Secure Sockets Layer in Security Technology
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) the most widely used and most powerful measure in security technology for creating an encrypted link between the Web Server web browsers. If the link is encrypted, they use https protocol. Secure receptacle Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) is the protocol above TCP, which can protect user’s confidentiality when they sending data from a customer side to a web server; this is an important protocol due to the extension of Internet. In fact, it is a long way to make the SSL/TLS protocol fully . However there are still flaw and problems during the development of SSL/TLS, and we cannot deny that theremaybe some other potential security hole in the latest version. sequential attack is fatal for both the user and the company in using these protocols to establish a safe channel to transfer information. This article will introduce three typical attacks: Cipher suite rollback attack, narration rollback attack and password exception in SSL/TLS channel.[1].
As the web and World Wide web become common, it is necessary to think about the system security. this can be because the plaintext flowing through the web is unencrypted, it is for cracker or hacker, even a user with none programming information, to intercept the message and modify it. The way to defend personal privacy, and a way to guarantee a secure on-line commerce.. These square measure the challenge for info Technology. SSL/TLS will created a legitimate secure channel between server and shopper which may code the plaintext, then the third party who intercept the message can not disclose the first message without decrypt it.[1].
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) could be a methodology for providing security for web primarily based applications. it is designed to create use of TCP to produce a reliable end-to-end secure service. SSL is not one protocol however rather two layers of protocols as illustrated It will be seen that one layer makes use of TCP directly. This layer is understood because the SSL Record Protocol and it provides basic security services to various higher layer protocols. an freelance protocol that creates use of the record protocol is that the hypertext language (HTTP) protocol. Another 3 higher level protocols that also create use of this layer are a part of the SSL stack.SSL include two phases: handshaking and information transfer. throughout the handshaking method, the consumer and server use a public-key encoding algorithm to work out secret key parameters, during the information transfer method, each side use the key to inscribe and decode successive information transmissions[1].


![C:UsersMBAppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsTemporary Internet FilesContent.IE5VUK12QUTthief_by_beachrain-d47s4sb[1].png](https://aaimagestore.s3.amazonaws.com/july2017/0005215.004.png)
![C:UsersMBAppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsTemporary Internet FilesContent.IE5SZNQQLAIcomputer-5[1].jpg](https://aaimagestore.s3.amazonaws.com/july2017/0005215.007.jpg)

![C:UsersMBAppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsTemporary Internet FilesContent.IE5SZNQQLAIcomputer-5[1].jpg](https://aaimagestore.s3.amazonaws.com/july2017/0005215.007.jpg)
SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a technology to encrypt communications between the user and the web server. It helps to prevent hacker attacks that are based on eavesdropping. When you use a web page that is protected by SSL, you see a padlock icon that assures you that the page is secure.
3.1 Is the web site really secure with SSL?
No. SSL secures the network communication link only. Although this is an important security layer for sensitive applications, most attacks on websites are not actually done this way. Most attacks on websites are actually done in one of the following ways:
- The server is attacked directly. SSL does not protect you from this. Rather, you need to have a good IT security policy to protect your server.
- The user is attacked directly, either by infecting their PC with malware, or by using “phishing” to steal their passwords. SSL does not protect you from this, either. To protect your own PC from this, you need to use a good anti-virus program, and use lots of common sense and a small amount of paranoia when on the Internet. However, it is unrealistic to expect that all the PCs of all of your website visitors will be adequately protected.
In other words, SSL does very little to prevent the website from being hacked. It only prevents 3rd parties from listening to communications between the user and the website.
In that case, when is SSL important to have?
If you are transmitting sensitive private data over the internet, SSL is an important additional security layer. Although eavesdropping may be a less common form of attack on the website, there is no reason not to protect against it if the consequences are serious.
Although the risk to the website may not be that great, the risk to individual users may be significant in some cases. For instance, any user accessing your website from a public wifi connection (such as at a coffee shop) can be eavesdropped on fairly easily by other users at the same location. Eavesdroppers can see what is typed into forms on non-SSL sites, so the risks will depend on what sorts of forms you have.
The most obvious high-risk form is your login form, which asks for username and password. An eavesdropper can potentially obtain these login credentials and then log in as that user. How risky or dangerous that is depends on what personal information the eavesdropper can obtain, or what harm they can cause with this information. Even if the risk is low with regards to your website, you should also consider that some users will re-use passwords on many websites, so the risk may extend to sites and situations that are beyond your control.
What kind of “sensitive private data” needs protection?
Private data is information that should only be known to you (the website owner) and the user. The most obvious example is credit card numbers. If you outsource your credit card processing to an external e-commerce gateway, the transactions are protected by your e-commerce provider’s SSL. Adding SSL on your website is not necessary in this case.
Passwords are the next most obvious thing to protect, as noted above. If you do not have a membership or public user base, then your own personal admin passwords may be the only ones you need to think about. If you do not do website administration from public wifi networks, then this is not a major concern.
Note that personal information such as names, email addresses, phone numbers, and mailing addresses are not private. This is information that is meant to be shared with others. SSL does not really protect information that is already publicly available in more accessible formats such as the phone book.
(However, you do need a good privacy policy when storing and using people’s personal information, to assure your users why you need their personal information, and what you intend to use it for. This is mostly because some organizations have a history of selling their databases of personal information against the wishes of their clients. SSL does not help with this, however.)
There is a grey zone between private data (which should be known only to you and the user), and personal data (which is known and used by many others). Individual pieces of personal data may not be a big deal, but if you collect enough personal data, identity theft may become a plausible threat. Special account or identity numbers (SSN, SIN, drivers license, health care, or passport numbers for example), along with birth dates, common security questions (eg. mother’s maiden name, names of family members), and information of that nature may collectively comprise an identity that could be stolen for nefarious purposes. The more of this sort of information you collect, the more SSL might be a worthwhile addition to your security policy.
The Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) Protocol was adopted by Netscape in 1994 as a response to the growing concern over Internet security. Netscape’s goal was to create an encrypted data path between a client and a server that was platform or OS agnostic. Netscape also embraced to take advantage of new encryption schemes such as the recent adoption of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), considered more secure than Data Encryption Standard (DES). Indeed, by June 2003, the US Government deemed AES secure enough to be used for classified information.
4.1 Birth of SSL
When web browser developed their applications programmer, they found that in the dealings between internet server and web browser, there should be some security methodology to guard the message alternated between shopper and server, particularly for a few business poppers. At first, web browser established some secret writing in their applications. However, they found that the secret writing didn’t support non-HTTP applications. SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) protocol was developed that is simply above the TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) to form this security.[1].
4.2 Development of SSL
During the previous few years, SSL developed rapidly, as a result of there’s invariably some secure holes and a few previous versions of SSL cannot forestall attacker to eavesdropping or intercept properly. as an example, Version 3.0 of SSL was destined to right a flaw in previous versions 2.0, the cipher-suite rollback attack, whereby Associate in Nursing entrant might get the parties to adopt a weak cryptosystem.[1].
TLS was discharged in response to the net community’s demands for a
standardized protocol. The IETF provided a venue for the new protocol to be overtly
discussed, and inspired developers to provide their input to the protocol.
The Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol was discharged in January 1999 to
create a customary for private communications. The protocol “allows client/server
applications to communicate in an exceedingly approach that’s designed to prevent eavesdropping,tampering or message forgery.According to the protocol’s creators, the goals of the TLS protocol square measure crypto graphical security, ability, extensibility, and relative potency. These goals square measure achieved through implementation of the TLS protocol on two levels:
- The TLS Record protocol and also the TLS handshake protocol.
- TLS Record Protocol
The TLS Record protocol negotiates a private, reliable connection between theclient and also the server. although the Record protocol will be used while not secret writing, ituses bilaterally symmetrical cryptography keys, to make sure a private connection. This connection issecured through the utilization of hash functions generated by employing a MessageAuthentication Code.TLS handshake ProtocolThe TLS acknowledgment protocol permits genuine communication to startbetween the server and client. This protocol permits the client and server to talk thesame language, permitting them to agree upon Associate in Nursing secret writing algorithmic rule and secret writingkeys before the chosen application protocol begins to send data. Using constant handshake protocol procedure as SSL, TLS provides forauthentication of the server, and optionally, the client. many changes were created tothe handshake protocol, and people are going to be mentioned during a later section. [2].
5.1 what different between SSL and TLS:
difference between TLS and SSL area unit their assortment of cipher suites. SSL cipher suites generally begin with SSL, whereas TLS cipher suites begin with TLS. Notably missing in TLS area unit the FORTEZZA cipher suites, that area unit supported in SSLv3. On the opposite hand, notably present within the later versions of TLS (more specifically, beginning at TLSv1.1) area unit the AES cipher suites. The Advanced coding normal (AES) cipher suites were integrated into TLS by virtue of RFC 3268[3].
I’m pretty positive there area unit many different variations however these area unit those that actually stand out for USA. If there are a unit those you think that we should always add, be at liberty to allow us to grasp.
6.1 Public key and private key
What is public key and private key?
The association of public key (sometimes known as asymmetric key) and personal key (also known as symmetric key or secret key) will make sure the safe dealing between internet server and browser, the most perform of this combine of secret is encrypting and decrypting info. privateKey, that saves in web server, can decode the data being sent from browser. However, browser encrypts its info within public key. [1].
6.2 Public-key encryption
The sender uses public key to cipher the message, and the receiver uses private key to decipher it. So every public key owner will send his or her encoded message and solely a non-public key owner will scan the message inside decoded the message. but decrypting a message, that encrypted with public key, may be a CPU intensive, like RSA ( Rivets -Shamir-Adelman) Another usage of public key’s the sender encodes the message inside secret key, and the receiver use the non-public key to decipher that message with the associated public key. this is often economical for message authentication, like a bank server sending their digital signature encrypted with private key, so any client will decipher the message inside private key and verify the message.[1].
6.3 How SSL secure a transaction
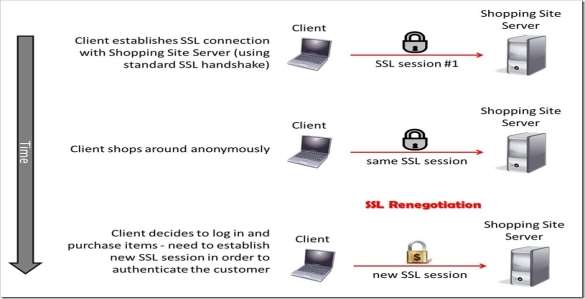
Figure 2SSL renegotiation messages
SSL renegotiation messages (including varieties of ciphers and secret writing keys) ar encrypted and so sent over the prevailing SSL connection. This feature is sweet as a result of it will produce a secure SSL session supported the very fact that a secure affiliation is already established. SSL renegotiation is helpful in many things wherever a normal SSL session is already established. Here ar some examples[2]:
- Client authentication is required
- A different set of encryption and decryption keys are needed
- A different set of encryption and hashing algorithms are used.
The shopper or the server will request renegotiation at any time. For the shopper to request renegotiation the shopper sends a “Client Hello” message within the already-established encrypted channel and also the server responds with a “Server Hello” and so the negotiation follows the conventional shake process. The server will initiate the renegotiation by causing the shopper a hello Request message. once the shopper receives the request, the shopper sends the “Client Hello” message and also the shake process takes place.[4].
One fast note of clarification: the shopper and server also can complete a session beginning vice a session renegotiation. A session beginning essentially resumes a previous session (using a previous session ID), and it saves the shopper and server the computing work of generating new cryptography keys. Renegotiation could be a method by that the complete shake method takes place over an already existing SSL association[1].
6.4 SSL/TLS From PHP (Server to Server)
As much as I love PHP as a programming language, the briefest survey of popular open source libraries makes it very clear that Transport Layer Security related vulnerabilities are extremely common and, by extension, are tolerated by the PHP community for absolutely no good reason other than it’s easier to subject users to privacy-invading security violations than fix the underlying problem. This is backed up by PHP itself suffering from a very poor implementation of SSL/TLS in PHP Streams which are used by everything from socket based HTTP clients to the and other file system functions. This shortcoming is then exacerbated by the fact that the PHP library makes no effort to discuss the security implications of SSL/TLS failures.
If you take nothing else from this section, my advice is to make sure that all HTTPS requests are performed using the CURL extension for PHP. This extension is configured to be secure by default and is backed up, in terms of expert peer review, by its large user base outside of PHP. Take this one simple step towards greater security and you will not regret it. A more ideal solution would be for PHP’s internal developers to wake up and apply the Secure By Default principle to its built-in SSL/TLS support.
My introduction to SSL/TLS in PHP is obviously very harsh. Transport Layer Security vulnerabilities are far more basic than most security issues and we are all familiar with the emphasis it receives in browsers. Our server-side applications are no less important in the chain of securing user data. Let’s examine SSL/TLS in PHP in more detail by looking in turn at PHP Streams and the superior CURL extension.
Figure 3example of google chrome
Our attacks are supported the subsequent scenario: the assaulter sniffs an oversized number of SSL connections encrypted with RC4,waiting for a “hit”; that’s the arrival of a weak key. Once a weak key arrives, the assaulter predicts the LSBs of the key streambytes, and uses these to extract the LSBs of the plaintext bytes from the cipher text with important advantage. In order to satisfy this state of affairs, the assaulter has to determine that SSL sessions ar those within which weak keys were used. For this isolation, the assaulter will use the actual fact that the primary encrypted bytes embrace the SSL “Finished” message and HTTP request, both having foreseeable data. Thus, once a weak key is used, the plaintext patterns are XOR-ed with key streampatterns, generatingcipher text patterns visible to the assaulter. and different previous attacks on SSL use little applied math biases to combination little items of plaintext data. so as to make this aggregation doable, the target object should be encrypted over and over, with a similar key in and with totally different keys.[5].
7.1 Decrypting traffic where the private key used for encrypting the information is available.
This is useful for situations where the traffic in the network is relayed through a transparent SSL proxy and the user has access to the private key used by the proxy for encrypting the traffic sent to the clients.[6].
7.2 Decrypting traffic in situations where the session keys are available.
This situation applies for traffic generated by Mozilla Firefox and Google Chrome browsers in rectify mode. The browsers can dump SSL session keys in NSS (Network Security Services) log format. The file is made within the path such that by the SSLKEYLOGFILE atmosphere variable.[6].
7.3 How Is the Attack Accomplished?
Using the renegotiation attack, associate degree attacker will inject commands into an HTTPS session, downgrade ahttps association to a HTTP association, inject custom responses, perform denial of service, etc. That explains to some extent however serious the matter is. it’s easier to know however the attack is accomplished.[7].
8.1 Advantages of SSL Certificates.
Entrust Advantage SSL Certificates secure ecommerce, communications and personal data passed from browser to internet server and between servers. Entrust Advantage SSL Certificates supply bigger set-up and preparation flexibility by permitting you to add a second absolutely qualified name for free of charge and secure domain.com once your certificate is for WWW.domain.com. Plus, you get added security services that notice malware on your website} and protect it site from obtaining blacklisted.
8.2 Disadvantages of SSL
With such a large amount of blessings, why would anyone not use SSL? are there any disadvantages to exploitation SSL certificates? value is a noticeable disadvantage. SSL suppliers ought to started a trustworthy infrastructure and validate your identity therefore there’s a value concerned. as a result of some providers are so renowned, their costs are often overpoweringly high.[8].
BEAST leverages a kind of science attack called a chosen-plaintext attack. The attacker mounts the attack by selecting a guess for the plaintext that is associated with a famed cipher text. to see if a guess is correct, the attacker wants access to AN encoding oracle7 to visualize if the encoding of the plaintext guess matches the famed cipher text. To defeat a chosen-plaintext attack, common configurations of TLS use 2 common mechanisms: an data format
vector (IV) and a cipher block chaining mode (CBC). an IV is a random string that’s XO Red with the plaintext message before cryptography even if you encrypt the same message double, the cipher text are totally different, because the messages were every encrypted with a special random IV. The IV isn’t secret; it simply adds randomness to messages, and is sent along with the message within the clear. it might be cumbersome to use and track a new IV for
every coding block (AES operates on 16-byte blocks), so for longer messages CBC mode simply uses the previous Cipher text block as the IV for the following plaintext block.[9].
9.1 ATTACKER’S PERSPECTIVE
In a single session the same secret/cookie is sent with every request by the browser. TLS has an optional compression feature where data can be compressed before it is encrypted. Even though TLS encrypts the content in the TLS layer,
an attacker can see the length of the encrypted request passing over the wire, and this length directly depends on the plaintextdata which is being compressed. Finally, an attacker can make the client generate compressed requests that contain attacker-controlled data in the same stream with secret data. The CRIME attack exploits these properties of browser-based SSL. To leverage these properties and successfully implement the CRIME attack, the following
Conditions must be met:
- The attacker can intercept the victim’s network traffic. (e.g. the attacker shares the victim’s (W)LAN or compromises victim’s router)
- Victim authenticates to a website over HTTPS and negotiates TLS compression with the server.
- Victim accesses a website that runs the attackers code.[9].
Secure sockets layer (SSL) is used to protect voluminous network users however how vulnerable is it? Over the last…
several years, there has been associate array of attacks designed to subvert SSL. whereas the technology is basically secure, attackers are invariably probing for loopholes to bypass security protocols and standards. And SSL could be a huge target. it’s wont to protect sensitive hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) traffic. Attackers, United Nations agency prefer to assume outside the box, are invariably seeking new ways in which to realize access to sensitive data. Let’s consider a number of the different ways in which hackers are attempting to break SSL.
- Trick, no treat: Trick the user to accept a foul certificate. this is often the classic approach once targeting users of SSL. the concept is to get the user to click through to a website despite the fact that a warning or error is flaunted to the tip user. whereas this attack is simple to launch, it needs the victim to just accept a certificate that clearly has issues. Most users can notice this kind of fraudulent activity; so, the threat level is low.
- Fraudulent certificates: whereas this approach might seem far-fetched, it’s been winning within the past. in a very few cases attackers are able to acquire valid certificates and use them maliciously. In one case, hackers breached a Dutch certificate authority’s security in 2011 and so created phone certificates for sites like Yahoo, Google, WordPress et al. With possession of valid certificates, the attackers got past HTTPS protections. Still, the threat level of this attack remains low.
- Take away the SSL and send data via clear text: In 2009, a new technique to subvert SSL was pioneered with one thing known as SSLStrip. rather than trying to urge the user to click through warnings, this tool acts as a proxy and strips off the S in httpso the user is instead bestowed with HTTP. SSLStrip conjointly permits the assaulter to gift the user with the favicon “lock” therefore the solely indication that one thing is wrong is that the browser’s show of http rather than HTTPS. If the user doesn’t notice this one small detail, the attacker will gain access to secure data. The threat level of this attack is medium.
- Crack the keys: Most certificates presently use 1,024-bit or 2,048-bit keys. The 2,048-bit-length keys are extraordinarily robust and would need eons of your time to crack employing a standard PC. That said, it’s been reportable that the National Security Agency has created nice strides in gaining access to SSL traffic. whereas some theorize that the NSA could have discovered new quantum computing techniques, it’s additionally entirely potential that the agency has merely obtained cryptography keys or maybe placed backdoors (entry points) into computer code and hardware. The threat level of the NSA or others accessing secure data during this approach is unknown.
- Man in the middle: This attack may be a style of active eavesdropping within which the attacker makes independent connections with the victim and relays messages to the server. Case in point: Lucky 13, named once 13-byte headers in Transport Layer Security Media Access management calculations. whereas this ciphertext attack is in theory potential, it’d need a controlled setting and a awfully long quantity of time; so, the threat level is taken into account terribly low.
- Side-channel attacks: Over the last several years, several side-channel attacks are incontestable that may be used to recover http requests and cookies used for authentication. Browser intelligence operation and Exfiltration via adaptive Compression of hypertext (BREACH) is one example. BREACH leverages compression and takes advantage of http responses, that are compressed victimisation mechanisms like gzip. For the applying to be vulnerable, it should use HTTP-level compression, mirror user input in http responses and expose cross-site request forgery tokens in http response bodies. whereas on paper attainable, controls is accustomed mitigate this attack, and therefore it’s thought-about an occasional threat.
10.1 What is DROWN?
It is a heavy loophole infect protocol HTTPS and different services that consider TLS, SSL and a few of the essential secret writing protocols for the security of the internet. These protocols enable everybody on the web to browse sites and electronic messaging, looking and transfer of vital data while not permitting a third party the flexibility to ascertain what’s being changed between a user and also the World Wide internet.The name of the shortcut Decrypting RSA with Obsolete and Weakened encryption.
10.2 

What do you get it from penetrating this gap?
Gets anything is passed between the user and the server, and includes, for example, user names and passwords, account numbers, e-mails, instant messages, important documents, and according to some Scenarios can also forward the work of spoof secure site content and intercept the requests and what the user sees.[10].
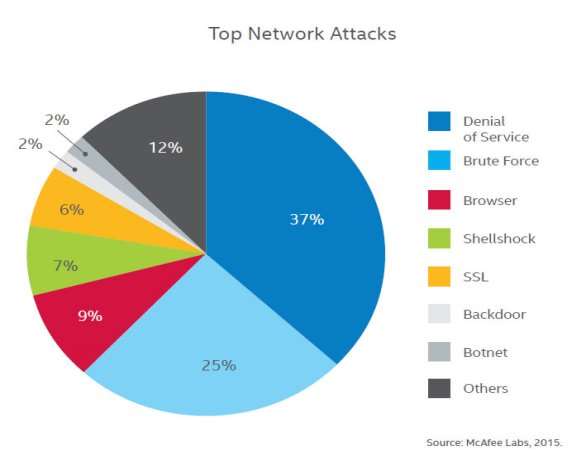
When you log in to an Access Enforcer, or any UTM device, you will see a number of network attacks detected and blocked. The number may be in the thousands, or even hundreds of thousands. Many of these attacks are scans – precursors to attack. Depending on your settings, a good number might also be firewall policy violations. But what are other types of network attacks? What are the most common ones today? One answer comes from the latest Threat Report from McAfee Labs. The chart below aggregates data from the company’s network of millions of sensors across the globe. It shows the most common network attacks detected in Q1 2015.[5].
SSL is important to net security. It provides a robust sense of confidentiality, message integrity, and server authentication to users. The business
of e-commerce is tied closely to client confidence within the operation of SSL across world wide web. within the future, SSL termination devices are
able to handle additional transactions at a quicker rate. The secret writing of key lengths and therefore the cipher suites used also will still evolve so as
to ensure the safety of sensitive info over the net. This way, e-commerce are ready to still grow in quality as users
grow additional intimate in searching and banking on-line, and clutches new on-line applications .
Â
[1]”Three attacks in SSL prot ocol and their solutions.” Hong lei Zhang , .
[2]”SANS Institute.pdf.”Holly Lynne McKinley, .
[3]”Secure Socket Layer (SSL) Secure Socket Layer (SSL).” Raj Jain, .
[4]”Transport Layer Security..”Giuseppe Bianchi, .
[5]”Attacking SSL when using RC4.”Imperva , .
[6]”Sourcefire_SSL_Appliance_Administration_and_Deployment_Guide-v36.pdf.” .
[7]”Cyber Security.” Planning Guide
[8]”secure sockets layer.” .
[9]”ATTACKS ON SSL.”Pratik Guha Sarkar ,Shawn Fitzgerald, .
[10]”drown-attack-paper.” .