UK Construction Industry Health and Safety Analysis
To formulate a Comparative Analysis of the Health and Safety Practices and Procedures to the UK Construction Industry and their application to a Large Commercial Construction Organisation
Rebecca Barraclough
Table of Contents
- Rationale
- Introduction
- Aims, Objectives & Hypothesis
- Aims
- Objectives
- Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis
- Initial Literature Review
- Methodology
1. Rationale
The increased emphasis on health and safety in the construction industry in more recent years is the key influence of this study. In particular the company I am employed by has upped its game in terms of safety measures and places a substantial emphasis on the importance of health and safety. I feel a comparative analysis of the company’s performance in comparison to how the rest of the industry is performing would provide them with beneficial information and help to identify strengths and weaknesses within the company.
2. Introduction
Health and safety within the workplace has come a long way particularly since the introduction of the Health and Safety at Work Act (HSWA) 1974. Historically people often accepted that accidents and ill-health were all part of having a job and greater risks were taken without much regard to safety measures. Over time health and safety within the work place has become increasingly dominant with a greater emphasis on safety measures. However, although statistics produced by the Health and safety Executive shows there has been a decline in the number of work place accidents, in the period of 2015/2016 alone 1.3 million working people suffered from a work-related illness. (HSE.gov) It is clear that this still remains a dominant issue and there is room for improvement.
Employees, members of public and visitors equally have a right to protection of their health and safety when in and around a work place. Legislation and regulations are firmly in place to regulate this; often issues are identified and improvement notices are issued nevertheless more serious injuries and fatalities are covered by Criminal Law and could lead to major fines and even imprisonment.
As reported by the Health and Safety Executive the construction industry is a major employer equating to around 6% of the workforce in the UK. This study will look into the background of health and safety in construction, analysing accident statistics and safety measures. It will include a comparative analysis of the performance of a large commercial construction company compared with other leading contractors within the industry.
3. Aims, Objectives & Hypothesis
3.1 Aims
- To analyse health, safety and welfare performance within the construction industry
- Compare the performance of a large commercial construction organisation to the wider industry and evaluate behavioural safety within the organisation
3.2 Objectives
- Background to construction health safety and welfare performance over the last 10 years
- To identify the 5 highest risk activities in the construction industry and the safety measures implemented to reduce the risk.
- Compare the performance of a large commercial construction organisation in comparison of how the rest of the industry is performing and evaluate their behavioural safety culture
- To capture and appraise any emerging trends to consider areas of good performance and possible areas of improvement
3.3 Hypothesis
Statistics will show that there has been a decrease in the number of accidents reported to the Health and Safety Executive within the construction industry over the past 10 years
3.4 Null hypothesis
Statistics will show that there has been an increase in the number of accidents reported to the Health and Safety Executive within the construction industry over the past 10 years
4. Initial Literature Review
4.1 Health and Safety Defined
Health and Safety in general terms can be defined as “Regulations and procedures intended to prevent accident or injury in workplaces or public environments” (oxforddictionaries.com)
4.2 Health and Safety at Work
Everyday masses of people leave the safety of their homes to go to work and earn a living; it is their right to return home at the end of the day free from injury and ill-health. Not only do employers have responsibilities to keep their employees safe but individuals also have a duty to protect their own wellbeing.
4.3 Health and Safety at Work Ack 1974 (HSWA)
The Health and Safety at Work Act was introduced in 1974 in attempts to improve health, safety and welfare within the work place. In England, Scotland and Wales this is the primary legislation of health and safety and sets out stringent guidelines and regulations, it also imposes legal duties on both employees and employers. Considerable amount of the legislation within the Act incorporates the recommendations made by Lord Roben in his health and safety at work report, published in 1972. The report aimed to identify any improvements necessary to the health and safety of persons at work by reviewing current provisions.
Some of the legal duties imposed on both employers and employees are set out below:
Employers Responsibilities;
- Protect the health, safety and welfare at work of all employees
- Provide and maintain plant and systems of work that are safe and without risk to health
- Have arrangements for ensuring safety and absence of risk to health in connection with use, handling, storage and transport of articles and substances
- Provide such information, instruction, training and supervision as is necessary to ensure health and safety at work of employees
- Maintain any place of work under their control in a condition that is safe and without risk to health, and with access to and egress from it, that are safe and without such risks
- Provide and maintain an environment that is safe, without risks to health and adequate as regards with the welfare of employees
(citb 2015, pg 5)
Employees Responsibilities:
- Take responsible care for the health and safety of themselves or others who may be affected by their acts or omissions
- Co-operate with their employer in all matters relating to health and safety
- Not intestinally or recklessly interfere with or misuse anything provided in the interests of health, safety or welfare
- Use anything provided by the employer in accordance with instructions
- Report anything that is thought to be dangerous
(citb 2015, pg 6)
4.4 The Health and Safety Commission
The Royal Assent of the HSWA was followed by the formation of the The Health and Safety Commission (HSC). The primary responsibility of the HSC’s was to ensure the security of people’s health, safety and welfare at work, to protect the public from potential harm caused by work situations and to provide guidance about the provisions enforced with in the Act to local authorities and the Health and Safety Executives.
4.5 The Health and Safety Executive
1975 saw the introduction of The Health and Safety Executive (HSE). The remit of the HSE was to enforce health and safety legislation within the workplace, they consist of health and safety inspectors who visit a workplace without notice and carry out inspections. They have the authority to issue improvement notices or prohibition notices when company/individuals are in breach of health and safety law or in some cases prosecute.
4.6 Health and Safety in Construction
The construction industry is diverse and could be seen as one of the higher risk industries due to the nature of works and specialist activities that take place on a construction site.
The HSE collate data and statistics on accident rates within the industry, research suggests that 5% of the UK industry is made up from construction. Although this appears to be minimal, figures show that 10% of minor injuries and 22% of fatalities reported occur within this sector. In the period of 2015-2016 they reported that 43 fatalities occurred in the construction industry alone. They estimate that around 4% of employees in construction are affected by a work related illness each year and 3% sustain an injury through work. This would equate to 2.2 million working days lost.
With all of this in mind it is clear that the emphasis of health and safety needs to remain a dominant influence.
4.7 Build UK
“Build UK focuses on key industry issues that can deliver change and enable the construction supply chain to improve the efficiency and delivery of construction projects for the benefit of the UK economy.” (builduk.org)
Health and safety is one of the issues focused on by Build UK, they aim to identify common standards that would improve health and safety performance and continually strive to improve the management of safety. Currently 27 large contractors are members of Build UK and their accident statistics are recorded annually. Such figures would from a basis for a comparative analysis between some of the leading contractors in the UK in terms of safety performance.
4.8 Statistics
At first glance it appears that there has been a decline in the in number of accidents occurring in the construction industry each year.
The table below was taken from the labour force survey and shows the trend of self-reported none-fatal injuries per 100,000 workers between the years 2000 to 2016;
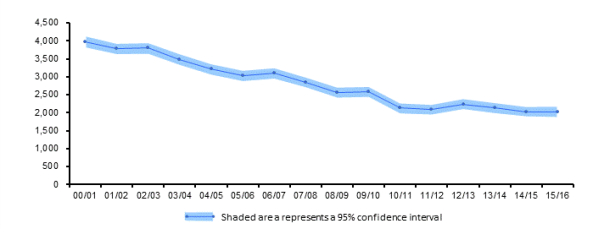
Source: Labour Force Survey (LFS)
4.9 Behavioural Safety
Often many accidents in the workplace could be easily avoided, a significant amount of accidents are caused by unreasonable behaviour or ignorance. Using behavioural safety models within a work place encourages manager and workforce participation and can often influence people’s attitudes and behaviours towards safety. It promotes communication and reinforces safe behaviour.
Below is the model used in the behavioural safety programme;
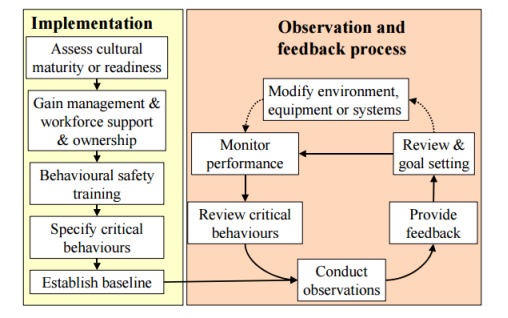
Source HSE.GOV
5. Methodology
Research can be described as a method of finding out new facts and drawing up conclusions, it is also a way of expanding existing knowledge.
- Triangulation
Triangulation in research can be defined as;
- using two or more sources
- using two or more methods
- more than one researcher exploring the same object
A triangulation method is to be used in this study to gather a varied amount of data to reflect the industry and increase validity. Both primary and secondary research will be incorporated; the source of the secondary research will be textbooks, official publications and official statistics. The primary research will include a mixed method approach of questionnaires and interviews.
- Methodological Model
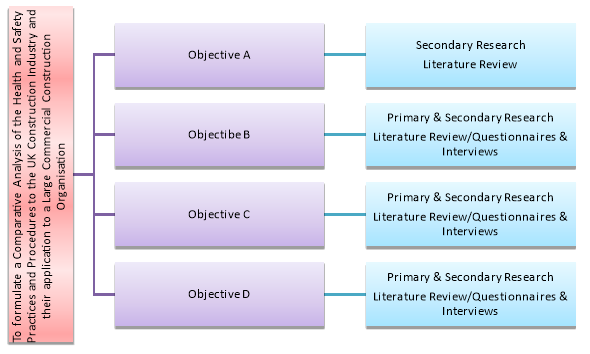
- Data Collection
Both the primary and secondary research will incorporate a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods in attempts to increase the validity of the information collected. There are advantages of both methods;
Quantitative;
- Data can be collected and analysed within a reasonable amount of time
- Results taken from a sample can be generalized if the response rate is reasonably high and if the sample is representable
- It is often reliable and repeatable research
- It can be anonymous and ethical
Qualitative;
- Topics can be explored in depth and with greater detail
- Uses subjective information
- Offers flexibility as fewer participants are needed
Semi-structured questionnaires including both open and closed ended question will be sent out to participants, a representable sample will be used from the hierarchy of construction to increase the validity of the data;
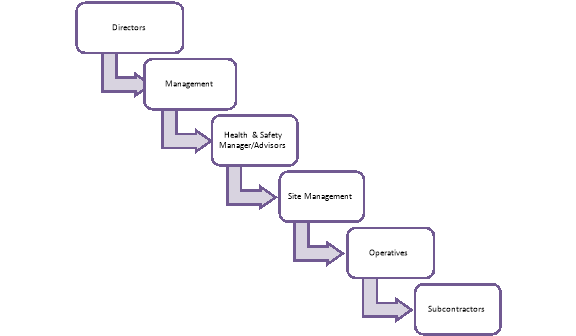
In attempts to increase the response rate a percentage of the questionnaires will be handed out following on from a site induction, I predict that 100% of these will be completed. The remaining will be emailed or handed out in person, in total I estimate that 70% of all questionnaires will returned.
Interviews will be carried out as the second part of the primary research; the interviewees will be within a large commercial construction organisation and will include a health and safety manager, a site manager and an operative. There will also be an interview carried on an employee of the HSE; this will be to gain an outside non bias perspective.
- Data Analysis
https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/health_and_safety
http://www.hse.gov.uk/statistics/history/index.htm
http://www.chsg.co.uk/news/health-and-safety-in-the-uk-construction-industry/
http://www.hse.gov.uk/statistics/
http://www.hse.gov.uk/STATISTICS/industry/construction/construction.pdf