What are the Impact of Brain Injuries?
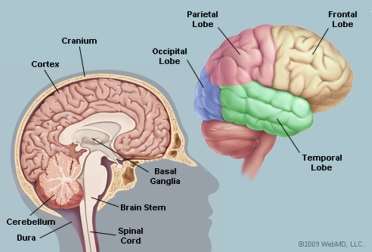
What Brain Injuries do to People and how their brain is affected?
The body is a very unique thing. It has so many parts and so many different actions that it does. The body is made up of several systems. The circulatory system is the body’s transport system. It is made up of different organs that specialize in transporting blood all over the body. The digestive system on the other hand breaks down food into protein, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, and fats, which allow body to repair, grow, and create energy. However, the endocrine system produces hormones which are ultimately messengers in the body. When you’re sick there is a system that helps with getting you better and preventing it. The immune system is our body’s defense system against infections and diseases. There are many more systems that all do great things for the body, but I believe that the most important system is the nervous system.
The nervous system is made up of the brain, the spinal cord, and nerves. It is hands down one of the most important systems in your body. The nervous system is your body’s control center. It sends, receives, and processes impulses throughout the body. These impulses tell your muscles and organs how and when to respond to certain situations. There are three parts of your nervous system that work together: the central nervous system, the peripheral nervous system, and the autonomic nervous system.
These three systems within the nervous system have different objectives and checklists that they do. Thecentral nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. This system sends out impulses and analyzes information, which then tells your brain about the things you hear, smell, feel, taste and see. Some may say that the central nervous system is the most important system in the nervous system, because of the five senses. What most people don’t realize is that the autonomic nervous system regulates actions, such as heart beats and digestion. Then you have the peripheral nervous system includes the craniospinal nerves that branch off from the brain and the spinal cord. It carries the impulses from the central nervous system to the muscles. With all these actions it leads me to believe that the nervous system and even more so the brain might have the most impact on your life besides your heart.[1]
The beginning of anyone’s life starts when we are in the whom. No one remembers this because the brain isn’t developed yet. The brain begins developing at the fifth week of pregnancy the brain grows at an amazing steady rate during development. At times during brain development, 250,000 neurons are added every minute! At birth, a person’s brain will have almost all the neurons that it will ever have or need. The brain continues to grow for a few years after a person is born. By the age of 2 years old, the brain is about 80% of the adult size.[2]
You may wonder, “How does the brain continue to grow, if the brain has most of the neurons it will get when you are born?” The answer is in glial cells. Glia cells are continually dividing and multiplying. Glia cells carry out important functions for normal brain functions, including insulating nerve cells with myelin. The neurons in the brain also make several new connections after birth.
The nervous system develops from embryonic tissue called the ectoderm. The first sign of the developing nervous system is a neural plate that can barely be seen on the 16th day of development. Over the next few days, a “trench” is formed in the neural plate. This could create a neural groove. By the 21st day of development, a neural tube is formed. This occurs only when the edges of the neural groove meet. The front part of the neural tubes goes on to develop into the brain and the rest developed into the spinal cord.
As babies grow and become born the best thing you can do for a kid is put him or her in the best environment to continue to develop the brain. A child’s brain develops rapidly during the first five years of life, especially the first three years. “It is a time of rapid cognitive, linguistic, social, emotional and motor development. For example, a child learns many words starting at around 15-18 months. Rapid language learning continues into the preschool years. The child’s brain grows as she or he sees, feels, tastes, smells and hears. Each time the child uses one of the senses, a neural connection is made in the child’s brain. New experiences repeated many times help make new connections, which shape the way the child thinks, feels, behaves and learns now and in the future.”[3]
A close relationship between a child and a parent is the best way to get the best growth in a child’s brain. When a parent plays with or sings, speaks, reads or tells a story to the child while nurturing him or her. Add in some healthy food and love and affection, and the child’s brain grows. Being healthy and interacting with parents and living in a safe and clean environment can make the biggest difference in a child’s growth and development. Babies need lots of care and affection in the early stages of a child’s life. By holding, cuddling and talking to the child, you stimulate brain growth and promote emotional development. Being kept close to the mother and breastfed on demand provide the infant with a sense of emotional security. The baby needs both nutrition and comfort.
As children’s brains develop, so do their emotions, which can be very misleading and powerful. Children may become frustrated if they are unable to do something, kind of like anyone and everyone, or can’t have something they want. They are often frightened by strangers or unfamiliar people and places, new situations or the dark. Children whose reactions are laughed at, punished or ignored may grow up shy and unable to express emotions normally. If parents are patient and sympathetic when a child expresses strong emotions, the child is more likely to grow up happy, and feel secure. Boys and girls have the same physical, mental, emotional and social needs. Both have the same capacity for learning. Both have the same need for affection, attention and approval.
Young children can experience excessive stress if they are physically or emotionally punished, are exposed to violence, are neglected or abused, or live in families with mental illness, such as depression or substance abuse. These stresses interfere with the developing brain and can lead to cognitive, social and emotional delays and behavior problems in childhood and later in life. The best way to raise a kid or developed a kid is putting them in situations to succeed as young as being newborn.
As kids grow up what is the first thing people usually put their kids into, sports right. Well sports are super fun and great until injuries happen. Everyone worries about their kid getting injured or hurt. So, how should parents go about sports? What age should we start them? What will happen if they get injured and it’s bad? Well there are several different ways to go about it. The most effective way is to just be careful and trust what you think is right. Everyone is different and some kids are ready and matured for sports at age four where as some maybe not until six. This has nothing to do with the fact that who is better and who fits the look of being an athlete. Some kids just don’t mature as fast so they are a little weaker and smaller. If this is the case maybe you hold off on sports until six. The worst thing that could happen to anyone is getting a head injury.
There are five main types of head injuries. Concussion, contusion, coup-countercoup, Diffuse Axonal, penetration are the most common types of injuries all of which have different effects bad different injuries that come with them. A Diffuse Axonal Injury can be caused by shaking or strong rotation of the head, as with Shaken Baby Syndrome, or by rotational forces, such as with a car accident.[4] Injury occurs because the unmoving brain lags behind the movement of the skull, causing brain structures to tear. There is extensive tearing of nerve tissue throughout the brain. This can cause brain chemicals to be released, causing additional injury. The tearing of the nerve tissue disrupts the brain’s regular communication and chemical processes. This disturbance in the brain can produce temporary or permanent widespread brain damage, coma, or death. A person with a diffuse axonal injury could present a variety of functional impairments depending on where the shearing (tears) occurred in the brain.
A concussion is the most common injury that people think of. It’s the most common head injury in sports. A concussion can be caused by direct blows to the head, gunshot wounds, violent shaking of the head, or force from a whiplash type injury. Both closed and open head injuries can produce a concussion. A concussion is the most common type of traumatic brain injury. A concussion is caused when the brain receives trauma from an impact or a sudden momentum or movement change. The blood vessels in the brain may stretch and cranial nerves may be damaged. A person may or may not experience a brief loss of consciousness (not exceeding 20 minutes). A person may remain conscious, but feel dazed. A concussion may or may not show up on a diagnostic imaging test, such as a CAT scan. Skull fracture, brain bleeding, or swelling may or may not be present. Therefore, concussion is sometimes defined by exclusion and is considered a complex neurobehavioral syndrome.[5]
A concussion can cause diffuse axonal type injury resulting in permanent or temporary damage. [6]It may take a few months to a few years for a concussion to heal. A contusion can be the result of a direct impact to the head. A contusion is a bruise or bleeding on the brain. Large contusions may need to be surgically removed. Coup-Countercoup Injury describes contusions that are both at the site of the impact and on the complete opposite side of the brain. This occurs when the force impacting the head is not only great enough to cause a contusion at the site of impact, but also is able to move the brain and cause it to slam into the opposite side of the skull, which causes the additional contusion. Both of these can be pretty traumatic.
Penetrating injuries to the brain occurs from the impact of a bullet, knife or other sharp object that forces hair, skin, bone and fragments from the object into the brain. Objects traveling at a low rate of speed through the skull and brain can ricochet within the skull, which widens the area of damage. A “through-and-through” injury occurs if an object enters the skull, goes through the brain, and exits the skull. Through-and-through traumatic brain injuries include the effects of penetration injuries, plus additional shearing, stretching and rupture of brain tissue. The devastating traumatic brain injuries caused by bullet wounds result in a 91% firearm-related death rate overall. Firearms are the single largest cause of death from traumatic brain injury. These types of injuries are very common unfortunately in today’s world. These injuries and how these injuries occur usually lead to death shortly after.[7]
The most common way that these injuries happen is from careless actions from you or someone else. In another sense people do not always do anything but get these injuries. Sometimes just playing a sport you love, like soccer or football or maybe even hockey. Sports are probably the number one activity that can get you hurt. Especially, the brain. There are so many different sports that involve the head or even contact that could rattle the head. All it takes is one hit to the head or one fall or one ball that hits your head to give you an injury.
The top ten sports/activities that get head injuries are Cycling( 85,389) Football (46,948) Baseball and Softball( 38,394) Basketball( 34,692) Water Sports such as, Diving, Scuba Diving, Surfing, Swimming, Water Polo, Water Skiing, Water Tubing( 28,716); Powered Recreational Vehicles which include ,ATVs, Dune Buggies, Go-Carts, Mini bikes, Off-road( 26,606) Soccer( 24,184). Skateboards/Scooters (23,114) Fitness/Exercise/Health Club (18,012) Winter Sports like: Skiing, Sledding, Snowboarding, And Snowmobiling (16,948). With all these sports all of them are very active and fun but come with a lot of risks. [8]
All sports injuries or injuries in general have different severity. Just like all injuries so do brain injuries. The most common known scale to determine the severity is The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS). GCS it is a scoring system used to describe the level of consciousness in a person following a traumatic brain injury. Basically, it is used to help gauge the severity of an acute brain injury. The test is simple, reliable, and correlates well with outcome following severe brain injury. This system works like this The GCS measures the following functions:
Eye Opening (E)
- 4 = spontaneous
- 3 = to voice
- 2 = to pain
- 1 = none
Verbal Response (V)
- 5 = normal conversation
- 4 = disoriented conversation
- 3 = words, but not coherent
- 2 = no words, only sounds
- 1 = none
Motor Response (M)
- 6 = normal
- 5 = localized to pain
- 4 = withdraws to pain
- 3 = decorticate posture (an abnormal posture that can include rigidity, clenched fists, legs held straight out, and arms bent inward toward the body with the wrists and fingers bend and held on the chest)
- 2 = decelerate (an abnormal posture that can include rigidity, arms and legs held straight out, toes pointed downward, head and neck arched backwards)
- 1 = none[9]
Clinicians use this scale to rate the best eye opening response, the best verbal response, and the best motor response an individual makes. The final GCS score or grade is the sum of these numbers. This scale leads to three categories Severe (GCS 3-8, you cannot score lower than a 3.) Moderate (GCS 9-12) and Mild Traumatic brain injuries( GCS 13-15).Mild traumatic brain injury occurs when a loss of consciousness is very brief, usually a few seconds or minutes. However, a loss of consciousness does not have to occur-the person may be just dazed or confused. You can also have testing or scans done of the brain and they may appear normal. A mild traumatic brain injury is diagnosed only when there is a change in the mental status at the time of injury-the person is dazed, confused, or loses consciousness. The change in mental status indicates that the person’s brain functioning has been altered, this is called a concussion.
[1]Eisenberg, John M. Rehabilitation for Traumatic Brain Injury: Summary. Rockville, MD: U.S.Dept. of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1998.
[2] Vay, David Le and Elise Cuschieri. Challenges in the Theory and Practice of Play Therapy. London: Routledge, 2016.
[3] Vay, David Le and Elise Cuschieri. Challenges in the Theory and Practice of Play Therapy. London: Routledge, 2016.
[4] “About Brain Injury.” About Brain Injury – BIAA. Accessed December 08, 2016. http://www.biausa.org/about-brain-injury.htm.
[5] “About Brain Injury.” About Brain Injury – BIAA. Accessed December 08, 2016. http://www.biausa.org/about-brain-injury.htm.
[6] Graham, Robert, Frederick P. Rivara, Morgan A. Ford and Carol Mason Spicer. Sports-related Concussions in Youth: Improving the Science, Changing the Culture. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press, 2014.
[7] “The American Association of Neurological Surgeons.” Traumatic Brain Injury. Accessed December 08, 2016. http://www.aans.org/Patient Information/Conditions and Treatments/Traumatic Brain Injury.aspx.
[8] “The American Association of Neurological Surgeons.” Traumatic Brain Injury. Accessed December 08, 2016. http://www.aans.org/Patient Information/Conditions and Treatments/Traumatic Brain Injury.aspx.
[9] “The American Association of Neurological Surgeons.” Traumatic Brain Injury. Accessed December 08, 2016. http://www.aans.org/Patient Information/Conditions and Treatments/Traumatic Brain Injury.aspx
Primary:
Secondary:
Books:
Eisenberg, John M. Rehabilitation for Traumatic Brain Injury: Summary. Rockville, MD: U.S.Dept. of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, Agency for Health Care Policy and Research, 1998.
Graham, Robert, Frederick P. Rivara, Morgan A. Ford and Carol Mason Spicer. Sports-related Concussions in Youth: Improving the Science, Changing the Culture. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press, 2014.
Pargman, David. Psychological Bases of Sport Injuries. Morgantown, WV: Fitness Information Technology, 1993.
Vay, David Le and Elise Cuschieri. Challenges in the Theory and Practice of Play Therapy. London: Routledge, 2016.
Zasler, Nathan D., Douglas I. Katz and Ross D. Zafonte. Brain Injury Medicine: Principles and Practice. New York: Demos, 2007.
Website:
“About Brain Injury.” About Brain Injury – BIAA. Accessed December 08, 2016.
http://www.biausa.org/about-brain-injury.htm.
“Concussions & Brain Injuries: Symptoms, Tests, Treatment.” EMedicineHealth.
http://www.emedicinehealth.com/slideshow_pictures_concussions_brain_injuries/article_em.htm.
( Accessed November 18, 2016.)
“Severe Brain Injury.” SpringerReference. doi:10.1007/springerreference_183092. Finish
“The American Association of Neurological Surgeons.” Traumatic Brain Injury. Accessed December 08, 2016. http://www.aans.org/Patient Information/Conditions and Treatments/Traumatic Brain Injury.aspx.
“Traumatic Brain Injury.” Traumatic Brain Injury – Mayo Clinic. Accessed November 18, 2016. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/traumatic-brain-injury/basics/definition/CON-20029302.
“Understanding TBI: Part 1 – What Happens to the Brain during Injury and the Early Stages of Recovery from TBI?” What Happens During Injury And In Early Stages Of Recovery. (Accessed November 18, 2016. )
http://www.msktc.org/tbi/factsheets/Understanding-TBI/What-Happens-During-Injury-And-In-Early-Stages-Of-Recovery.
Articles:
Chmielnicki, Eva. “Brain: Bouncing Back after Brain Injury.” Nature Medicine 18, no. 5 (2012): 670. doi:10.1038/nm.2783.
Schmutz, Jörg. “Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury.” Handbook on Hyperbaric Medicine: 585-90. doi:10.1007/1-4020-4448-8_34.
“Secondary Brain Injury.” SpringerReference. doi:10.1007/springerreference_183091.
“Severe Brain Injury.” SpringerReference. doi:10.1007/springerreference_183092.
“Sports and Brain Injury.” AccessScience. doi:10.1036/1097-8542.yb140815.