Threat Analysis and Risk assessment
Case articulation
Staysure.co.uk Ltd specialises in insurance and financial services in the UK and Europe. It was formed in 2004 to provide travel insurance and expanded further to provide home, motor, health and life insurance along with some insurance products. In October 2013 Staysure.co.uk faced a security breach wherein over 100,00 live credit card details along with other personal details of the customers were compromised. This security breach affected 7% of the customers who had purchased insurance from Staysure before May 2012.
Before May 2012 the firm stored the card numbers of the customers along with the CVV numbers and other personal details like customer name and addresses. The card details were encrypted but the CVV numbers were fed as plain text into the database even though the card security details should not have been stored at all according to the industry rules. The chief executive of the company said that these details were stored in the system to help customers in their renewal process. After May 2012 the company ceased storing these details. The server on which the website server was based had a software vulnerability and even though a software patch was published in 2010 and 2013 the data controller failed to update software both the times due to lack of formal process to review and apply software updates. The failure to update the database software and the security flaws in the IT security system made the company very vulnerable to a cyber-attack.
The security flaws in the company’s JBoss Application web server were exploited between 14th and 28th October 2013. The attacker used the vulnerability in the application server to inject a malicious JavaScript code called “JSPSpy” on the firm’s website. JSPSpy enabled the attackers to remotely view and modify the source code of the website and query the database containing the details of the customers. It also let the attackers open a command shell allowing them to remotely execute privileged operating system commands. The attackers specifically targeted and downloaded the payment card details. Even though the card numbers were encrypted the attackers were able to identify the keys used in the encryption and hence could decrypt the card numbers. At the time of the attack the database contained a total of 110,096 live card details, which were at a risk of being accessed and used in fraudulent transactions. The firm became aware of the attack on 14th November 2013 and immediately hired independent forensic data experts and wrote to 93,389 affected customers, to make them aware of the attack. The company also offered the affected customers free access to Data Patrol, which is an identity fraud monitoring service.
After the attack Staysure was fined with an amount of £175,00 by the ICO since the company did not comply to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) , which is a standard administered by PCI Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) to increase payment card security and decrease the transaction frauds over the internet.
References:
http://securityaffairs.co/wordpress/21002/cyber-crime/staysure-hacked.html
http://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/2321017/staysure-travel-insurer-admits-to-credit-card-theft
http://trainsure.com/news-posts/insurance-times-reports-another-cyber-attack/
http://www.moneywise.co.uk/news/2014-01-06/staysure-insurance-customer-data-stolen-hackers
Threat Analysis and Risk assessment
The purpose of threat analysis and risk assessment is to maximize the protection of the three main pillars of security namely confidentiality, Integrity and Accessibility while still providing usability and functionality. A Risk to any organization or an individual is an interactive relationship of threat, asset and vulnerability. The various levels of risk can be represented as the product of the impact and probability (likelihood).
|
Quantitative Measure |
Qualitattive Measure |
Description |
|
5 |
High |
A high level risk can occur frequently and can have a drastic effect on the organization. Sever measures will be needed in order to mitigate a high level risk. |
|
4 |
Medium High |
A medium high risk can occur/recur with high probability but might not persist. If it occurs the organization can have a significant or sever effect. |
|
3 |
Medium |
A medium level risk is likely to occur under many circumstances and if a medium level attack occurs it can have moderate to severe effects on the organization. |
|
2 |
Low Medium |
A low medium risk can be considered when the organization will have a minor or moderate impact as a result of an attack. A low medium risk can occur occasionally or might not occur at all and can be mitigated easily. |
|
1 |
Low |
The risk is considered to be low when the likelihood of an attack on an entity is low and the impact of the attack on the entity is negligible or minor. Low risks will never or rarely happen and can be mitigated easily. |
Table 1: Risk Rating Scale
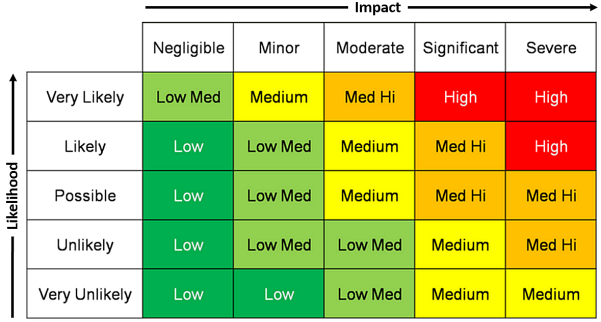
Figure1.
Figure 1 shows a risk matrix which represents the various levels of risk. A vulnerability is a weakness in the system that can be exploited by an attacker or can be unintentionally triggered by a person within the organization. The likelihood is the possibility that any vulnerability will be taken advantage of or the vulnerability will be triggered by someone unintentionally. The likelihood is related to attacker’s intent, attacker’s ability and attacker’s target. If a certain vulnerability is exploited the impact on an organization can be expressed in terms like Negligible, Minor, Moderate, Significant, Severe.
The table below shows a risk assessment architecture for Staysure.co.uk. The Firm had several security flaws in the system, which the attackers exploited to gain access to customer information.
|
Asset |
Threat |
Vulnerability |
Threat Actor |
Threat vector |
Consequences |
Likeli hood |
Impact |
Risk |
|
Customer Personal details |
Can be assessed and manipulated |
The database had no security procedure in place hence the data was highly accessible. |
Hackers or a person within the organization (insider). |
Gaining access to the database by getting access to the webserver or SQL injections. |
Personal details of the employees like name, address, phone can be accessed and used or even modified. |
Possible (3/5) |
Significant (4/5) |
Medium High |
|
Company website |
Source code of the website can be modified and malicious code can be injected and made to run on the browser (Cross site scripting). |
Cross site scripting can be performed on the website if security measures are not taken care of while developing the website. |
Hackers or an insider. |
Web pages |
Malicious code can be injected into the web pages thus allowing access to the web server and the database. |
Very Likely (5/5) |
Severe    (5/5) |
High |
|
Data controllers system |
No intrusion detection system. |
A system with no proper security measures can be easily penetrated. |
Hackers or an insider trying to get unauthorized access. |
Backdoor created in the web server. |
Getting access to the data controllers system enables the threat actor to execute Privileged operating system commands |
Very likely (5/5) |
Severe (5/5) |
High |
|
Financial card details |
Storing financial data incorrectly. |
Unencrypted card details stored in the database |
Hackers or an insider trying to get unauthorized access. |
Web site source code can be used to query the database |
Card details can be used to make fraudulent transaction and cloning. |
Very likely (5/5) |
Severe (5/5) |
High |
|
Encryption key |
Encryption algorithms can be used to calculate the encryption key |
Simple encryption algorithm used to form an encryption key. |
Hackers or an insider. |
Reverse engineering. |
If the encryption key is compromised all the encrypted data can be decrypted. |
Possible (3/5) |
Severe (5/5) |
Medium High |
|
CVV number |
Storing CVV numbers in the database is a high risk. |
CVV numbers if not encrypted can be easily read if the attacker gets access to the database. |
Hackers or an insider. |
Web site source code can be used to query the database for CVV numbers. |
CVV numbers can be used to prove authentication while doing online transactions. |
Very likely (5/5) |
Severe (5/5) |
High |
|
JBoss Application Server |
Unpatched and out of date software’s and no intrusion detection system |
Scripts can be uploaded to the server which when executed gives remote administration access to the server. |
Hackers or an unauthorised insider. |
Backdoor’s created on the server via malicious script. |
Once administration access is acquired on the server various admin activities can be initiated and the hosted web servers can be accessed. |
Likely (4/5) |
Severe (5/5) |
High |
|
Database |
Database injections and unmanaged data |
The data in the database can highly vulnerable to SQL injections and can be highly inconsistent. |
Hackers |
SQL injections |
Data can be erased and stolen from the database and used in a fraudulent manner. |
Likely (4/5) |
Severe (5/5) |
High |
https://www.towergateinsurance.co.uk/liability-insurance/smes-and-cyber-attacks — remove later
http://resources.infosecinstitute.com/how-to-prevent-cross-site-scripting-attacks/ –remove later
Security Architecture
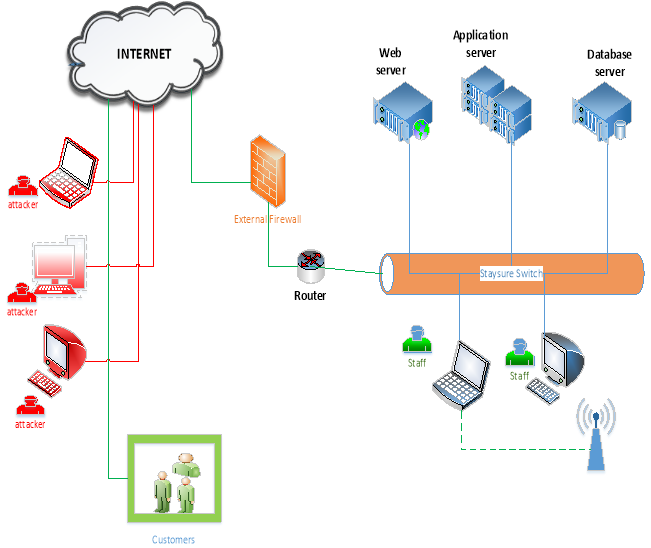
Figure: 2
Figure 2 shows security architecture for Staysure during the time of the attack
Security Recommendations
Staysure.co.uk had no security policies in place which can be sited as the base for the cyber-attack. Being an insurance company and holding personal records of millions of customers the company should have had security procedures in place. It is important that the employees of a company are trained and made aware of the importance of information data security. The fact that the attackers took advantage of the software vulnerability in the JBoss application server even though there were patches available to fix the vulnerabilities shows the ignorance of the data controller towards information security. Table 2 lists security recommendations which would have prevented the attack.
|
Security Recommendations |
Descriptions |
|
Security policies |
Security policies is an integral part of any organization. Staysure being an insurance company and handling millions of customer records should have had strict company security policies which could have prevented the attack. |
|
Security training and awareness |
The employees of Staysure were clearly not aware of the importance of data security and management. The employees should have been provided good data security and data management training and made aware of information security. |
|
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) – add appendix |
When an organization handles personal records of customers it is necessary that the organization follows certain industry standards for data storage. According to PCI DSS the CVV numbers should not have been stored in the database. If the standards were followed the attack would not have a major impact. |
|
Data storage and data security |
Data storage has both physical and logical security aspects. The logical aspect being data authorization, authentication and encryption. The physical aspects include the place in which the servers are placed, it should be safe from heat-waves, power fluctuations and other physical elements. In case of Staysure the payment card details and the CVV numbers should have been encrypted with a strong encryption algorithm from the very beginning and the database server should have had an intrusion detection and prevention system which would have prevented access to the database. |
|
Patch management |
Unpatched systems and software’s pose a big threat to an organization. The most efficient way to shield from attacks is to have patch management procedure to make sure that all the systems and software’s are patched on regular basis. If Staysure had patched the vulnerabilities in the Jboss application server and software, the attackers would not have been able to exploit the vulnerability. |
|
DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) |
The servers that are faced towards the public should be kept in the DMZ, so that they can be separated from the private network. If a malicious party gains access to the server, he will be isolated in the DMZ and will not be able to attack the private network. If Staysure had a DMZ the attackers would not be able to access data on the private network. |
|
Encryption |
Encrypting any valuable information of customers is necessary in order to protect customer data from being accessible and using a strong encryption key is vital to serve the purpose of encryption. The data controller should have had made sure to encrypt the CVV and the card number and should have used a strong encryption key. |
|
IDS |
Staysure should have had Intrusion detection systems so that the intrusion by the attacker could have been detected and would alert the authorities thus preventing high impact |
|
Firewalls |
|
|
Prevention of human errors |
http://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/SSTFWG_4.3.1/com.ibm.tivoli.itcm.doc/CMPMmst20.htm — patch management policy.
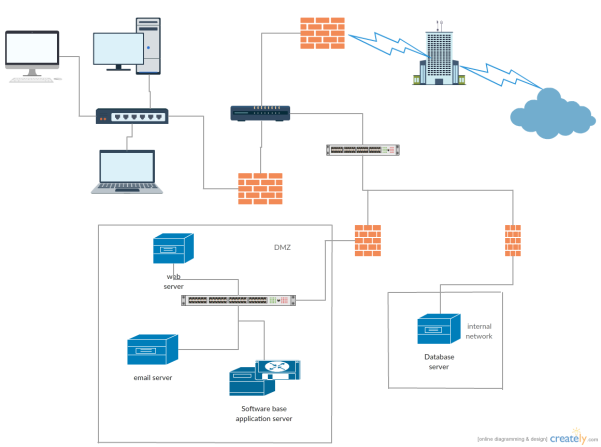
High level security diagram to prevent attacks