01284g/mol
Molecular mass of 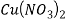 =187.554g/mol
=187.554g/mol
Mole of Cu =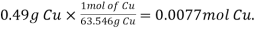
Theoretical yield of 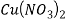 =
=
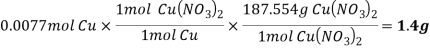
/3
3. For Reaction 1 between Cu and HNO3, confirm that HNO3 was present in excess. (Show a calculation to support your answer)
Answer- Reaction 1. 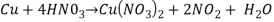
Molecular mass of Cu =63.546g/mol
Molecular mass of HN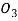 =63.01284g/mol
=63.01284g/mol
Molecular mass of 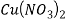 =187.554g/mol
=187.554g/mol
Mole of Cu =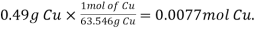
Theoretical yield of 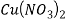 =
=
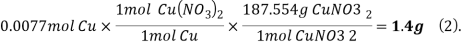
/2
4. For Reaction 2, calculate how many moles of NaOH you added.
Answer-
Reaction 2
Molecular mass of 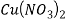 =187.54g/mol
=187.54g/mol
Mole of NaOH=1.4g 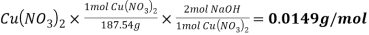
/2
Questions
- What compound was being removed in the procedural step where 150 mL of hot R.O. water was added to the solid CuO precipitate? Do you think that all of this compound was removed by this washing? How could this error affect your percent yield? How could this error be minimized?
Answer-Hydroxide atoms was being removed in the step of procedure where 150 ml hot water was added to CuO solid precipitate.
No, I don’t think so that all of compound was taken off by washing it. Some particles were added by human error, which resulted in increased amount of the product which affected the final result i.e. percent yield of copper.
The chances of error can be reduced by various methods. One such method is by making some changes in procedure i.e. washing of precipitates entirely until the particles are removed thoroughly or by increasing dissolution process.
/6
2. List two errors that could increase your % yield and two errors that could decrease % yield. Describe one of each type in details.
Answer– Two errors that may occur during conducting the experiment which could increase the % yield of copper are as follows-:
- By human error, i.e. while washing method some of the water cannot be removed from NaNO3 particles from copper hydroxide particles which will result in increased mass of final product.
- In the final result we got more mass than the actual mass because zinc does not fully react with CuSO4. Some particles still remain inside with the copper.
Two errors that may occur during the experiment which could decrease %yield are as follows-:
- Some particles remain left inside the beaker while transferring from one to another which reduced the weight resulted in %yield.
- Some particles get transferred into the beaker with water and there was loss in the weight which affected the result and we get more mass than actual mass value. /8
Conclusion(s) /3
To sum up, the final mass of copper which is obtained after performing the experiment was greater than the initial copper mass.
Reference(s)
1.https://slate.sheridancollege.ca/d2l/le/content/348286/viewContent/5357151/View (accessed on 20.feb.2017)
2. AC1 Experiment 6/Template_Copper& Percent Yield, Ques 2.
/2
Teacher Evaluation (Students leave this part blank)
Overall organization of lab report: formatting of chemical and mathematical equations; clarity of answers; spelling and grammar; attention to details; completed cover sheet; use of headers and footers.
Laboratory performance: punctuality; time management; team work; attention to safety; use of personal protection equipment; using appropriate lab techniques; preparation of lab data book in advance of the lab; cleanup of lab work area.
/5
Total laboratory grade: /55
Professor’s suggestions for improvement:

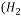 O ) is a Liquid.
O ) is a Liquid.