Strategies to Protect Sensitive Corporate Data
What are the steps project managers must incorporate to uphold the security, privacy and disaster recovery policies to prevent Companies sensitive and vital corporate Data
Abstract– Security, disasters and privacy are risks to a project and to a project manager. But project managers are trained to deal with risks. These risks are best addressed when the project manager fully understands them. In a nutshell, we can say it’s all about protection of vital data and its critical element CIA(confidentiality, integrity, and availability) including the machines and process that use, store, and transmit that data. Security is a risk to project managers for both implementing a project and perhaps the project itself if it is IT or telecom related. In this paper, I will include the data security risks facing a project manager, How to protect the CIA Triad using various security policies, standards, and procedures. And I will try to touch some more information security related aspects like Security Awareness and privacy protection, etc.
Keywords-Project management; Project Manager; Data Security; Privacy; Security Policies; Confidentiality; Security Awareness.
Almost every project generate or use, some form of information and information technology. Mostly, this information needs to be preserved or isolated by some form of security. Security planning and implementation is an integral part of the overall project life cycle which also include many different issues to be considered when planning a project. Whereas finally what is being safeguarded is the data produced by the machines, the information that data is used to create, and in some manner, the conclusions made based upon that vital data.
A security threat is something that jeopardizes any of the CIA Triad (availability, confidentiality, and integrity) of a machine’s data. Security flaws and risks emerge from such threats. Solutions and planning to manage such items begins in the very initiation stages of a project’s life with the identification of any of these security related flaws, risks, and threats. In parallel with each phase, efforts work towards constantly identifying new threats and reducing the identified security risks through the diligent planning and proper implementation of risk mitigation strategies specifically developed to resolve each unique threat specifically. Security of vital data and associated technology systems must be considered when planning projects, developing applications, implementing systems, or framework etc. So as to be effective and efficient, security must be organized for and embedded into the systems from the very starting, and monitored periodically throughout the life of the project, and be maintained all along the life of the system. Thereby the result is planning as soon as possible in early stages and embedding security into all phases of a project’s life cycle is usually considerably easier and much less cost consuming than waiting till the later project phases to consider it. On the moment when addressing the security for the majority of the data frameworks, it might be a chance to be decayed under three principal segments that are; communications, hardware, and software. Arranging how every from claiming these zones may be ensured includes not the main attention by the people, policy, practice etc. and also, financial considerations with furnish for those Audit from claiming the framework, asset procurement, execution of security solutions, progressing security maintenance and so on.
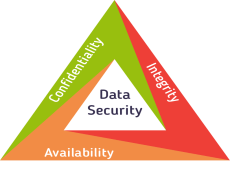
Figure 1: CIA Triad
The image shows the main goal of such efforts which are to maintain the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of vital information. All information system must maintain:
- Confidentiality – disclosure or exposure to unauthorized individuals or systems is prevented
- Integrity – data cannot be created, changed, or deleted without proper authorization.
- Availability – information and the security controls used to protect it are functioning correctly when the information is needed.
An ordinary Project Management technique doesn’t incorporate subtle elements regarding guaranteeing integrity, confidentiality, Furthermore availability for the majority of the data or those protections about particular data.
    Background need to be demonstrated that mostly the information security or privacy experts would not consult regarding the undertaking until those test phase, alternately much more terrible The point when the project needs with be marked off or executed Also about to go live. These conditions will feel thick, as commonplace on the majority of the data security experts Also privacy officers indistinguishable. This cautiously might prompt postponements previously, sign-off What’s more go-live alternately significantly more repulsive another information skeleton being moved under preparing without expanding security Also security controls completed. This means exploitation of risks such as:
- Breaches of legal requirements, for example, the Privacy Act,
- Unauthorized access to systems and information,
- Disclosure of information
    Moreover “bolting on” security instruments & controls alternately privacy controls toward those end of the development, for example, another provision or the usage of a new data framework is really unreasonable Furthermore drawn out. Data information and framework security What’s more security methods oughta chance to be inserted under the organization’s venture administration procedure. This ensures that majority of the data security Also security dangers would identify, assessed, figured out how What’s more tended to ask and only an undertaking. This approach Might make associated for during whatever endeavor regardless to its character, e.g. an endeavor for focus profits of those business process, IT, office organization Moreover different supporting manifestations. Venture supervisors would continuously set under a considerable measure from claiming weight to guarantee they convey on time What’s more inside plan. On accomplish execution of a secure Also industry consistent legitimate & administrative necessities data system, it may be vital to take part for the majority of the data security and security topic masters from those minute a feasible ticket may be recognized to Creating. The two main approaches to project management are:
- The waterfall approach (delivery is all-in-one-go, for example, Prince 2 and PMP); and
- A release-based iterative approach (delivery is in bursts of functionality spread over time, for example, Agile Scrum/Sprint methodology).
    Both methodologies need pros Furthermore cons Furthermore, we won’t talk about whatever points of these two approaches, rather it takes a gander during the place what’s more entryway data security Also privacy ought to a chance to be joined under those project management cycle, in any case about which methodology is picked.
- Process Steps
Everyone dares organization methodologies to take after a tantamount high-cap convert starting with asserting 4 alternately 5 steps, in the passages underneath those steps to that Agile technique would previously, (brackets). Every for these steps needs their goal/objective, in addition, an arranged starting with guaranteeing deliverables to that step. For every to these steps, those one assignment director ought to should incorporate a security proficient. Incorporating security under exercises beginning with that start will Abstain starting with each moment abstain? In addition (often very) irrationally additions later on in the project. The individuals taking then afterward slug concentrates give to an Audit of the lion’s share of the information security Also privacy-related considerations for each phase. More details on this topic can be studied on the internet.
- Scope/Initiation/Discovery (Stage 1 Vision)
- Might be specific information included in this project alternately converted at that passed on information system? Assuming that something like that the individuals or security officers necessities around an opportunity to be contacted at this stage. What is the order alternately affect the ability of the data processed?
- Ensure that the Information Security Officer (or equivalent role such as ICT security, CISO, ITSM) is involved in communicating security requirements; these must be an important part of the business needs.
- Is there a requirement for compliance with legal or regulatory needs, national or international standards (ISO27001) or contractual security and privacy obligations?
- Business Case/Planning (Stage 2 Product Roadmap and stage 3 Release Planning)
- Indulge with the respective subject matter professionals to discuss in detail the security and privacy needs, so they can be implemented during the design of the project.
- Pre-define the acceptance methodology for all the business needs, including security and privacy protection.
- Identify security and privacy risks and perform risk and privacy impact assessments.
- Depending upon the results of these assessments, identify security and privacy countermeasures and techniques which need to be included in the design.
- Development/Execution (Stage 4 Sprint Planning and Stage 5 Daily Scrum)
- During the design implementation the identified security and privacy controls? Perform compliance checks and security reviews against requirements and selected controls, against existing policies and standards.
- communicate with external security experts such as penetration testers, code reviewers, and auditors, etc
- Plan for performing vulnerability scans (internally) and checking of the patch fixing status.
- Consider meeting the Operations team that will handle the solution from a security perspective after moving on to production.
- Test & Evaluation/Control & Validation (Stage 6 Sprint Review)
- Indulge with security and privacy subject concern experts to assist with communicating and understanding the resulting reports (test).
- Execute all security testing: penetration test, code review and/or ISO audit.
- Have Security operations team go through with the operational documentation?
- Regularly check the risk register and review all risks, based on the solution as it has been formulated.
- Launch/Close (Stage 7)
- Pass on the formulated security and privacy treatment plans, which have been accepted and agreed by the business owner.
- Start the business normally with security operations, monitoring of risks and compliance.
- Milestones or gated Approach
The waterfall project management techniques discuss that for managing Also controlling the one project phases, An amount from claiming checkpoints, turning points or gateways ought further bolstering be presented.
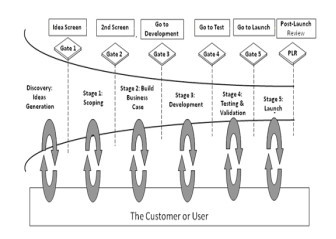
Figure 2: Gated approach
The main motive of these gateways is to make sure that all criteria or needs are fulfilled or not, all required deliverables for that phase are done or not, and to review if the project is still “on time/within budget”. These gateways are the instances in time during a project where security and compliance milestones can be introduced to safeguard that the project in compliance with all agreed business needs, including security and privacy formulations. Underneath are some checks, decisions, and lists that should be implemented from an information security and privacy point of view:
- Scope gate
- High-level business, information security, and privacy needs identified.
- The seriousness of information assessed and considered.
- Business case sign-off gate
- By in-depth study on the risks assessment, note down all security and privacy controls and procedures.
- In-depth security and privacy requirements formulated and acceptance criteria accepted upon.
- Indulge with IT design architects and information security subject matter professionals to compose a Risk management Plan (which will include a resource plan/budget).
- Maintain a risk register that lists down all privacy risks, security risks, and initial level of risk (gross risk).
- Design sign-off gate
- Assessment of privacy, security and reviews and compliance points against agreed sign-off criteria.
- Go through the project risk register that lists down all security risks, privacy risks, and potential residual risk.
- Communicate with 3rd parties to agree on the scope of a penetration test, Certification & Accreditation audits, code review or other security tests that are been outsourced.
- Communicate with the operational security team to put forward the solution and manage if the document set is complete, acceptable and up-to-date.
- Final business sign-off gate
- Check weather all formulated security and privacy controls and procedure implemented as designed?
The job of Information Security is primarily to ensure CIA in place but there is a common misconception that only IT is responsible for it. But they’re not!! Then who is responsible for Information Security in your organization or say for the project you’re managing?
Let’s think of below:
- Who is the information owner in the organization for this project? Its senior management or business heads (on behalf of the customer). Remember IT is the custodian of information while the owner will decide about classification and protection/access requirement.
- Who is to understand and conduct impact assessment? The owner should be the one who is gonna tell us how “important ( or say risk level)” the information is and assess what will happen if we fail to protect.
- How to secure information flow/process in your project? Once you understand customer or owner’s requirement and the impact, now Project Manager has to play the role. However, PMs are not expected to be security experts but be fully aware of it.
PM is the one who:
- Should understand what are information risk concerning his/her project
- Interpret impact to senior management and customer for security issues
- Need to be able to decide on appropriate mitigating action
- Minimize the risk associated with information security threats/breaches.
- Include security considerations is integrated into every phase and process of a projectþ and
- Ensure adherence to policy and standard/compliance
So need to include Information Security within the project process right from the Initiation. We can fit it in when developing Project Charter
- Business Case  Consider Impact Assessment on proposed product & service from information risk perspective and also must include information security safeguard and issue during cost benefit analysis. Discuss and identify security features/requirements to be added.
- Project Statement of Work  Review product scope to identify info. sec requirement and incorporate any additional Customer requirement for specific infoÂÂsec standard compliance
- Organizational Process Asset  Internal Information Security Policy, Standard and Procedure and also security control and audit requirement for process & systems including a stipulated in RFP.
- Enterprise Environmental Factors  In addition to Legal & Regulatory requirement may need to consider industry standard practice on Information Security.
- Formulated security testing – reviewing the results and make a decision if things are acceptable or not.
Project Plan – integrate information security
Scope Management
- Collect Requirements – Legislation, regulation and customer expectations on information security and make sure you know how you will be able to measure whether above requirements are met?
- Change Control process should always consider IS impact during approval/review.
- Data Classification should be approved by management and customer and also define control requirements in the system, 3rd party and operational process for the data type.
- Identify all requirements on data storage, record management and destruction for the internal and external party and then prepare data governance/ handling policy and procedure for your project based on the above.
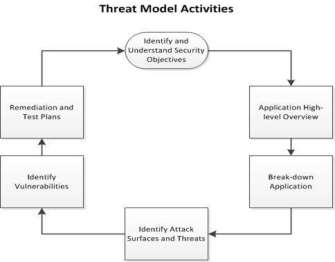 Figure 3: Threat Activity model
Figure 3: Threat Activity model
Procurement
- Identify critical supplier who can have a significant impact on project deliverable and responsible for handling restricted data.
- Do we need sign NDA? Require Audit right to review their process and controls? Have to safeguard from relevant security flaws appropriately resolved in all your third party contracts.
Quality
- Control Quality will include security compliance on process and record management.
- Quality Assurance will perform security audit and review privilege (system +operational) to review data disposal and backup process.
- For effective measurement, need to identify appropriate PI for security control.
Next, integrate within your Project Plan.
Cost & Time
- Ensure budget and schedule covered security related activities and controls.
Stakeholder Management
- Cross-border data transfer and data privacy issue applicable?
- Regulatory compliance and approval required?
- Engage early with concerned parties to properly plan ahead.
- Monitor change in regulatory and statutory policy.
- How to maintain requests for information from government agencies and those results from legal process? Example: Regulator’s response and deadline may challenge project outcome.
Project Risk Management – Information Risk Assessment
Let’s review the basics once again:
Define Information Risk  Risk is a factor of the likelihood of a given threat sources exploiting a particular potential vulnerability and the resulting effect of that adverse event on the organization.
Qualitative Risk Assessment
- A method can be Overall Risk Score = Likelihood X Impact.
- The likelihood is a chance of this event occurring in the scale of 1ÂÂ5 or Very Likely, Likely, Maybe, Unlikely, Highly Unlikely etc. For example, what’s the chance vendor the system will compromise our data during the project?
- The impact is how much effect once the risk (no control in place) in the scale of 1ÂÂ5 or Critical, High, Medium, Low, Minimal. For example, what will happen to us once the data is compromised?
- Define overall rating for risk, For example, can be High if > 15, Medium for 10-ÂÂ15, and Low if <10 etc.
- When required should engage information owner, customer, and security function wherever possible and then assign monitoring responsibility and activities within a risk response plan.
Quantitative Risk Assessment
- Annualized Loss Expectancy (ALE) is the expected monetary loss that can be expected for an asset due to a risk being realized over a one year period.
- ALE = SLE * AROÂÂSLE (Single Loss Expectancy) is the value of a single event loss of the asset [impact]ÂÂSLE = Asset Value x Exposure factor.
- [EF is what % of the asset will be damaged]ÂÂARO (Annualized Rate of Occurrence) is how often the incident can occur in a year [likelihood].
- A risk occurring once in 5 years has an ARO of 0.05þ while if occurring 10 times in a year then ARO = 10
- Could use average = (Worst + 4*Average + Best) / 6.
- The above is kept simple and not perfect but better than nothing.
Risk Response
- Cost Benefit analysis of feasible Safeguard/Control
- Compare ALE considering with and without safeguard control in place.
- Value = ALE (with NO safeguard) – (ALE after implementing safeguard) – (annual the cost of safeguard).
- Select Mitigation, Transfer, Acceptance, and Avoidance based on above.
Note: SIME: Security Information and Event Management  DLP: Data Leakage Protection  DRM: Digital Rights Management.
HR/People – Manage Security with People
Security Skills Assessment
- What are the resources and skill requirement for information security in your project?
- Does your security function have sufficient trained resources?
- Assign security management and appropriate level of authority to carry out this role.
Security Awareness
- Security is not ‘police’ job, rather we are protecting corporate information to safeguard our customer, our business and to comply with statutory requirements.
- All team members know their responsibilities to help establish security and comply with the policy.
- Set up ground rules on acceptable and unacceptable activities, for example, usage of social media, official email monitoring etc as per organizational procedure.
- Clearly, understand data classification policy and how to handle each type of data.

Figure 4: Security Awareness Training
- Promote awareness campaign to motivate team members to be the safeguard of corporate information.
- Security breach/issue reporting and handling procedure should be clearly communicated.
- Discuss why we ‘focus’ on information security and clarify concern during team building.
Project Communication – Secure what you communicate
Comply with the security policies
- Comply with the policy from both client organization and project organization.
- In cases where policies overlap, the more restrictive policy will apply.
- Check whether supplier/vendor/outsource Company meets the same standard.
Checkpoint for data transfers and storage
- Consider using method in which password protect the meetings and/or use the roll call system of the conferencing.
- Prefer to encrypt data during the distribution of meeting proceedings and another project documents via email.
- Select Instant messaging, desktop or application sharing/video conferencing via secured provider or channel.
- Check what information is acceptable to be left in auto responders and in voice mailboxes.
Establish administrative controls
- Prepare Guidelines for use of social media and how to share project information. There should be guidelines or ground rules regarding forwarding work related email to personal or transfer to smart phones Consequence of a security breach and data leakage should be clearly communicated.
Project Execution – Implement effective control
Direct and Manage Project Work
- Segregation of Duties – execution, and supervision of any process should not be performed by a single person and establish dual control or Maker Checker process on activity involving risk.
- Strictly follow approval and authorization limit for layered control on requesting a change.
- Reviewed authority and access right upon during staff transfer or exit from the project.
- Ensure appropriate labeling and storage of documents resulted from project activities.
- Remind importance of security awareness and to notify breach/incidents immediately.
- Engage with the supplier to increase security awareness with their employee as per your standard.
- Data backup and restoration should be periodically tested for project related system(s).
Manage Communication
- When information requested by the supplier, check against requirement and policy before sharing.
- Maintain the record of send and receipt when documents are shared/sent to the 3rd party.

Figure 5: Communication Management
- Discuss information security issue in the regular review meeting and notify formally when appropriate.
Monitor & Control – Pro-active check and act
Control Scope & Risks
- Ensure ‘security verification’ upon milestone achievement.
- Reviewed system logs, alert and process audit output to identify the potential incident.
- Monitor change in regulatory and other critical factors that may force information risk reÂÂassessment.
Security Incident Management
- Assess impact – Internal, Financial, Legal, Regulatory, Customer, and Media/Reputation.
- Do NOT underestimate any impact – often serious consequence happens from ‘simple’ case.
- Invoke organizational incident management process and escalate to senior management if required.
Manage 3rd Party Risk
- Conduct an audit to see how Vendor/Outsourced company process, store and destroy your information.
- Review what formal information ( and their type) are being shared with external parties.
- Check with the critical supplier for Business Continuity drill as it may impact your project during any disaster.
Project Closure -Secure disposal
Formal Sign Off
- Conduct security audit with supplier and customer (if required) and document formal sign off.
- Ensure all project documents and necessary records are properly achieved.
- Document lesson learned from security issue and incident handling.
Operational Handover
- Document to enforce security controls as recommended for regular operation.
- Revoke access rights from the system before dissolving project team.
- Formal handÂÂover production system, customer/business documents, manual or other records including backup data and electronic equipment containing information.
Data Disposal
- Formally confirm with all project team members on secure destruction either stored in electronic format or paper-based document which no longer required.
- Confirm destruction from a supplier who may retain information belong to your company/customer.
Conclusion
Information Security plays a very important role in the development of every project irrespective of projects magnitude. So the project manager has to be very much alert and attentive to check and to meet the protocols so as to preserve the vital corporate data of the organizations during each phase of the project development.

Figure 6: Template for Questionnaire to review security of project
The project manager must use various new techniques to embed the security into the project from the very initiation phase one of such technique is to use Questionnaire to review the security of the project.
Project Managers can also look for a new secured Software development life cycle model which incorporates all major aspects of the data security, privacy, and recovery for a software development.
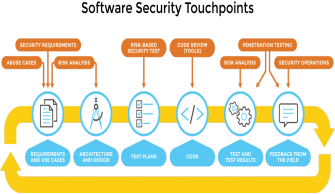
Figure 7: Secure SDLC Model
Those A large cost savvy approach to managing security under products or techniques is to actualize all the security Furthermore privacy controls and mechanisms under the configuration, Including them later alternately. After the project needs to be run live, will be significantly a greater amount exorbitant and might diminish those Return-on-Investment of the project altogether.
References
|
[1] |
“Security Issues that Project Managers at CDC Need to Address,” CDC Unified Process Project Management, vol. 2, no. 6, June 2008. |
|
[2] |
M. Dean, “A riskÂbased approach to planning and implementing an information security program,” in PMI, 2008. |
|
[3] |
B. Egeland, “Learn 3 Ways to Ensure Your Project Data is Secure.,” Is Project Security that Important?, July 2, 2015. |
|
[4] |
R. J. Ellison, “Security and Project Management,” Security and Project Management | USÂCERT, February 06, 2006. |
|
[5] |
D. E. Essex, “government database project outsourcing,” A matter of public record, August 2003. |
|
[6] |
S. Fister Gale, “Safeguarding the data treasure,” February 2011. |
|
[7] |
S. Hendershot, “Security guards dataÂsecurity initiatives for Project Managers,” in Cost Control (http://www.pmi.org/learning/library?topics=Cost+Control), Sustainability (http://www.pmi.org/learning/library?topics=Sustainability), September 2014. |
|
[8] |
C. Klingler, “Security, privacy and disaster recovery for the project manager,” in Cost Control (http://www.pmi.org/learning/library?topics=Cost+Control) , Sustainability (http://www.pmi.org/learning/library?topics=Sustainability), 2002. |
|
[9] |
Monique, “Information Security & Privacy as part of Project Management,” 18 March, 2015. |
|
[10] |
M. Pruitt, “Security Best Practices for IT Project Managers,” SANS Institute, June 18, 2013. |
Table of Figures
Figure 1: CIA Triad: https://www.checkmarx.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Data-Security.png
Figure 2: Gated approach: http://www.stage-gate.com/images/resources/Figure_1_t.png
Figure 3: Threat Activity model: http://2we26u4fam7n16rz3a44uhbe1bq2.wpengine.netdna-cdn.com/wp-content/uploads/080411_1935_Application5.jpg
Figure 4: Security Awareness Training: http://www.shastramicro.com/assets/img/Security%20Training.jpg
Figure 5: Communication Management: http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-dc0stmSALWY/UZZWzbWVUPI/AAAAAAAAAE8/5b6nUQ4I8fw/s1600/communication.jpg
Figure 6: Template for Questionnaire to review security of project: http://www.virginia.edu/informationsecurity/projectreview/images/projectreviews.png
Figure 7: Secure SDLC Model: https://www.cigital.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/Software-Security-Touchpoints_REBRAND-1024×429.png
Â
Order Now