Supply Side Policies
Supply Side Policy
Supply Side Policy
Â
Supply Side Policies are policies which are designed to increase the ‘productive potential’ of an economy
- They tend to be associated with the right of the political spectrum.
These are mainly the macro-economic policies which are aimed making
the marketing also industries to function proficiently and subsidise for a much faster underlying-rate of development.
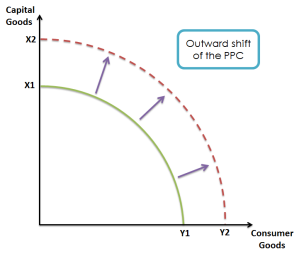
Policies that are successful can have the effect of the LRAS curve shifting on the right which is leading to a raise in the impending output.
- However, governments of any colour may use them!
Furthermost governments consider by improving the supply side policy routine is the way to achieve a sustained growth without it causing it to rise in the inflation. By keeping inflation under control can achieve a steady sustainable growth of GDP getting more people back into work and lifting the average living standards, which can be improving trade performance on the balance of payments and achieving equitable distribution of income and wealth.
 What have they set out to do
What have they set out to do
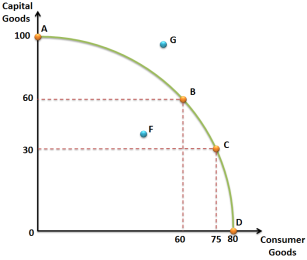
- As shown in these diagrams. Invalid source specified.
- They hope to achieve an increase in Long Run Aggregate Supply
Long run aggregate supply is the longer ability to the economy is to produce goods and services that meet the demand and is based on the state of production technology which the availability and the quality of factor inputs.
- Improvements to Education – Increases productivity and quality of the Labour  force.
To have better education and training and improve the skills will improve labor productivity, and with the marginal output that’s generated by factors inputs. By using the tax system can provide incentives and help to stimulate factor output instead of altering the demand which can be seen central supply side policy. With education training to improve skills and flexibility, mobility, spending on education and training to improve on the labour productivity for the supply side policy. (Fogiel, 2002)
(http://www.economicsonline.co.uk/Global_economics/Supply-side_policies.html)
- Tax Cuts – Encourages an increase in supply of labour, incentive to work
In general, the measure increases the personal allowance to £11,500 for 2017/18 with the basic rate increase to £33,500 for2017/18 and the higher rate threshold will be £45,00 2017/18. The government have an objective to raise the personal allowance to £12,500 with the higher rate threshold to £50,000. These measures are affective from 6th April 2017 or after this date.
- Cuts to Corporation Tax – Attempts to stimulate investment from business
In the autumn statement November last year, government intends to offer British business a olive branch which followed a series of disputes by vowing to cut corporation tax to a record low, more than 15% which trump hand promised. This will be the lowest of all the world’s top 20 economies. (Dominiczak, 2016)
Income tax

If you’re on a moderate income you’ll be giving up more than a third of your wages to the taxman, but with the new tax allowance your free personal allowance which is going up, and rising to £11.000 from the £10,600 and then the following year from the 6th of April 2017 looks like we all getting a pay rise!!
By reducing tax cuts, could improve the economy by boosting spending. (D.Hyde, 2010)
Tax Banding
The standard VAT rate is 20% VAT rates for goods and servicesÂÂ
VAT rates for goods and services
|
Rate |
% of VAT |
What the rate applies to |
|
Standard |
20% |
Most goods and services |
|
Reduced rate |
5% |
Some goods and services, e.g. children’s car seats and home energy |
|
Zero rate |
0% |
Zero-rated goods and services, e.g. most food and children’s clothes |
(Gov.uk, 2017)
Production Frontier (PPF) this is a hypocritical representation of a maximum level of output goods by shifting resources with other factors and that all inputs used efficiently.
Production Possibility Frontier (PPF) this is a hypocritical representation of a maximum level of output for two goods by shifting resources with other factors and that they all inputs used efficiently. (Fogiel, 2002)
- Chancellor of the Exchequer had resisted pressure from Brussels to scrap Britain’s VAT on children’s clothes.
Margaret Thatcher won the zero-rates in 1980s, this was when Commission tried to pull the national indirect policies.

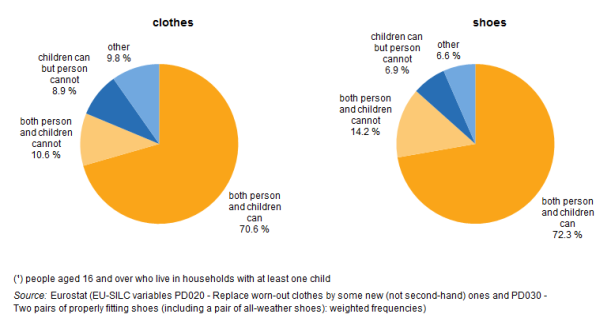
- Monetary poverty was the most widespread form of poverty or social exclusion among children affecting almost 11 % of children in the EU-28 in 2013.
Tax on children’s clothes
Now with Britain having no tax on children’s clothes and the EU wanting to put it on, some family’s will not have the ability to afford new clothes and shoes within their household for all their children.
At the moment with Britain having no tax on children’s clothes and the EU wanting to put it on, some family’s will not have the ability to afford new clothes and shoes within their household for all their children.
As you can see by the graph there is a small percentage of household unable to provide for there children. (Metroeconomica).
By charging zero rate of VAT on children’s clothes which has been by their age and height and designed for young children with maximum sizing of 13 years the older child.
It has stated within the parameters for VAT across the EU in 1991.
 t-rates
t-rates
By charging zero rate of VAT on children’s clothes which has been by there age and height and designed for young children with maximum sizing of 13 years the older child.
It has stated within the parameters for VAT across the EU in 1991
When do they charge VAT for kid’s clothes
Zero rate for kid’s clothes and footwear are designed for the under 14yrs, these can include members and group organisation’s such as: brownies or beaver.
- Which is usually done either by the physical measurements or the body size, some adults may get away with this.
https://www.gov.uk/vat-rates
This part is crucial as it as it’s the incentive for you to earn and the marginal tax rate shows how much of your earnings is turned over to tax, as well as how much each individual keep. By increasing the tax rates people get less of there earnings. This can have effects on the output on economy in two ways.
1. Having a high marginal rate reduces the money getting paid to workers, so they will unwilling to save as much or spend on luxury’s.
Marginal tax rates can have real output and can affect government revenue, by an increase within the e marginal tax rate can shrink the tax base which could discourage the work effort but also encourage the tax avoidance and evasion. doesn’t necessarily lead to increase tax rates but can lead to less than increase in tax revenue.
Aspromourgos, T., 2011. Metroeconomica. 23 07.Volume 62.
Fogiel, D. M., 2002. Economics Problem Solver. Virginia: Reasearch and Education Association.
Fogiel, D. M., 2002. Economics Problem Solver. New York: Research & Education Assoc..
Ltd, A. N., 2003. No children s clothes VAT, EU told. [Online]
Available at: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-196024/No-children-s-clothes-VAT-EU-told.html